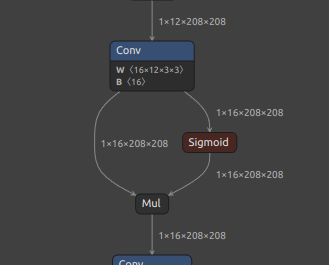
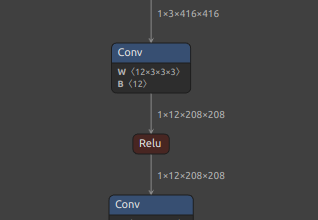
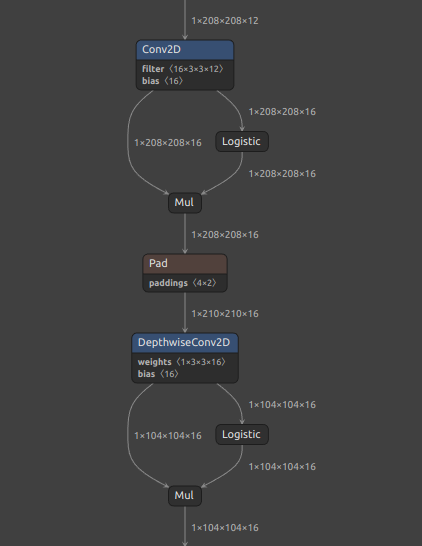
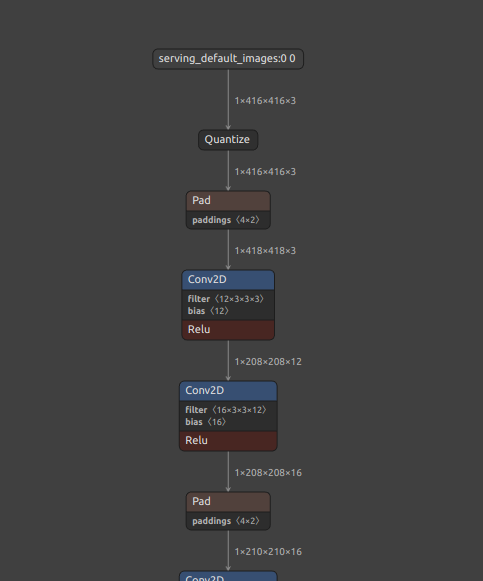
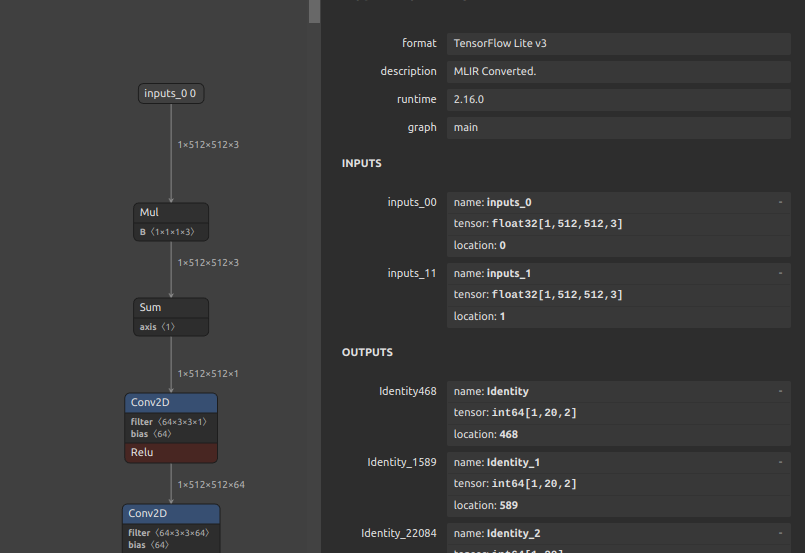
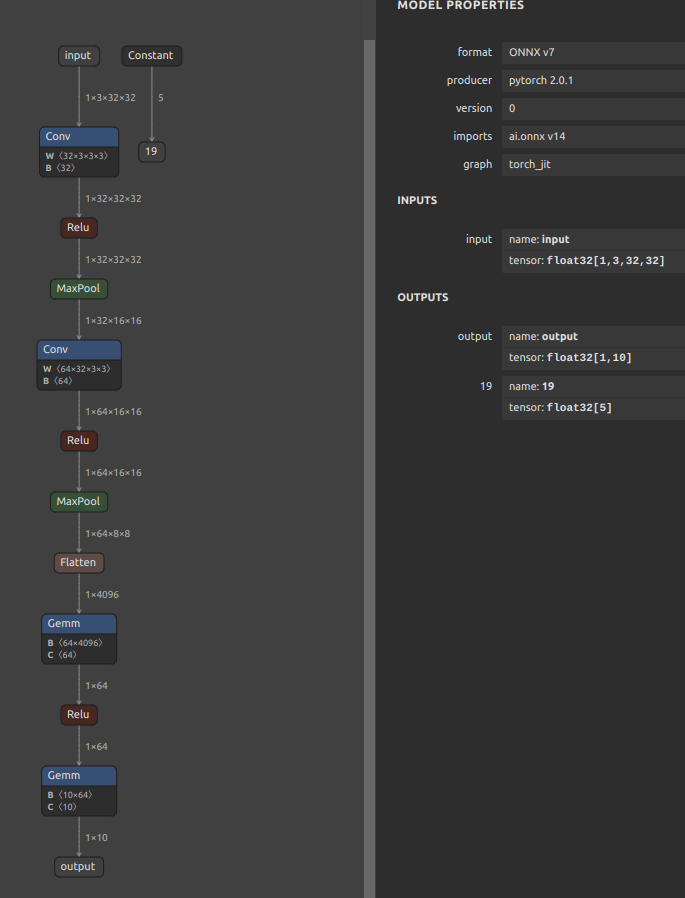
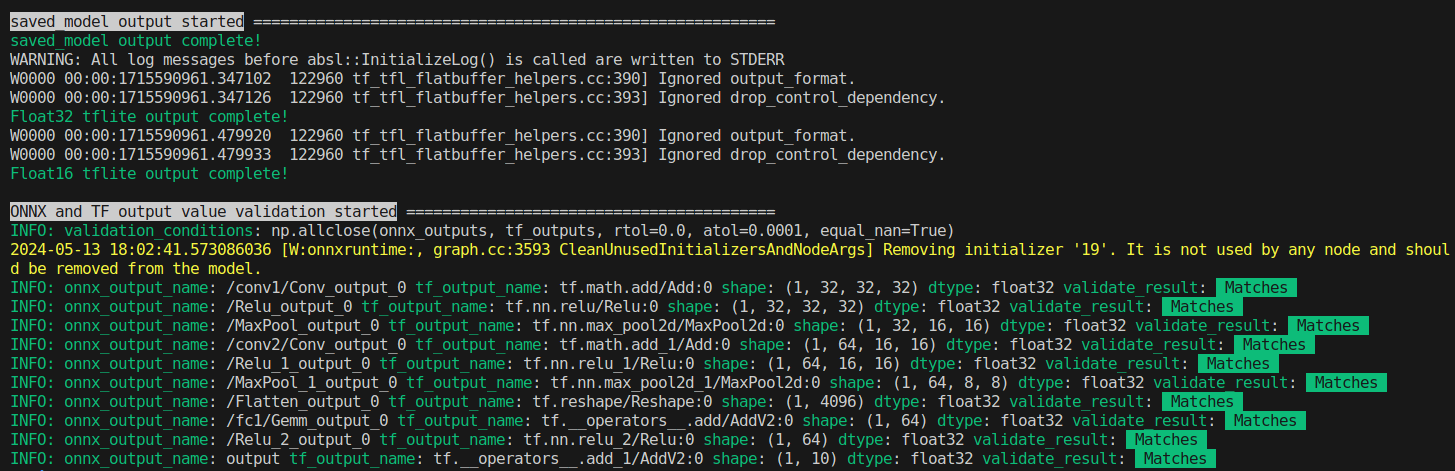
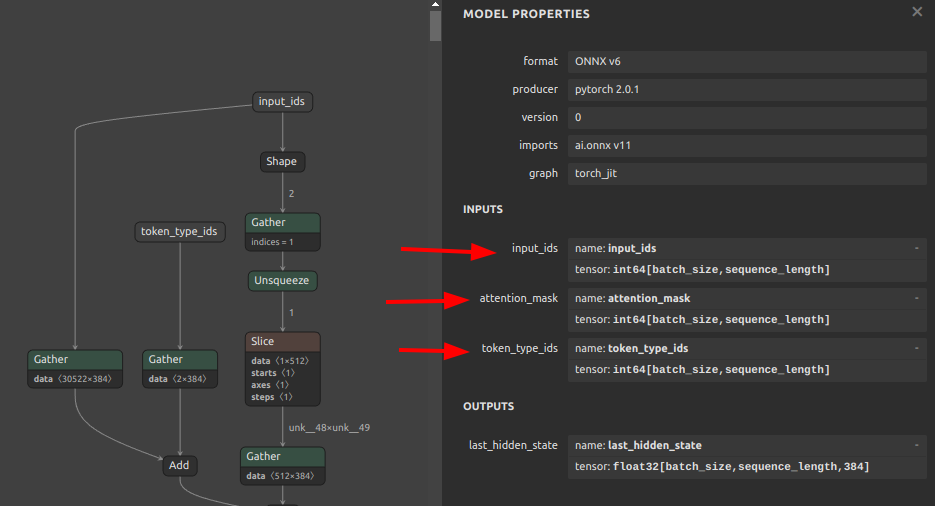
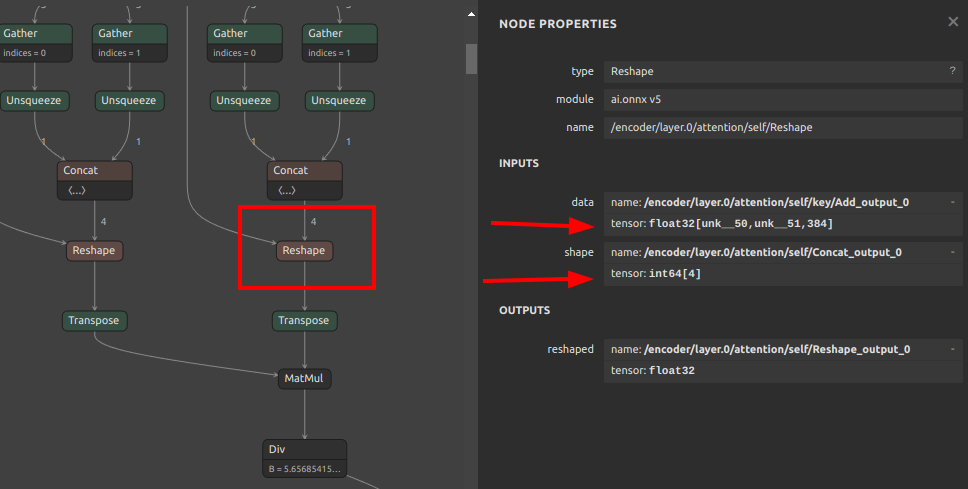
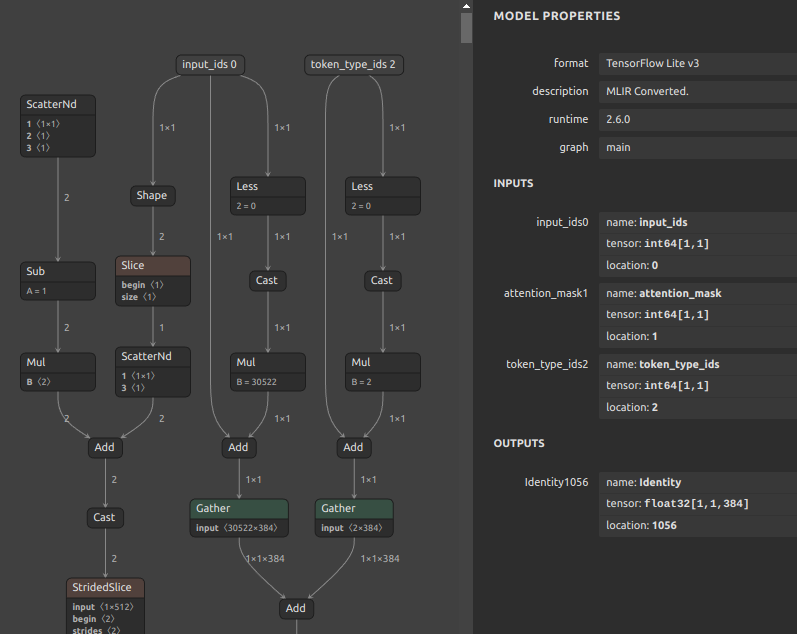
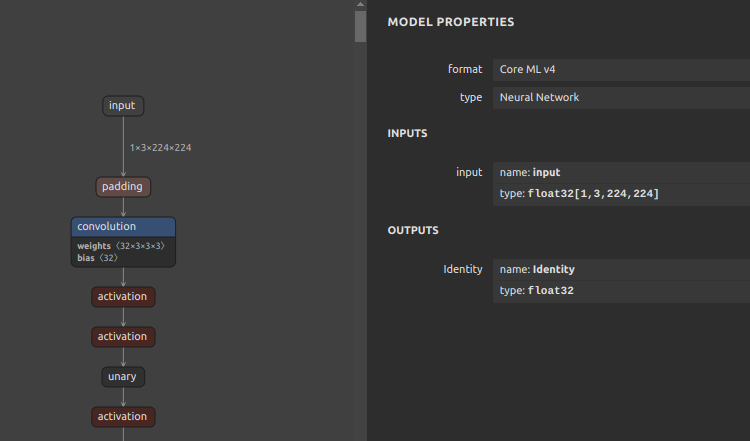
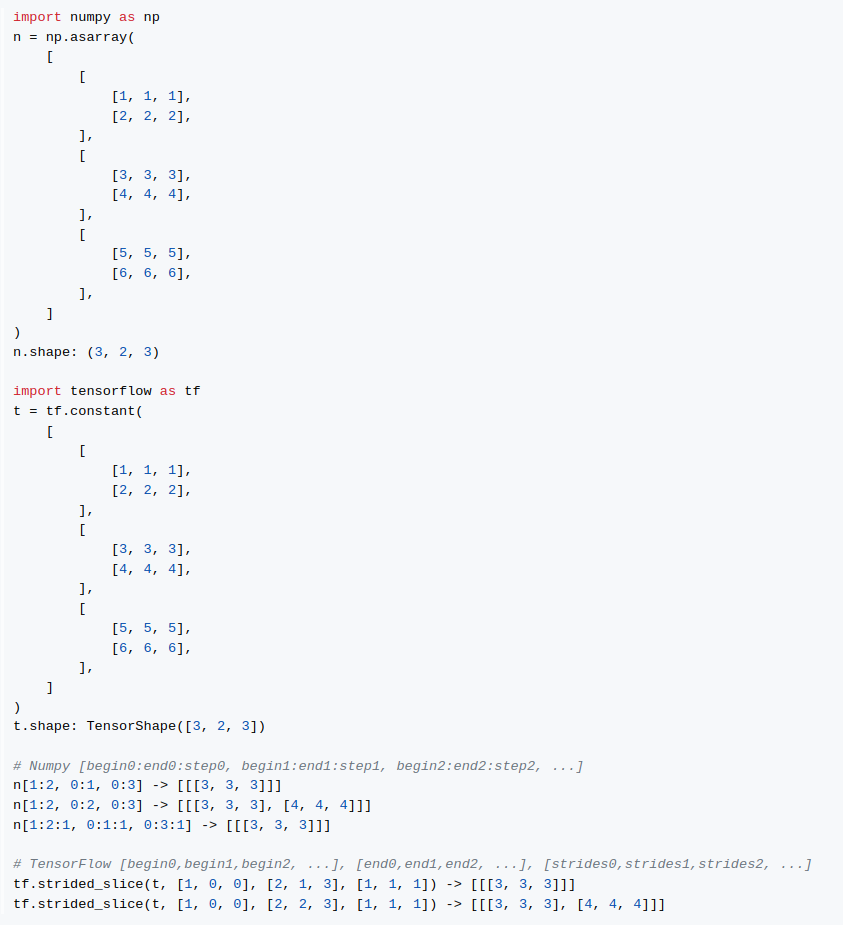
Self-Created Tools to convert ONNX files (NCHW) to TensorFlow/TFLite/Keras format (NHWC). The purpose of this tool is to solve the massive Transpose extrapolation problem in onnx-tensorflow (onnx-tf).
Project description
onnx2tf
Self-Created Tools to convert ONNX files (NCHW) to TensorFlow/TFLite/Keras format (NHWC).
You should use LiteRT Torch rather than onnx2tf. https://github.com/google-ai-edge/litert-torch
Note
Click to Click to expand
-
The torch.script-based
torch.onnx.exporthas already been moved to maintenance mode, and we recommend moving to the FX graph-basedtorch.onnx.dynamo_exportstarting with PyTorch v2.2.0. -
The greatest advantage of ONNX generated by
torch.onnx.dynamo_exportwould be that it directly references the PyTorch implementation, allowing for the conversion of any OP that was previously difficult to convert to ONNX. -
The maintainers of ONNX and PyTorch have assured us that they will not add new OPs after
opset=18to the existingtorch.onnx.export. -
https://pytorch.org/docs/stable/onnx_dynamo.html#torch.onnx.dynamo_export
-
This can be converted directly into an ONNX graph using Pythonic code using
onnxscript. -
For future model versatility, it would be a good idea to consider moving to
torch.onnx.dynamo_exportat an early stage. -
Google AI Edge Torch AI Edge Torch is a python library that supports converting PyTorch models into a .tflite format, which can then be run with TensorFlow Lite and MediaPipe. This enables applications for Android, iOS and IOT that can run models completely on-device. AI Edge Torch offers broad CPU coverage, with initial GPU and NPU support. AI Edge Torch seeks to closely integrate with PyTorch, building on top of torch.export() and providing good coverage of Core ATen operators.
https://github.com/google-ai-edge/ai-edge-torch?tab=readme-ov-file#pytorch-converter
import torch import torchvision import ai_edge_torch # Use resnet18 with pre-trained weights. resnet18 = torchvision.models.resnet18(torchvision.models.ResNet18_Weights.IMAGENET1K_V1) sample_inputs = (torch.randn(1, 3, 224, 224),) # Convert and serialize PyTorch model to a tflite flatbuffer. Note that we # are setting the model to evaluation mode prior to conversion. edge_model = ai_edge_torch.convert(resnet18.eval(), sample_inputs) edge_model.export("resnet18.tflite")
-
Google for Developers Blog MAY 14, 2024 - AI Edge Torch: High Performance Inference of PyTorch Models on Mobile Devices
-
Considering the compatibility of Pythonic code with TensorFlow/Keras/TFLite and the beauty of the conversion workflow, nobuco is the most optimal choice going forward.
-
The role of
onnx2tfwill end within the next one to two years. I don't intend to stop the maintenance ofonnx2tfitself anytime soon, but I will continue to maintain it little by little as long as there is demand for it from everyone. The end ofonnx2tfwill be whenTensorRTand other runtimes support porting from FX Graph based models.
Model Conversion Status
https://github.com/PINTO0309/onnx2tf/wiki/model_status
Supported layers
-
:heavy_check_mark:: Supported :white_check_mark:: Partial support Help wanted: Pull Request are welcome
See the list of supported layers
OP Status Abs :heavy_check_mark: Acosh :heavy_check_mark: Acos :heavy_check_mark: Add :heavy_check_mark: AffineGrid :heavy_check_mark: And :heavy_check_mark: ArgMax :heavy_check_mark: ArgMin :heavy_check_mark: Asinh :heavy_check_mark: Asin :heavy_check_mark: Atanh :heavy_check_mark: Atan :heavy_check_mark: Attention :heavy_check_mark: AveragePool :heavy_check_mark: BatchNormalization :heavy_check_mark: Bernoulli :heavy_check_mark: BitShift :heavy_check_mark: BitwiseAnd :heavy_check_mark: BitwiseNot :heavy_check_mark: BitwiseOr :heavy_check_mark: BitwiseXor :heavy_check_mark: BlackmanWindow :heavy_check_mark: Cast :heavy_check_mark: Ceil :heavy_check_mark: Celu :heavy_check_mark: CenterCropPad :heavy_check_mark: Clip :heavy_check_mark: Col2Im :white_check_mark: Compress :heavy_check_mark: ConcatFromSequence :heavy_check_mark: Concat :heavy_check_mark: ConstantOfShape :heavy_check_mark: Constant :heavy_check_mark: Conv :heavy_check_mark: ConvInteger :white_check_mark: ConvTranspose :heavy_check_mark: Cosh :heavy_check_mark: Cos :heavy_check_mark: CumProd :heavy_check_mark: CumSum :heavy_check_mark: DeformConv :white_check_mark: DepthToSpace :heavy_check_mark: Det :heavy_check_mark: DequantizeLinear :heavy_check_mark: DFT :white_check_mark: Div :heavy_check_mark: Dropout :heavy_check_mark: DynamicQuantizeLinear :heavy_check_mark: Einsum :heavy_check_mark: Elu :heavy_check_mark: Equal :heavy_check_mark: Erf :heavy_check_mark: Expand :heavy_check_mark: Exp :heavy_check_mark: EyeLike :heavy_check_mark: Flatten :heavy_check_mark: Floor :heavy_check_mark: FusedConv :heavy_check_mark: GatherElements :heavy_check_mark: GatherND :heavy_check_mark: Gather :heavy_check_mark: Gelu :heavy_check_mark: Gemm :heavy_check_mark: GlobalAveragePool :heavy_check_mark: GlobalLpPool :heavy_check_mark: GlobalMaxPool :heavy_check_mark: GreaterOrEqual :heavy_check_mark: Greater :heavy_check_mark: GridSample :white_check_mark: GroupNormalization :heavy_check_mark: GRU :heavy_check_mark: HammingWindow :white_check_mark: HannWindow :white_check_mark: Hardmax :heavy_check_mark: HardSigmoid :heavy_check_mark: HardSwish :heavy_check_mark: Identity :heavy_check_mark: If :heavy_check_mark: ImageDecoder :white_check_mark: Input :heavy_check_mark: InstanceNormalization :heavy_check_mark: Inverse :heavy_check_mark: IsInf :heavy_check_mark: IsNaN :heavy_check_mark: LayerNormalization :heavy_check_mark: LeakyRelu :heavy_check_mark: LessOrEqual :heavy_check_mark: Less :heavy_check_mark: Log :heavy_check_mark: LogSoftmax :heavy_check_mark: Loop :heavy_check_mark: LpNormalization :heavy_check_mark: LpPool :heavy_check_mark: LRN :heavy_check_mark: LSTM :heavy_check_mark: MatMul :heavy_check_mark: MatMulInteger :heavy_check_mark: MaxPool :heavy_check_mark: Max :heavy_check_mark: MaxRoiPool :heavy_check_mark: MaxUnpool :heavy_check_mark: Mean :heavy_check_mark: MeanVarianceNormalization :heavy_check_mark: MelWeightMatrix :heavy_check_mark: Min :heavy_check_mark: Mish :heavy_check_mark: Mod :heavy_check_mark: Mul :heavy_check_mark: Multinomial :heavy_check_mark: Neg :heavy_check_mark: NegativeLogLikelihoodLoss :heavy_check_mark: NonMaxSuppression :heavy_check_mark: NonZero :heavy_check_mark: Optional :heavy_check_mark: OptionalGetElement :heavy_check_mark: OptionalHasElement :heavy_check_mark: Not :heavy_check_mark: OneHot :heavy_check_mark: Or :heavy_check_mark: Pad :heavy_check_mark: Pow :heavy_check_mark: PRelu :heavy_check_mark: QLinearAdd :heavy_check_mark: QLinearAveragePool :heavy_check_mark: QLinearConcat :heavy_check_mark: QLinearConv :heavy_check_mark: QGemm :heavy_check_mark: QLinearGlobalAveragePool :heavy_check_mark: QLinearLeakyRelu :heavy_check_mark: QLinearMatMul :heavy_check_mark: QLinearMul :heavy_check_mark: QLinearSigmoid :heavy_check_mark: QLinearSoftmax :heavy_check_mark: QuantizeLinear :heavy_check_mark: RandomNormalLike :heavy_check_mark: RandomNormal :heavy_check_mark: RandomUniformLike :heavy_check_mark: RandomUniform :heavy_check_mark: Range :heavy_check_mark: Reciprocal :heavy_check_mark: ReduceL1 :heavy_check_mark: ReduceL2 :heavy_check_mark: ReduceLogSum :heavy_check_mark: ReduceLogSumExp :heavy_check_mark: ReduceMax :heavy_check_mark: ReduceMean :heavy_check_mark: ReduceMin :heavy_check_mark: ReduceProd :heavy_check_mark: ReduceSum :heavy_check_mark: ReduceSumSquare :heavy_check_mark: RegexFullMatch :heavy_check_mark: Relu :heavy_check_mark: Reshape :heavy_check_mark: Resize :heavy_check_mark: ReverseSequence :heavy_check_mark: RNN :heavy_check_mark: RoiAlign :heavy_check_mark: RotaryEmbedding :heavy_check_mark: Round :heavy_check_mark: ScaleAndTranslate :heavy_check_mark: Scatter :heavy_check_mark: ScatterElements :heavy_check_mark: ScatterND :heavy_check_mark: Scan :heavy_check_mark: Selu :heavy_check_mark: SequenceAt :heavy_check_mark: SequenceConstruct :heavy_check_mark: SequenceEmpty :heavy_check_mark: SequenceErase :heavy_check_mark: SequenceInsert :heavy_check_mark: SequenceLength :heavy_check_mark: Shape :heavy_check_mark: Shrink :heavy_check_mark: Sigmoid :heavy_check_mark: Sign :heavy_check_mark: Sinh :heavy_check_mark: Sin :heavy_check_mark: Size :heavy_check_mark: Slice :heavy_check_mark: Softmax :heavy_check_mark: SoftmaxCrossEntropyLoss :heavy_check_mark: Softplus :heavy_check_mark: Softsign :heavy_check_mark: SpaceToDepth :heavy_check_mark: Split :heavy_check_mark: SplitToSequence :heavy_check_mark: Sqrt :heavy_check_mark: Squeeze :heavy_check_mark: STFT :white_check_mark: StringConcat :heavy_check_mark: StringNormalizer :heavy_check_mark: StringSplit :heavy_check_mark: Sub :heavy_check_mark: Sum :heavy_check_mark: Tan :heavy_check_mark: Tanh :heavy_check_mark: TensorScatter :heavy_check_mark: TfIdfVectorizer :white_check_mark: ThresholdedRelu :heavy_check_mark: Tile :heavy_check_mark: TopK :heavy_check_mark: Transpose :heavy_check_mark: Trilu :heavy_check_mark: Unique :heavy_check_mark: Unsqueeze :heavy_check_mark: Upsample :heavy_check_mark: Where :heavy_check_mark: Xor :heavy_check_mark:
[!WARNING]
flatbuffer_directis an experimental backend. Behavior, supported patterns, and conversion quality may change between releases. For production use, keeptf_converteras baseline and validateflatbuffer_directper model with--report_op_coverage.
flatbuffer_directnow runs a layout-transpose chain optimizer during lowering. For NCW/NCHW/NCDHW <-> NWC/NHWC/NDHWC conversion paths, inverseTransposepairs are removed automatically when safe.Transpose -> (Quantize/Dequantize) -> inverse TransposeandTranspose -> Quantize -> Dequantize -> inverse Transposeare also folded for per-tensor quantization.Transpose -> (ADD/SUB/MUL/DIV) -> inverse Transposeis folded when both binary inputs share the same pre-transpose permutation. For float outputs, terminalQUANTIZE -> DEQUANTIZEpairs are also removed when the pair is isolated and output-only.
[WIP・experimental] flatbuffer_direct support status for ONNX ops in this list
The flatbuffer_direct conversion option exists to convert a QAT quantized ONNX model to an optimized quantized tflite (LiteRT) model. By the way, if you want to generate a highly optimized quantized tflite for your ONNX model, I recommend using this package. https://github.com/NXP/eiq-onnx2tflite
| INT8 ONNX | INT8 TFLite(LiteRT) |
|---|---|
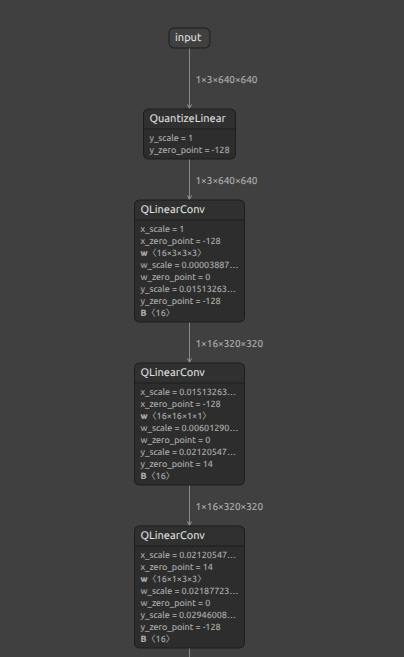 |
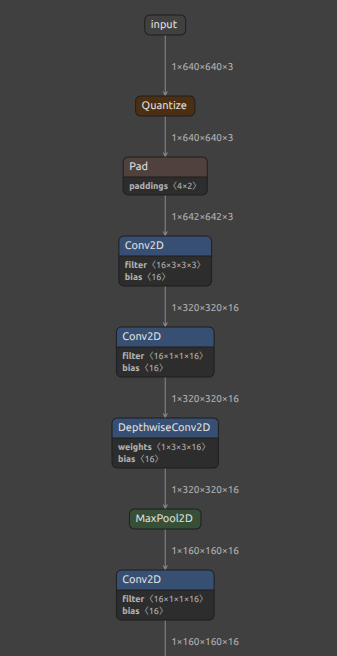 |
Click to expand
- Scope: ONNX ops listed in the
Supported layerstable above. - Source of truth:
onnx2tf/tflite_builder/op_registry.pyand--report_op_coverageoutput. - Current summary:
- Listed ONNX ops in this README section:
208 - Policy counts are generated in
*_op_coverage_report.json(schema_policy_counts). - Check each conversion run with
--report_op_coveragefor the latest numbers.
- Listed ONNX ops in this README section:
Notes:
flatbuffer_directsupports only a subset of ONNX ops as TFLite builtins.- Some ops are conditionally supported (rank/attribute/constant-input constraints).
- For model-specific results, use
--report_op_coverageand check*_op_coverage_report.json.
Builtin supported (ONNX -> TFLite) in flatbuffer_direct
| ONNX OP | TFLite OP | Key constraints (flatbuffer_direct) |
|---|---|---|
| Abs | ABS | - |
| Acos | MUL + SUB + SQRT + ATAN2 | Input/output dtype must be FLOAT16 or FLOAT32 |
| Acosh | SUB + ADD + SQRT + MUL + LOG | Input/output dtype must be FLOAT16 or FLOAT32 |
| Add | ADD | - |
| And | LOGICAL_AND | - |
| ArgMax | ARG_MAX (+ optional RESHAPE for keepdims) | axis must be in range, keepdims must be 0 or 1, select_last_index=0, output dtype must be INT32 or INT64 |
| ArgMin | ARG_MIN (+ optional RESHAPE for keepdims) | axis must be in range, keepdims must be 0 or 1, select_last_index=0, output dtype must be INT32 or INT64 |
| Asin | MUL + SUB + SQRT + ATAN2 | Input/output dtype must be FLOAT16 or FLOAT32 |
| Asinh | MUL + ADD + SQRT + LOG | Input/output dtype must be FLOAT16 or FLOAT32 |
| Atan | ATAN2 | Input/output dtype must be FLOAT16 or FLOAT32 |
| Atanh | ADD + SUB + DIV + LOG + MUL | Input/output dtype must be FLOAT16 or FLOAT32 |
| AveragePool | AVERAGE_POOL_2D | 2D only (rank=4), ceil_mode=0, zero pads or auto_pad=SAME_* |
| BatchNormalization | MUL + ADD | All parameter inputs (scale, bias, mean, var) must be constant |
| BitShift | RIGHT_SHIFT (RIGHT) or MUL-based (LEFT) | LHS/RHS must be integer tensors, direction must be LEFT or RIGHT; LEFT requires constant shift input |
| BitwiseAnd | LOGICAL_AND | BOOL tensors only |
| BitwiseNot | LOGICAL_NOT / SUB + CAST | Input dtype must be BOOL or integer |
| BitwiseOr | LOGICAL_OR | BOOL tensors only |
| BitwiseXor | BITWISE_XOR | Input dtypes must match and be BOOL/integer |
| Cast | CAST | - |
| Ceil | CEIL | - |
| Celu | MAXIMUM + MINIMUM + DIV + EXP + SUB + MUL + ADD | Input/output dtype must be FLOAT16 or FLOAT32 |
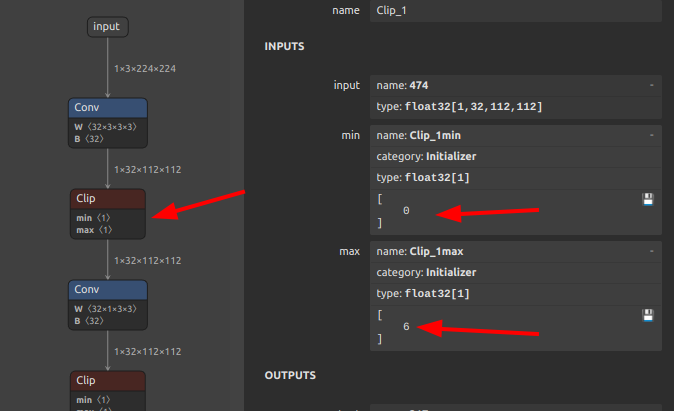
| Clip | RELU / RELU6 / MAXIMUM + MINIMUM | General constant clip ranges are supported via MAXIMUM/MINIMUM decomposition. ReLU fast-path: min=0,max=+inf; ReLU6 fast-path: min=0,max=6 |
| Concat | CONCATENATION | - |
| ConstantOfShape | CAST + FILL | Shape input must be rank-1 integer tensor; value attribute must be scalar (or omitted for zero-fill) |
| Conv | CONV_2D / DEPTHWISE_CONV_2D | 2D only (rank=4), weights must be constant, grouped conv only regular/depthwise, zero pads or auto_pad=SAME_* |
| ConvTranspose | TRANSPOSE_CONV (+ optional ADD bias) | 2D only (input rank=4), weight must be constant rank=4, group=1, dilations=[1,1], output_padding=[0,0], and padding must be auto_pad=SAME_* or zero pads (auto_pad in {NOTSET,VALID}) |
| Cos | COS | - |
| Cosh | SUB + EXP + ADD + MUL | Input/output dtype must be FLOAT16 or FLOAT32 |
| DequantizeLinear | DEQUANTIZE | scale must be constant, zero_point (if provided) must be constant, per-axis axis must be in range |
| Div | DIV or MUL (when divisor is constant reciprocal) | For non-floating outputs, lowered as CAST -> MUL(reciprocal) -> CAST to preserve output dtype without using unsupported integer DIV paths |
| DynamicQuantizeLinear | NEG + REDUCE_MAX + MINIMUM + MAXIMUM + SUB + DIV + ADD + CAST | Input dtype must be FLOAT16/FLOAT32, output dtypes must be Y=UINT8, Y_Scale=FLOAT16/FLOAT32, Y_ZeroPoint=UINT8; scale/zero-point outputs must be scalar |
| Einsum | FULLY_CONNECTED | Rank-2 matmul-style equation only (ij,jk->ik), rhs input must be constant weights |
| Elu | ELU | - |
| Equal | EQUAL | - |
| Exp | EXP | - |
| Expand | RESHAPE + MUL (broadcast via const ones) | Output shape must be statically known, non-negative, and broadcast-compatible with input shape (current direct lowering uses static RESHAPE + MUL) |
| EyeLike | RESHAPE (from const eye) | Output must be rank-2 with fully static positive shape |
| Flatten | RESHAPE | Input rank must be >= 1 |
| Floor | FLOOR | - |
| FusedMatMul | BATCH_MATMUL (+ optional MUL for alpha) |
Input rank >= 2, dtypes FLOAT16/FLOAT32 only, transA/transB must be 0 or 1, finite alpha required |
| Gather | GATHER | batch_dims=0 only |
| GatherElements | CAST + RESHAPE + CONCATENATION + GATHER_ND | Data/indices ranks must match, output shape must equal indices shape, static positive output dims required, axis must be in range |
| GatherND | CAST + GATHER_ND | batch_dims=0 only; indices must be integer type; indices last dim must be static positive and <= params_rank |
| Gelu | GELU | - |
| Gemm | FULLY_CONNECTED | Input rank=2, weight rank=2 + constant, transA=0 only |
| Greater | GREATER | - |
| GRU | TRANSPOSE + SLICE + SQUEEZE + BATCH_MATMUL + ADD + MUL + SUB + LOGISTIC + TANH + RESHAPE + CONCATENATION + EXPAND_DIMS | layout=0; direction in {forward, reverse, bidirectional}; sequence_lens unsupported; W/R must be constant rank-3; linear_before_reset in {0,1}; activations [Sigmoid,Tanh]; clip=0 |
| Hardmax | TRANSPOSE + ARG_MAX + ONE_HOT | axis must be in range; target axis size must be static positive |
| HardSigmoid | MUL + ADD + MAXIMUM + MINIMUM | Input/output dtype must be FLOAT16 or FLOAT32 |
| Identity | RESHAPE | - |
| Less | LESS | - |
| LessOrEqual | LESS_EQUAL | - |
| LogSoftmax | SOFTMAX + LOG (+ transpose in/out for non-last axis) | axis must be in range (negative axis normalized) |
| LpNormalization | L2_NORMALIZATION | p=2, axis=last only |
| LRN | LOCAL_RESPONSE_NORMALIZATION (+ transpose in/out) | Input rank must be 4, size must be a positive odd integer |
| LSTM | BIDIRECTIONAL_SEQUENCE_LSTM + SPLIT + RESHAPE/EXPAND_DIMS + CONCATENATION | direction=bidirectional, layout=0, input_forget=0; W/R must be constant rank-3 with num_directions=2; optional B must be constant shape [2, 8*hidden_size]; initial_h/initial_c must be constant zero tensors of shape [2, batch, hidden]; sequence_lens and peephole input P unsupported; outputs Y_h/Y_c unsupported when consumed |
| MatMul | BATCH_MATMUL | Input rank >= 2. Dynamic rhs input is supported (no constant-weight requirement) |
| MatMulInteger | CAST + SUB + BATCH_MATMUL | A/B input rank must be >=2 (rank=1 placeholder allowed), A/B dtypes must be integer tensor types (INT8/UINT8/INT16/UINT16/INT32), output dtype must be INT32/INT64; optional zero-point inputs must be scalar/1D and shape-compatible |
| MaxPool | MAX_POOL_2D | 2D only (rank=4), ceil_mode=0, zero pads or auto_pad=SAME_* |
| Mish | EXP + ADD + LOG + TANH + MUL | Input/output dtype must be FLOAT16 or FLOAT32 |
| Mod | FLOOR_MOD | fmod=0 only |
| Mul | MUL | - |
| Neg | NEG | - |
| NonMaxSuppression | ARG_MAX + REDUCE_MAX + SQUEEZE + NON_MAX_SUPPRESSION_V4 + SLICE + GATHER + SUB + CAST + RESHAPE + CONCATENATION | Rank-3 boxes/scores only; center_point_box=0; currently batch=1; class dim >1 requires --output_nms_with_argmax; optional thresholds/max_output must be scalar constants |
| NonZero | NOT_EQUAL + WHERE + TRANSPOSE + CAST | Input rank must be >=1; output rank must be 2 |
| Not | LOGICAL_NOT | - |
| OneHot | CAST + ADD + FLOOR_MOD + ONE_HOT | depth input must be constant scalar and >0; values input must be constant 2-element tensor [off_value,on_value]; normalized axis must be in range |
| Or | LOGICAL_OR | - |
| Pad | PAD | mode=constant only, pads must be constant, constant pad value (if provided) must be zero |
| Pow | POW | Output dtype must be FLOAT16 or FLOAT32 |
| PRelu | PRELU | slope must be constant (scalar or per-channel) |
| QGemm | FULLY_CONNECTED | Input rank=1 or 2, weight must be constant rank=2, bias must be constant, quantization params must be constant, transA=0, transB in {0,1} |
| QLinearAdd | ADD | All quantization params (a/b/c scale, a/b/c zero_point) must be constant |
| QLinearAveragePool | DEQUANTIZE + TRANSPOSE + AVERAGE_POOL_2D + TRANSPOSE + QUANTIZE | Input rank=4 only, all quantization params (x scale/zero_point, y scale/zero_point) must be constant, kernel_shape/strides must be 2D, dilations=[1,1], ceil_mode=0, count_include_pad=0, and pads must satisfy flatbuffer_direct pool constraints (zero/symmetric or auto_pad=SAME_*) |
| QLinearConcat | DEQUANTIZE + CONCATENATION + QUANTIZE | y scale/zero_point and each input triplet (x scale/zero_point) must be constant, input ranks must match, axis must be in range |
| QLinearConv | CONV_2D / DEPTHWISE_CONV_2D | Input/output rank=4, weight must be constant rank=4, all quantization params constant, group conv only regular/depthwise (depthwise detection uses group and weight shape), optional bias must be constant |
| QLinearGlobalAveragePool | AVERAGE_POOL_2D (preferred) / DEQUANTIZE + MEAN + QUANTIZE (fallback) | All quantization params (x scale/zero_point, y scale/zero_point) must be constant, input rank >= 3, channels_last must be 0 or 1. Quantized AVERAGE_POOL_2D path is used for rank-4 with static spatial dims and per-tensor quantization |
| QLinearMatMul | FULLY_CONNECTED | Input rank=1 or 2, weight must be constant rank=2, all quantization params constant |
| QLinearMul | MUL | All quantization params (a/b/c scale, a/b/c zero_point) must be constant |
| QLinearSigmoid | DEQUANTIZE + LOGISTIC + QUANTIZE | All quantization params (x scale/zero_point, y scale/zero_point) must be constant |
| QuantizeLinear | QUANTIZE | scale must be constant, zero_point (if provided) must be constant, per-axis axis must be in range |
| Range | CAST + SQUEEZE + RANGE | Each of start/limit/delta must be scalar-like rank-1 length-1 tensor |
| Reciprocal | DIV | Input/output dtype must be FLOAT16 or FLOAT32 |
| ReduceL1 | ABS + SUM | Reduce axes must be constant when provided via input tensor |
| ReduceL2 | MUL + SUM + SQRT + CAST | Reduce axes must be constant when provided via input tensor |
| ReduceMax | REDUCE_MAX | Reduce axes must be constant when provided via input tensor |
| ReduceMean | MEAN | Reduce axes must be constant when provided via input tensor |
| ReduceSum | SUM | Reduce axes must be constant when provided via input tensor |
| Relu | RELU | - |
| Reshape | RESHAPE | Shape input must be constant |
| Resize | RESIZE_NEAREST_NEIGHBOR / RESIZE_BILINEAR | Rank-4 only; supported modes: nearest/linear (limited attr combinations). Parameters must be either constant scales/sizes or dynamic rank-1 integer sizes (INT32/INT64) |
| RNN | UNIDIRECTIONAL_SEQUENCE_RNN + TRANSPOSE + EXPAND_DIMS + SLICE + RESHAPE | direction=forward, layout=0; sequence_lens unsupported; W/R must be constant rank-3 with num_directions=1; activations in {tanh,relu,sigmoid}; clip=0 |
| Round | ROUND | - |
| Selu | MAXIMUM + MINIMUM + EXP + SUB + MUL + ADD | Input/output dtype must be FLOAT16 or FLOAT32 |
| Shape | SHAPE (+ SLICE for start/end) |
Output dtype must be INT32 or INT64; start/end slicing follows ONNX normalization |
| Sigmoid | LOGISTIC | - |
| Sign | SIGN | - |
| Sin | SIN | - |
| Sinh | SUB + EXP + MUL | Input/output dtype must be FLOAT16 or FLOAT32 |
| Softmax | SOFTMAX (+ transpose in/out for non-last axis) | axis must be in range (negative axis normalized) |
| Softplus | EXP + ADD + LOG | Input/output dtype must be FLOAT16 or FLOAT32 |
| Softsign | ABS + ADD + DIV | Input/output dtype must be FLOAT16 or FLOAT32 |
| SpaceToDepth | SPACE_TO_DEPTH | blocksize > 1, rank=4 (NCHW) |
| Sqrt | SQRT | - |
| Squeeze | SQUEEZE | Axes must be constant when provided via input tensor |
| Sub | SUB | - |
| Tan | SIN + COS + DIV | Input/output dtype must be FLOAT16 or FLOAT32 |
| Tanh | TANH | - |
| Transpose | TRANSPOSE | Permutation input must be constant |
| Trilu | MUL / LOGICAL_AND | Input rank must be >=2; matrix dims must be static positive; optional k input must be constant |
| Unsqueeze | RESHAPE | Axes must be constant and in range |
| Where | CAST + SELECT | Condition input dtype must be BOOL or numeric |
| Xor | NOT_EQUAL | - |
Custom-op candidates in flatbuffer_direct (opt-in)
| ONNX OP | Default policy | When enabled |
|---|---|---|
| DeformConv | explicit_error (custom_op_candidate_disabled) |
Lowered to TFLite CUSTOM when --flatbuffer_direct_allow_custom_ops is enabled and allowlist passes |
| GridSample | explicit_error (custom_op_candidate_disabled) |
Lowered to TFLite CUSTOM when --flatbuffer_direct_allow_custom_ops is enabled and allowlist passes |
| If | explicit_error (custom_op_candidate_disabled) |
Lowered to TFLite CUSTOM when --flatbuffer_direct_allow_custom_ops is enabled and allowlist passes |
| Loop | explicit_error (custom_op_candidate_disabled) |
Lowered to TFLite CUSTOM when --flatbuffer_direct_allow_custom_ops is enabled and allowlist passes |
| RoiAlign | explicit_error (custom_op_candidate_disabled) |
Lowered to TFLite CUSTOM when --flatbuffer_direct_allow_custom_ops is enabled and allowlist passes |
| Scan | explicit_error (custom_op_candidate_disabled) |
Lowered to TFLite CUSTOM when --flatbuffer_direct_allow_custom_ops is enabled and allowlist passes |
| ScatterElements | explicit_error (custom_op_candidate_disabled) |
Lowered to TFLite CUSTOM when --flatbuffer_direct_allow_custom_ops is enabled and allowlist passes |
| SequenceAt | explicit_error (custom_op_candidate_disabled) |
Lowered to TFLite CUSTOM when --flatbuffer_direct_allow_custom_ops is enabled and allowlist passes |
| SequenceConstruct | explicit_error (custom_op_candidate_disabled) |
Lowered to TFLite CUSTOM when --flatbuffer_direct_allow_custom_ops is enabled and allowlist passes |
| SequenceErase | explicit_error (custom_op_candidate_disabled) |
Lowered to TFLite CUSTOM when --flatbuffer_direct_allow_custom_ops is enabled and allowlist passes |
| SequenceInsert | explicit_error (custom_op_candidate_disabled) |
Lowered to TFLite CUSTOM when --flatbuffer_direct_allow_custom_ops is enabled and allowlist passes |
| SequenceLength | explicit_error (custom_op_candidate_disabled) |
Lowered to TFLite CUSTOM when --flatbuffer_direct_allow_custom_ops is enabled and allowlist passes |
| TopK | explicit_error (custom_op_candidate_disabled) |
Lowered to TFLite CUSTOM when --flatbuffer_direct_allow_custom_ops is enabled and allowlist passes |
| Unique | explicit_error (custom_op_candidate_disabled) |
Lowered to TFLite CUSTOM when --flatbuffer_direct_allow_custom_ops is enabled and allowlist passes |
Notes:
Einsumis now treated asbuiltin_supportedwhen it matches builtin constraints; unsupportedEinsumpatterns may still fallback toCUSTOMif custom-op mode is enabled.QLinearConvis treated asbuiltin_supportedfor regular/depthwise patterns; unsupported grouped patterns may still fallback toCUSTOMwhen custom-op mode is enabled.LogSoftmaxis now treated asbuiltin_supportedwhen builtin constraints pass; unsupported patterns may still fallback toCUSTOMif custom-op mode is enabled.LSTMis now treated asbuiltin_supportedfor constrained bidirectional patterns; unsupported patterns may still fallback toCUSTOMif custom-op mode is enabled.NonMaxSuppressionis now treated asbuiltin_supportedwhen builtin constraints pass; unsupported patterns may still fallback toCUSTOMif custom-op mode is enabled.DynamicQuantizeLinearis now treated asbuiltin_supportedfor constrained float-input/uint8-output patterns; unsupported patterns may still fallback toCUSTOMif custom-op mode is enabled.OneHot,MatMulInteger,Pow, andReciprocalare now treated asbuiltin_supportedwhen builtin constraints pass.- Newly added builtin-covered ops in this update include:
Abs,Acos,Acosh,And,ArgMin,Asin,Asinh,Atan,Atanh,BitShift,BitwiseAnd,BitwiseNot,BitwiseOr,BitwiseXor,Ceil,Celu,Cos,Cosh,Elu,Equal,EyeLike,Floor,GatherND,Gelu,Greater,GRU,Hardmax,Less,LessOrEqual,Mish,NonZero,Not,Or,Range,ReduceL1,ReduceL2,RNN,Round,Selu,Sign,Sin,Sinh,Softplus,Softsign,Tan,Trilu,Where, andXor. Resizebuiltin path now accepts dynamic rank-1 integersizesinput in addition to constantscales/sizes.
tf_converter vs flatbuffer_direct (operational differences)
| Item | tf_converter (default) |
flatbuffer_direct |
|---|---|---|
| Final backend | TensorFlow Lite Converter | Direct FlatBuffer builder (schema.fbs) |
| Model optimization source | Large set of existing TF-path graph rewrites/heuristics | Dedicated direct preprocess pipeline + direct dispatch constraints |
| Failure behavior | Often absorbed by TF-side graph lowering | Explicit reason_code-based failure on unsupported patterns |
| Custom op handling | Typically avoided by TF-side replacement when possible | Opt-in only (--flatbuffer_direct_allow_custom_ops) with allowlist |
| Diagnostics | Standard conversion logs | *_op_coverage_report.json (dispatch_mode, unsupported_reason_counts, custom_op_policy, preprocess_report) |
| Fallback | N/A | --flatbuffer_direct_fallback_to_tf_converter available |
flatbuffer_direct preprocess absorption scope
flatbuffer_direct runs staged preprocess rules before lowering. Current major coverage:
pattern_fusion_wave2Relu -> Clip(min=0,max=6)chain normalization- GELU chain fusion (
Div -> Erf -> Add -> Mul -> Mul) Reshape -> Transpose -> ReshapetoSpaceToDepth
quant_chain_fusion_wave3DequantizeLinear -> BatchNormalization -> PRelu -> QuantizeLinearchain rewrite- BatchNormalization parameter folding into
Mul + Add
pseudo_ops_wave1HardSwish,LeakyRelu,Gelu, limitedPowrewrites to builtin-friendly forms
constant_fold_a5- Limited constant folding for shape/axes and arithmetic helper chains
- Includes
DequantizeLinear(axis/block-size aware) and downstreamReshapefolding for constant-weight subgraphs
normalize_attrs_a5- Normalize
perm/axes/negative-axis forms and softmax-axis bridge rewrites
- Normalize
Notes:
- This reduces, but does not fully match, the TF-path replacement coverage.
- To inspect what was applied, use
--report_op_coverageand checkpreprocess_report.applied_rules.
Known constraints and workaround options
Symptom (reason_code) |
Meaning | Recommended action |
|---|---|---|
unsupported_onnx_op |
No direct builtin/custom path for the node | Use --tflite_backend tf_converter, or enable --flatbuffer_direct_fallback_to_tf_converter |
requires_constant_input |
Node requires compile-time constant input (e.g., axes/perm/shape) | Pre-fold ONNX graph (onnxsim) or rewrite model to constantize the input |
unsupported_attribute_value |
Attribute/rank/value not accepted by direct builtin constraints | Adjust ONNX export options or rewrite offending subgraph before conversion |
custom_op_candidate_disabled |
Op is in custom-candidate set but custom lowering is disabled | Enable --flatbuffer_direct_allow_custom_ops when runtime supports the custom op |
custom_op_not_in_allowlist |
Custom lowering enabled but op is not allowlisted | Add op to --flatbuffer_direct_custom_op_allowlist explicitly |
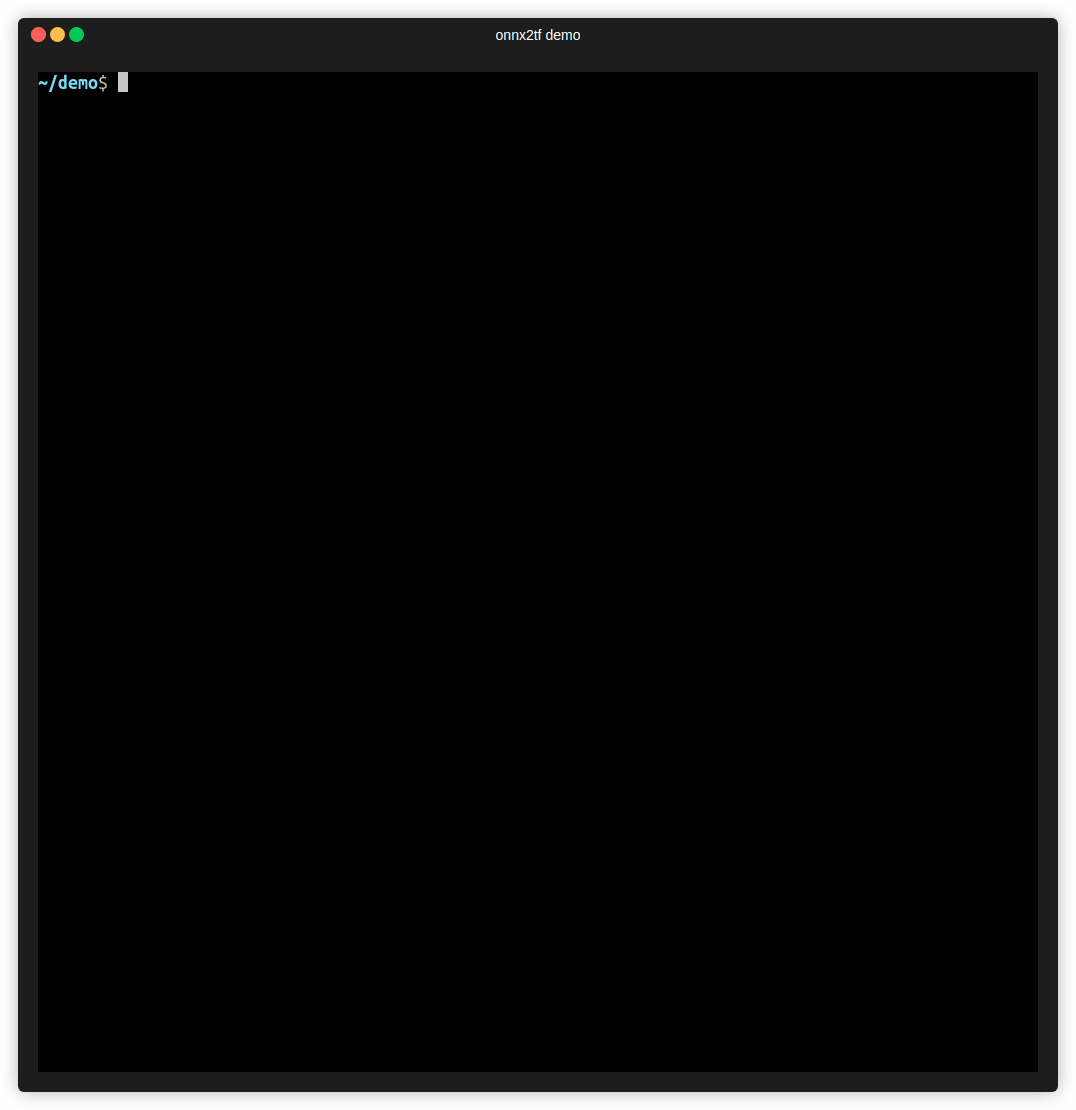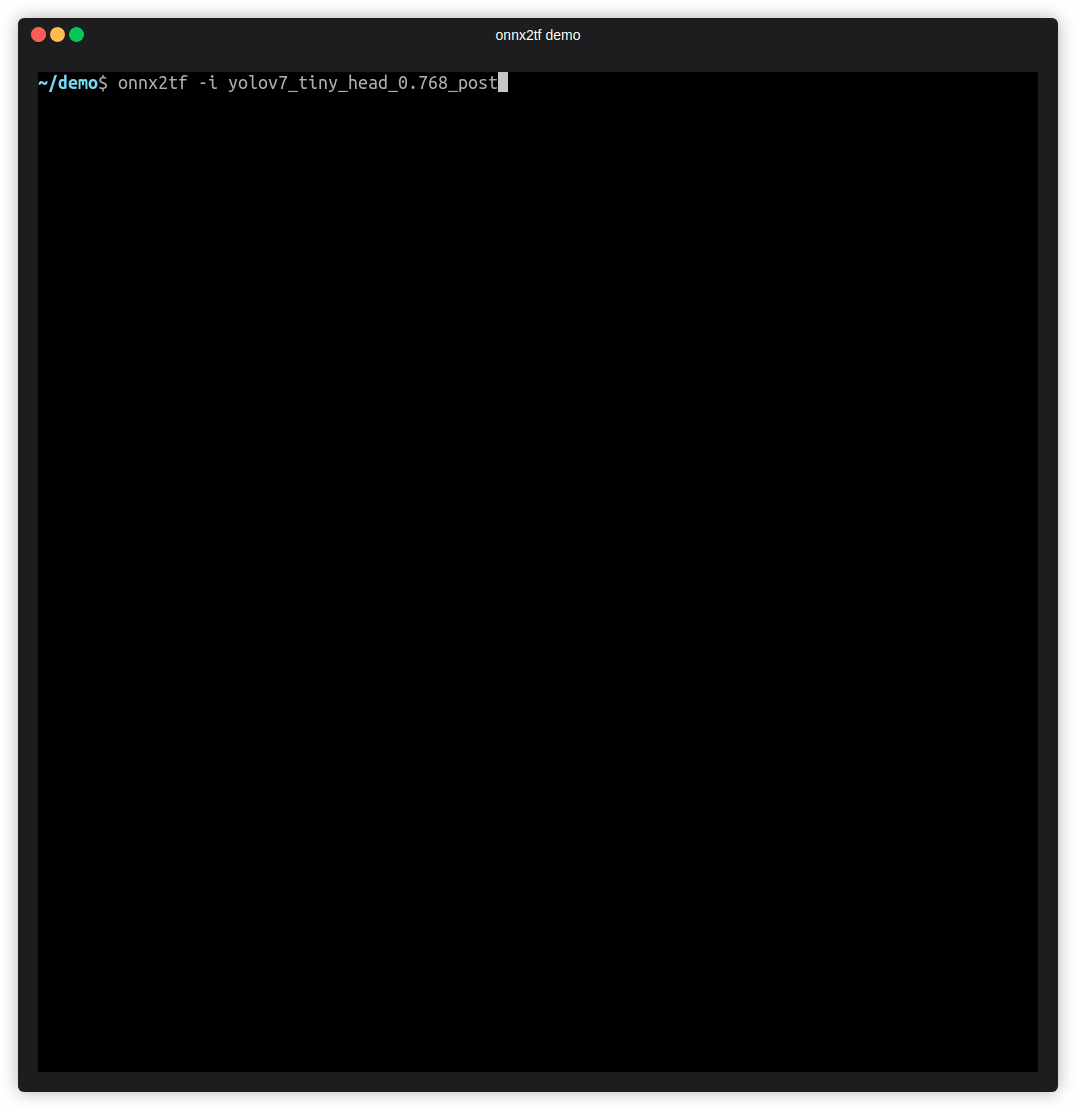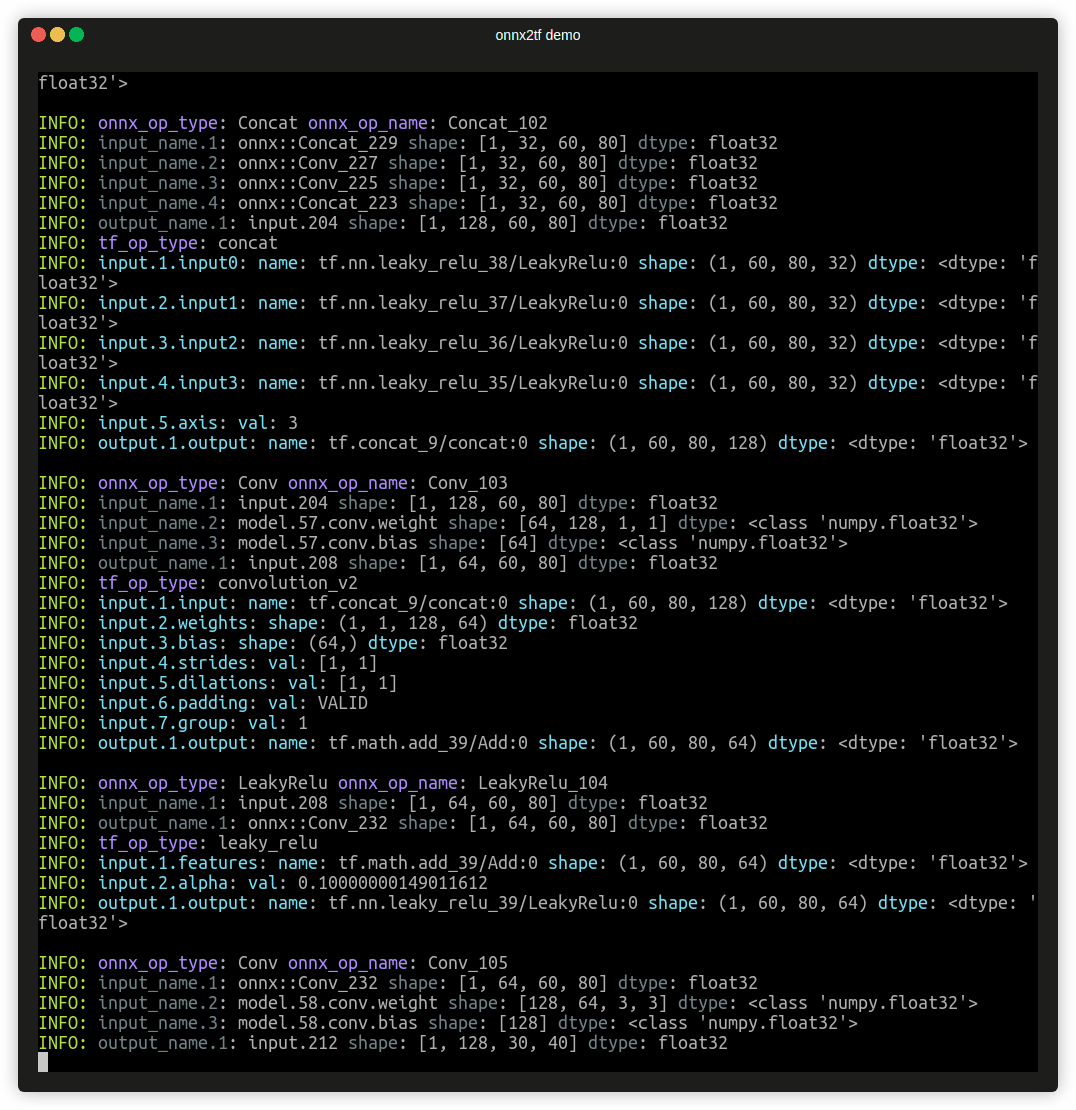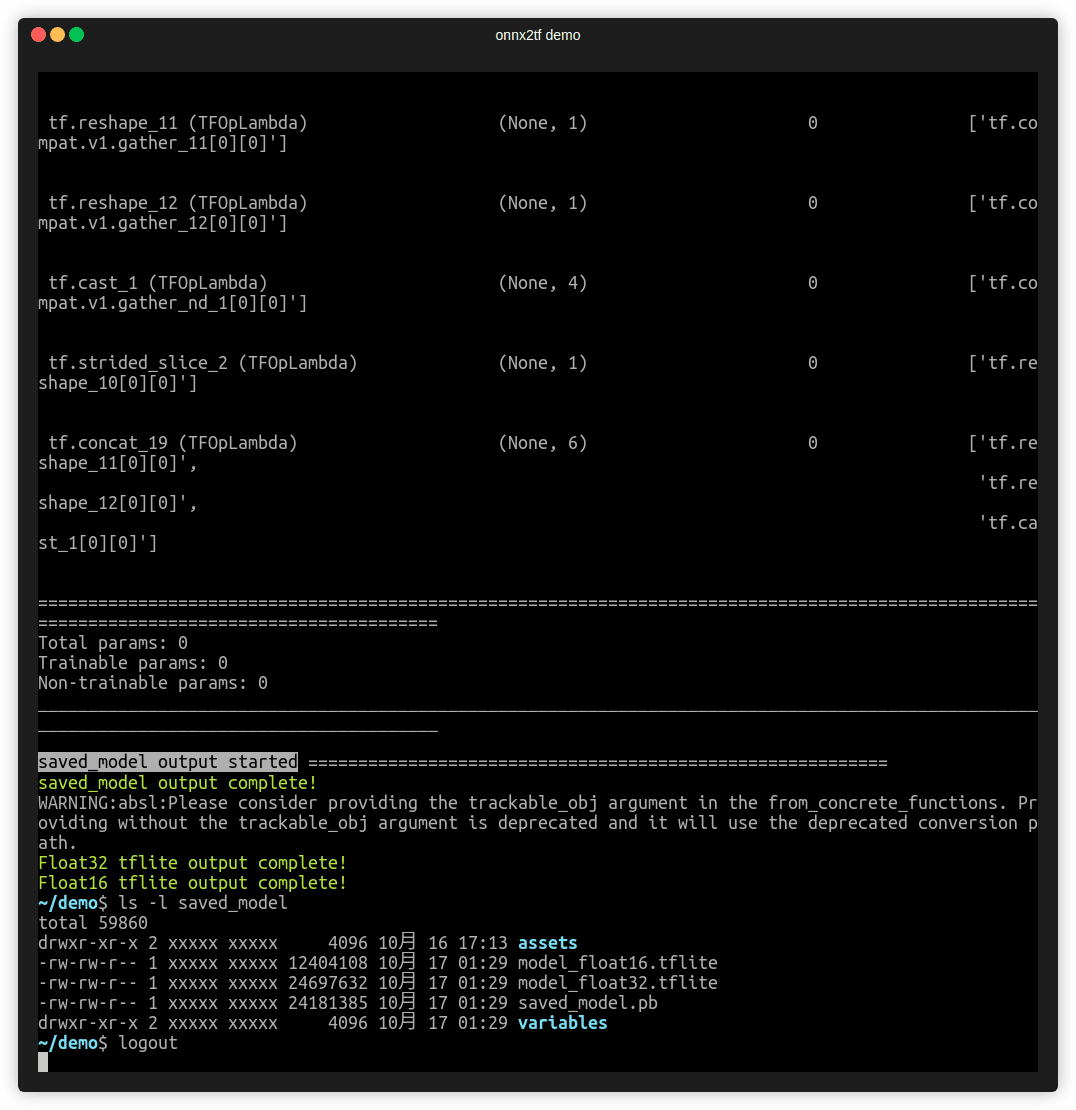
Demo
Video speed is adjusted approximately 50 times slower than actual speed.
Environment
- Linux / Windows
- onnx==1.20.1
- onnxruntime==1.24.1
- onnxsim-prebuilt==0.4.39.post2
- onnxoptimizer==0.4.2
- sne4onnx>=2.0.0
- sng4onnx>=2.0.0
- tensorflow==2.19.0
- tf-keras==2.19.0
- ai-edge-litert==2.1.2
- h5py==3.12.1
- psutil==5.9.5
- ml_dtypes==0.5.1
- flatbuffers-compiler (Optional, Only when using the
-coionoption. Executable file namedflatc.) - flatbuffers>=23.1.21
# Custom flatc binary for Ubuntu 22.04+ # https://github.com/PINTO0309/onnx2tf/issues/196 # x86_64/amd64 v23.5.26 wget https://github.com/PINTO0309/onnx2tf/releases/download/1.16.31/flatc.tar.gz \ && tar -zxvf flatc.tar.gz \ && sudo chmod +x flatc \ && sudo mv flatc /usr/bin/ # arm64 v23.1.21 wget https://github.com/PINTO0309/onnx2tf/releases/download/1.26.6/flatc_arm64.tar.gz \ && tar -zxvf flatc_arm64.tar.gz \ && sudo chmod +x flatc \ && sudo mv flatc /usr/bin/
Sample Usage
1. Install
Note:
1. If you are using TensorFlow v2.13.0 or earlier, use a version older than onnx2tf v1.17.5. onnx2tf v1.17.6 or later will not work properly due to changes in TensorFlow's API.
2. The latest onnx2tf implementation is based on Keras API 3 and will not work properly if you install TensorFlow v2.15.0 or earlier.
3. Starting with onnx2tf v2.0.0, due to onnxruntime issues, onnx2tf will no longer support environments older than Python 3.10. Accordingly, the Docker Image has been upgraded to Ubuntu 24.04. The dependency on onnx-graphsurgeon has also been completely removed. onnxruntime v1.24.1: https://github.com/microsoft/onnxruntime/releases/tag/v1.24.1
-
HostPC
Click to expand
-
When using GHCR, see
Authenticating to the Container registry
# PAT authentication is required to pull from GHCR. docker login ghcr.io Username (xxxx): {Enter} Password: {Personal Access Token} Login Succeeded # Start an interactive session on the terminal. docker run --rm -it \ -v `pwd`:/workdir \ -w /workdir \ ghcr.io/pinto0309/onnx2tf:2.0.19 or # Authentication is not required for pulls from Docker Hub. # Start an interactive session on the terminal. docker run --rm -it \ -v `pwd`:/workdir \ -w /workdir \ docker.io/pinto0309/onnx2tf:2.0.19 or # Direct execution in Docker # The model conversion is performed within Docker, # but the model is output to the host PC's storage. docker run --rm \ --user $(id -u):$(id -g) \ -v $(pwd):/work \ docker.io/pinto0309/onnx2tf:2.0.19 \ onnx2tf -i /work/densenet-12.onnx -o /work/saved_model or curl -LsSf https://astral.sh/uv/install.sh | sh uv python install 3.12.12 uv venv -p 3.12.12 .venv source .venv/bin/activate uv pip install -U onnx2tf or curl -LsSf https://astral.sh/uv/install.sh | sh uv python install 3.12.12 uv venv -p 3.12.12 .venv source .venv/bin/activate uv sync or pip install -e . or docker buildx build \ --platform linux/amd64 \ --build-arg BUILD_ARCH=linux/amd64 \ --progress=plain \ -t onnx2tf:amd64 \ --load . or # It is possible to cross-compile an arm64 environment on an x64 environment. docker buildx build \ --platform linux/arm64 \ --build-arg BUILD_ARCH=linux/arm64 \ --progress=plain \ -t onnx2tf:arm64 \ --load .
-
2. Run test
Only patterns that are considered to be used particularly frequently are described. In addition, there are several other options, such as disabling Flex OP and additional options to improve inference performance. See: CLI Parameter
# Float32, Float16
# This is the fastest way to generate tflite.
# Improved to automatically generate `signature` without `-osd` starting from v1.25.3.
# Also, starting from v1.24.0, efficient TFLite can be generated
# without unrolling `GroupConvolution`. e.g. YOLOv9, YOLOvN
# Conversion to other frameworks. e.g. TensorFlow.js, CoreML, etc
# https://github.com/PINTO0309/onnx2tf#19-conversion-to-tensorflowjs
# https://github.com/PINTO0309/onnx2tf#20-conversion-to-coreml
wget https://github.com/PINTO0309/onnx2tf/releases/download/0.0.2/resnet18-v1-7.onnx
onnx2tf -i resnet18-v1-7.onnx
ls -lh saved_model/
assets
fingerprint.pb
resnet18-v1-7_float16.tflite
resnet18-v1-7_float32.tflite
saved_model.pb
variables
TF_CPP_MIN_LOG_LEVEL=3 \
saved_model_cli show \
--dir saved_model \
--signature_def serving_default \
--tag_set serve
The given SavedModel SignatureDef contains the following input(s):
inputs['data'] tensor_info:
dtype: DT_FLOAT
shape: (-1, 224, 224, 3)
name: serving_default_data:0
The given SavedModel SignatureDef contains the following output(s):
outputs['output_0'] tensor_info:
dtype: DT_FLOAT
shape: (-1, 1000)
name: PartitionedCall:0
Method name is: tensorflow/serving/predict
# In the interest of efficiency for my development and debugging of onnx2tf,
# the default configuration shows a large amount of debug level logs.
# However, for most users, a large number of debug logs are unnecessary.
# If you want to reduce the amount of information displayed in the conversion log,
# you can change the amount of information in the log by specifying the
# `--verbosity` or `-v` option as follows.
# Possible values are "debug", "info", "warn", and "error".
wget https://github.com/PINTO0309/onnx2tf/releases/download/0.0.2/resnet18-v1-7.onnx
onnx2tf -i resnet18-v1-7.onnx -v info
# Override undefined batch size or other dimensions with static values.
# If the model has undefined dimensions, rewriting them to a static size will significantly
# improve the success rate of the conversion.
# The `-b` option overwrites the zero-dimensional batch size with the number specified
# without input OP name.
# Note that if there are multiple input OPs, the zero dimension of all input OPs is
# forced to be rewritten.
# The `-sh/--shape-hints` option provides shape hints for input tensors with undefined
# dimensions, significantly improving the conversion success rate for models with dynamic
# input shapes. Specifying this option in combination with the `-b` option will further
# improve the success rate of model conversion. The `-sh` option does not change ONNX
# input OPs to static shapes.
# The `-ois/--overwrite_input_shape` option allows undefined dimensions in all dimensions,
# including the zero dimensionality, to be overwritten to a static shape, but requires
# the input OP name to be specified.
# e.g. -ois data1:1,3,224,224 data2:1,255 data3:1,224,6
wget https://github.com/PINTO0309/onnx2tf/releases/download/0.0.2/resnet18-v1-7.onnx
onnx2tf -i resnet18-v1-7.onnx -b 1
or
onnx2tf -i resnet18-v1-7.onnx -sh data:1,3,224,224 -b 1
or
onnx2tf -i resnet18-v1-7.onnx -ois data:1,3,224,224
# Suppress automatic transposition of input OPs from NCW, NCHW, NCDHW to NWC, NHWC, NDHWC.
# onnx2tf is a specification that automatically transposes the input OP to [N,H,W,C] format
# before converting the model. However, since onnx2tf cannot determine from the structure of
# the model whether the input data is image, audio data, or something else, it unconditionally
# transposes the channels. Therefore, it is the models of STT/TTS models where the input is
# not NHWC that tend to have particular problems with the automatic transposition of the
# input OP.
# If you do not want input OPs to be automatically transposed, you can disable automatic
# transposition of input OPs by specifying the `-kat` option.
wget https://github.com/PINTO0309/onnx2tf/releases/download/1.1.28/double_gru.onnx
# INPUT OPs: "spec": float32[1,3,257,1], "states_in": float32[2,1,32]
# The following command suppresses the automatic transposition of "states_in" and converts it.
onnx2tf -i double_gru.onnx -kat states_in
# Keras h5 format
# .h5, .json, .keras, .weights.h5, .weights.keras, .data-00000-of-00001, .index
wget https://github.com/PINTO0309/onnx2tf/releases/download/0.0.2/resnet18-v1-7.onnx
onnx2tf -i resnet18-v1-7.onnx -oh5
# Keras keras_v3 format (TensorFlow v2.12.0 or later only)
wget https://github.com/PINTO0309/onnx2tf/releases/download/0.0.2/resnet18-v1-7.onnx
onnx2tf -i resnet18-v1-7.onnx -okv3
# TensorFlow v1 (.pb) format
wget https://github.com/PINTO0309/onnx2tf/releases/download/0.0.2/resnet18-v1-7.onnx
onnx2tf -i resnet18-v1-7.onnx -otfv1pb
# Automatic JSON generation only
# Generates an optimal parameter replacement JSON file for model conversion.
# The JSON file is saved to {model_name}_auto.json when conversion errors occur
# or accuracy issues are detected and the feature is explicitly enabled.
onnx2tf -i model.onnx -agj
# Accuracy validation only (no JSON generation)
# Validates the accuracy between ONNX and TensorFlow outputs without generating
# any parameter replacement JSON file.
onnx2tf -i model.onnx -cotof
# Accuracy validation + automatic JSON generation
# First generates an optimal parameter replacement JSON file, then uses it
# to validate the model accuracy. This ensures the best possible conversion accuracy.
onnx2tf -i model.onnx -agj -cotof
# Accuracy validation with opt-in JSON generation on error
# Generates a parameter replacement JSON only when accuracy errors greater than 1e-2
# are detected during validation.
onnx2tf -i model.onnx -cotof -agje
# INT8 Quantization, Full INT8 Quantization
# INT8 Quantization with INT16 activation, Full INT8 Quantization with INT16 activation
# Dynamic Range Quantization
wget https://github.com/PINTO0309/onnx2tf/releases/download/1.1.1/emotion-ferplus-8.onnx
# INT8 Quantization (per-channel)
onnx2tf -i emotion-ferplus-8.onnx -oiqt
# INT8 Quantization (per-tensor)
onnx2tf -i emotion-ferplus-8.onnx -oiqt -qt per-tensor
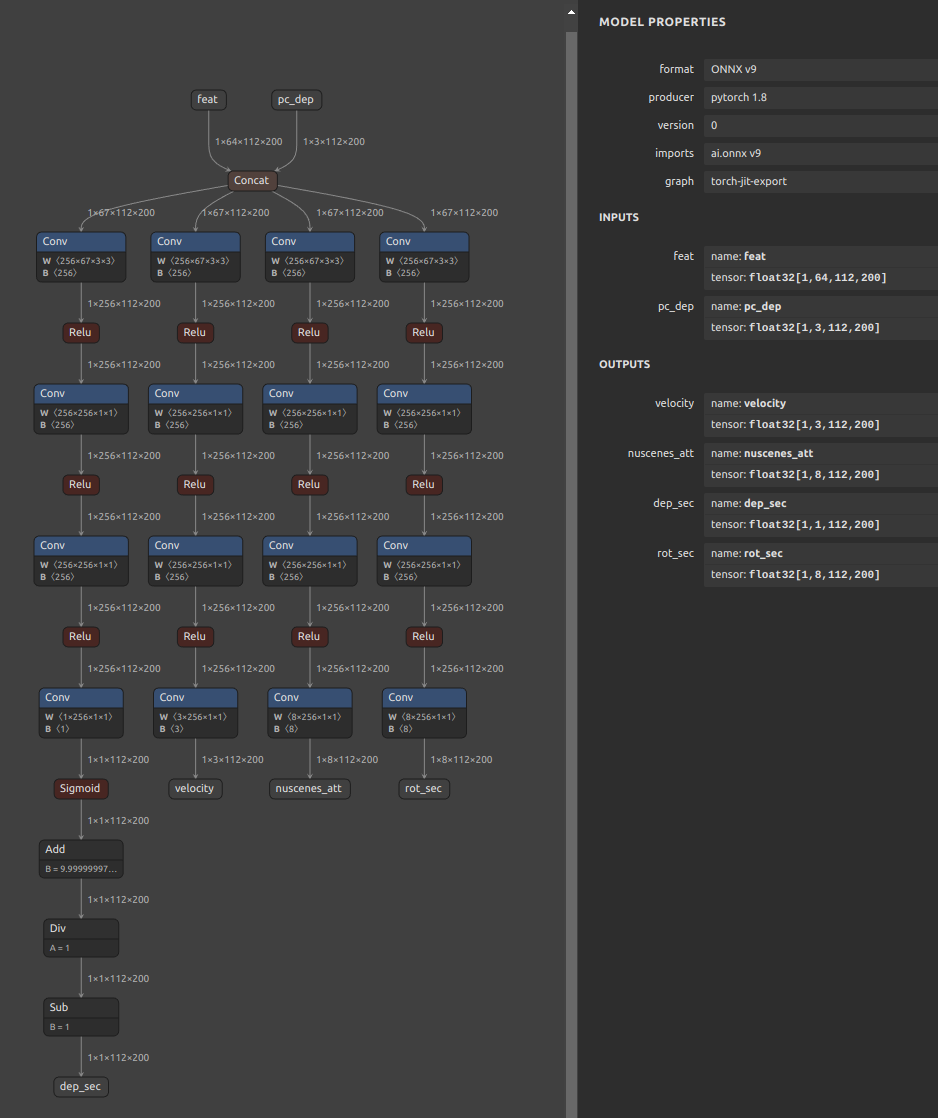
# Split the model at the middle position for debugging
# Specify the input name of the OP
wget https://github.com/PINTO0309/onnx2tf/releases/download/1.25.0/cf_fus.onnx
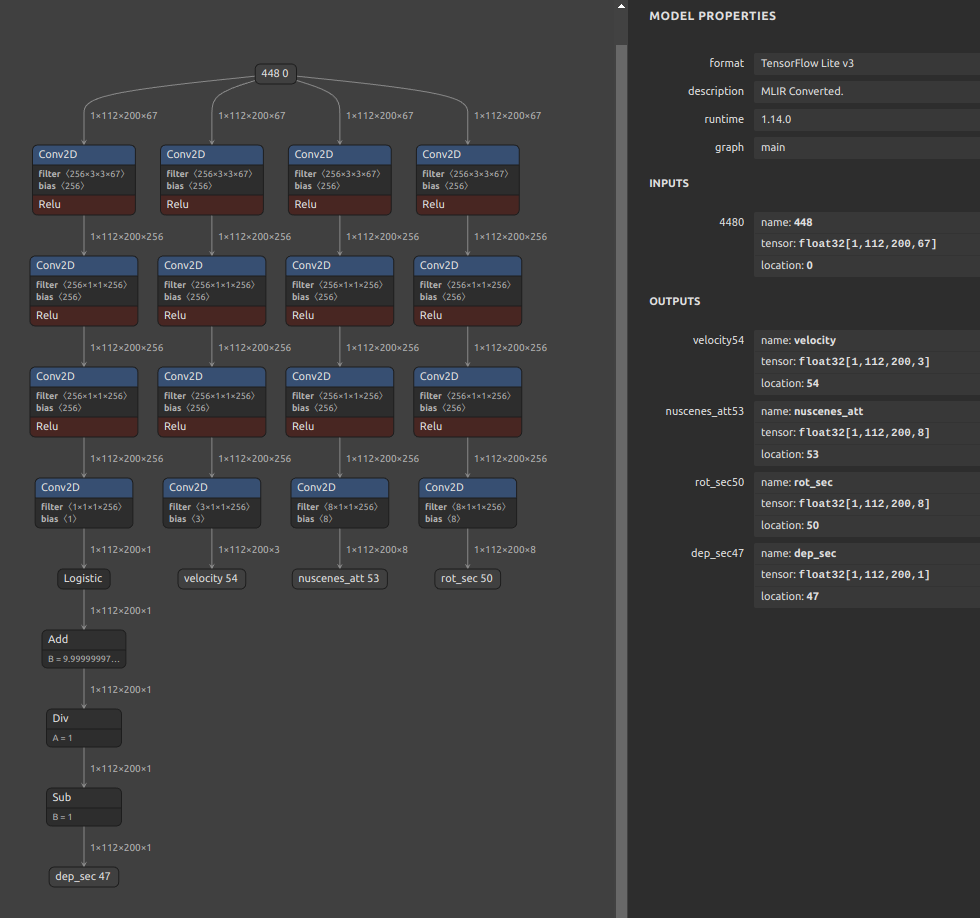
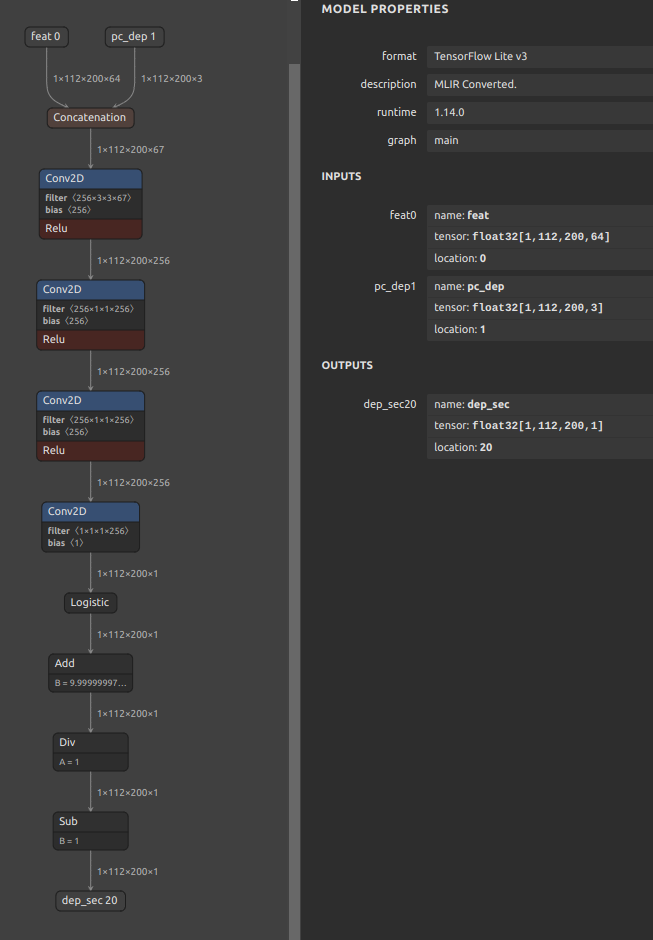
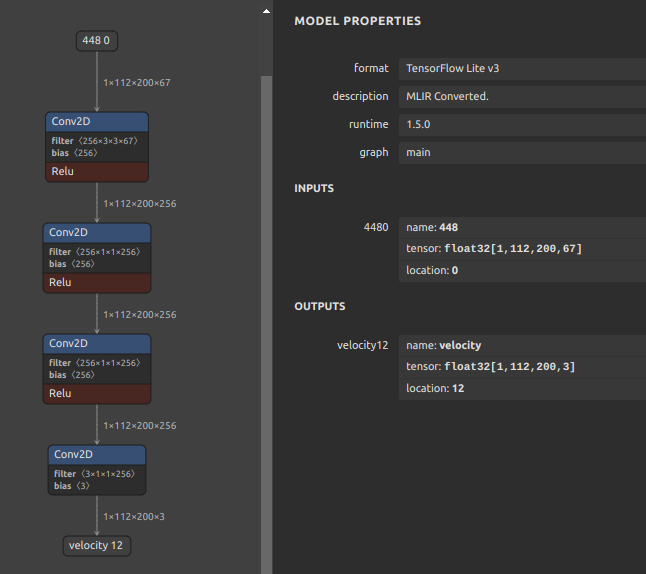
onnx2tf -i cf_fus.onnx -inimc 448
# Split the model at the middle position for debugging
# Specify the output name of the OP
wget https://github.com/PINTO0309/onnx2tf/releases/download/1.25.0/cf_fus.onnx
onnx2tf -i cf_fus.onnx -onimc dep_sec
# Split the model at the middle position for debugging
# Specify the input/output name of the OP
wget https://github.com/PINTO0309/onnx2tf/releases/download/1.25.0/cf_fus.onnx
onnx2tf -i cf_fus.onnx -inimc 448 -onimc velocity
# Suppress generation of Flex OP and replace with Pseudo-Function
# [
# Asin, Acos, Atan, Abs, PReLU,
# LeakyReLU, Power, GatherND,
# Neg, HardSwish, Erf, GeLU, MatMulInteger,
# ]
# Below is a sample of replacing Erf with another set of operations.
wget https://s3.ap-northeast-2.wasabisys.com/temp-models/onnx2tf_readme/Erf_11.onnx
onnx2tf -i Erf_11.onnx -rtpo Erf
# High-dimensional Transpose decomposition
# If you do not like FlexTranspose being generated, try `-nodaftc`.
# Suppresses the generation of FlexTranspose by decomposing Transpose
# to the specified number of dimensions.
# In TensorFlow v2.12.0 and later, up to 6 dimensions are converted to normal Transpose;
# in v2.11.0 and earlier, up to 5 dimensions are converted to normal Transpose.
# Note that specifying `2` for the `-nodaftc` option causes all Transpose OPs to disappear
# from the model structure.
# Below is an example of decomposing a Transpose of 5 or more dimensions into a Transpose
# of 4 dimensions.
onnx2tf -i xxxx.onnx -nodaftc 4
# High-dimensional Slice(StridedSlice) decomposition
# If your special circumstances do not allow you to deploy a `StridedSlice` with more than
# 5 dimensions to a device, you can use the `-nodafsc` option to decompose the `StridedSlice`
# into a process with 4 or fewer dimensions.
# Below is an example of decomposing a `StridedSlice` of 5 or more dimensions into a
# `StridedSlice` of 4 dimensions.
onnx2tf -i xxxx.onnx -nodafsc 4
# Float16 inference doubling on devices with ARM64 ARMv8.2 or higher instruction set
# Double the inference speed with Float16 precision tflite models on devices with
# high-performance CPUs such as Snapdragon.
# (Pixel 3a, Pixel 5a, Pixel 7, Galaxy M12 and Galaxy S22, ...)
# XNNPACK float16 inference on certain ARM64 cores is 2x faster.
# Unfortunately, Float16 inference cannot be accelerated when using the RaspberryPi4's
# ARM64 CPU.
onnx2tf -i xxxx.onnx -eatfp16
# Parameter replacement (Resize,Transpose,Softmax)
rm replace.json
wget https://github.com/PINTO0309/onnx2tf/releases/download/1.1.27/human_segmentation_pphumanseg_2021oct.onnx
wget https://github.com/PINTO0309/onnx2tf/releases/download/1.1.27/replace.json
onnx2tf -i human_segmentation_pphumanseg_2021oct.onnx -prf replace.json
3. Accuracy check
Click to expand
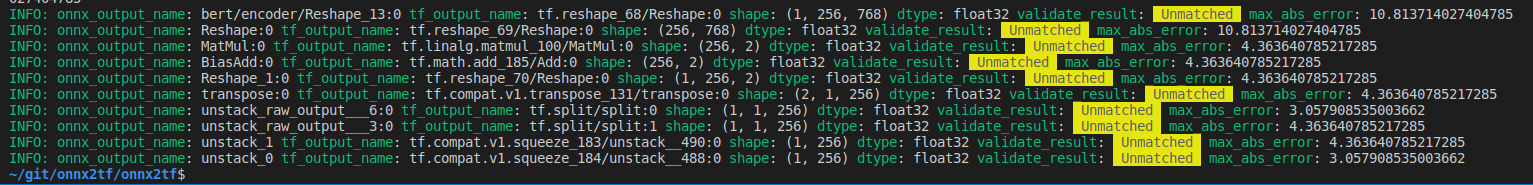
Perform error checking of ONNX output and TensorFlow output. Verify that the error of all outputs, one operation at a time, is below a certain threshold. Automatically determines before and after which OPs the tool's automatic conversion of the model failed. Know where dimensional compression, dimensional expansion, and dimensional transposition by Reshape and Traspose are failing. Once you have identified the problem area, you can refer to the tutorial on Parameter replacement to modify the tool's behavior.
After many upgrades, the need for JSON parameter correction has become much less common, but there are still some edge cases where JSON correction is required. If the PC has sufficient free space in its RAM, onnx2tf will convert the model while carefully performing accuracy checks on all OPs. Thus, at the cost of successful model conversion, the conversion speed is a little slower. If the amount of RAM required for the accuracy check is expected to exceed 80% of the total available RAM capacity of the entire PC, the conversion operation will be performed without an accuracy check. Therefore, if the accuracy of the converted model is found to be significantly degraded, the accuracy may be automatically corrected by re-conversion on a PC with a large amount of RAM. For example, my PC has 128GB of RAM, but the StableDiffusion v1.5 model is too complex in its structure and consumed about 180GB of RAM in total with 50GB of SWAP space.
-ois an option to overwrite the input OP to a static size if it has undefined dimensions. -cotof option checks the accuracy of all OPs one by one. -cotoa is the error value of the threshold for determining an accuracy error. If there are undefined dimensions in the input OP, it is better to fix them to the static geometry to improve the accuracy of the accuracy measurement.
Also, you can use the -cind option to specify custom input for -cotof, instead of using the default dummy input. Otherwise, all input values will be set to 1. You can override the dummy input values with --value_hints (scalar only, *:default supported). For more information about the -cind option, please refer to here. If your input is image data in NHWC format, you can also use --test_data_nhwc_path to provide fixed test samples for validation.
Quick difference between -tdnp and -cind:
-tdnp(--test_data_nhwc_path): Validation-only test data for accuracy checks. Expects one NHWC RGB.npy([N,H,W,3]). Nomean/std. For multi-input models, this single array is reused across inputs (per-input mapping is not supported).-cind(--custom_input_op_name_np_data_path): Per-input custom data mapping by input name. Supports multi-input/non-image inputs. Also used for INT8 calibration (-oiqt) with optionalmean/std.
The -cotof option only compares the original ONNX and converted TensorFlow (Keras) models at Float32 precision, not at Float16 or INT8 precision.
onnx2tf -i mobilenetv2-12.onnx -ois input:1,3,224,224 -cotof -cotoa 1e-1
or
onnx2tf -i mobilenetv2-12.onnx -b 1 -cotof -cotoa 1e-1
or
onnx2tf -i mobilenetv2-12.onnx -cotof -cotoa 1e-1 -cind "input" "/your/path/x.npy"
or
onnx2tf -i mobilenetv2-12.onnx -cotof -cotoa 1e-1 -tdnp "/your/path/test_data_nhwc.npy"
or
onnx2tf -i mobilenetv2-12.onnx -cotof -cotoa 1e-1 --value_hints "input:0.5" "*:1.0"
4. Match tflite input/output names and input/output order to ONNX
Click to expand
If you want to match tflite's input/output OP names and the order of input/output OPs with ONNX, you can use the interpreter.get_signature_runner() to infer this after using the -coion / --copy_onnx_input_output_names_to_tflite option to output tflite file. See: https://github.com/PINTO0309/onnx2tf/issues/228
onnx2tf automatically compares the final input/output shapes of ONNX and the generated TFLite and tries to automatically correct the input/output order as much as possible if there is a difference. However, if INT8 quantization is used and there are multiple inputs and outputs with the same shape, automatic correction may fail. This is because TFLiteConverter shuffles the input-output order by itself only when INT8 quantization is performed.
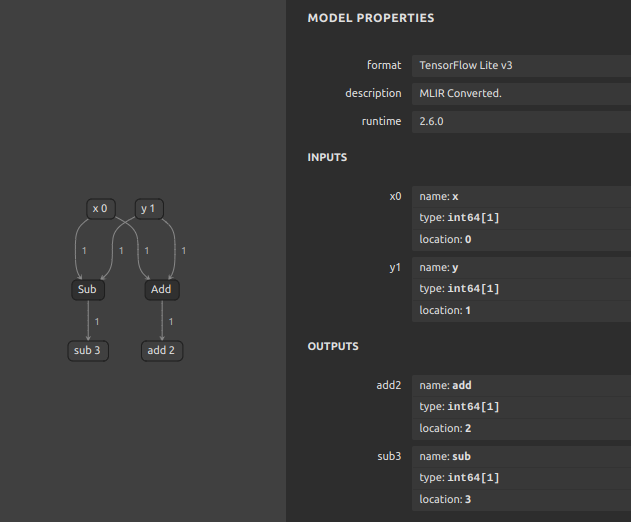
import torch
import onnxruntime
import numpy as np
import onnx2tf
import tensorflow as tf
from ai_edge_litert.interpreter import Interpreter
class Model(torch.nn.Module):
def forward(self, x, y):
return {
"add": x + y,
"sub": x - y,
}
# Let's double check what PyTorch gives us
model = Model()
pytorch_output = model.forward(10, 2)
print("[PyTorch] Model Predictions:", pytorch_output)
# First, export the above model to ONNX
torch.onnx.export(
Model(),
{"x": 10, "y": 2},
"model.onnx",
opset_version=16,
input_names=["x", "y"],
output_names=["add", "sub"],
)
# And check its output
session = onnxruntime.InferenceSession("model.onnx")
onnx_output = session.run(["add", "sub"], {"x": np.array(10), "y": np.array(2)})
print("[ONNX] Model Outputs:", [o.name for o in session.get_outputs()])
print("[ONNX] Model Predictions:", onnx_output)
# Now, let's convert the ONNX model to TF
onnx2tf.convert(
input_onnx_file_path="model.onnx",
output_folder_path="model.tf",
copy_onnx_input_output_names_to_tflite=True,
non_verbose=True,
)
# Now, test the newer TFLite model
interpreter = Interpreter(model_path="model.tf/model_float32.tflite")
tf_lite_model = interpreter.get_signature_runner()
inputs = {
'x': np.asarray([10], dtype=np.int64),
'y': np.asarray([2], dtype=np.int64),
}
tf_lite_output = tf_lite_model(**inputs)
print("[TFLite] Model Predictions:", tf_lite_output)
[PyTorch] Model Predictions:
{
'add': 12,
'sub': 8
}
[ONNX] Model Outputs:
[
'add',
'sub'
]
[ONNX] Model Predictions:
[
array(12, dtype=int64),
array(8, dtype=int64)
]
[TFLite] Model Predictions:
{
'add': array([12]),
'sub': array([8])
}
5. Rewriting of tflite input/output OP names and signature_defs
Click to expand
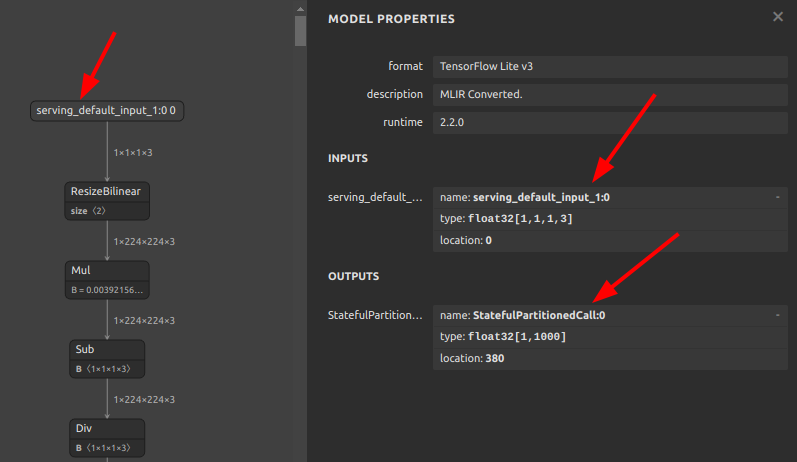
If you do not like tflite input/output names such as serving_default_*:0 or StatefulPartitionedCall:0, you can rewrite them using the following tools and procedures. It can be rewritten from any name to any name, so it does not have to be serving_default_*:0 or StatefulPartitionedCall:0.
https://github.com/PINTO0309/tflite-input-output-rewriter
# Install custom flatc
wget https://github.com/PINTO0309/onnx2tf/releases/download/1.7.3/flatc.tar.gz \
&& tar -zxvf flatc.tar.gz \
&& sudo chmod +x flatc \
&& sudo mv flatc /usr/bin/ \
&& rm flatc.tar.gz
# Path check
which flatc
/usr/bin/flatc
# Install tfliteiorewriter
pip install -U tfliteiorewriter
-
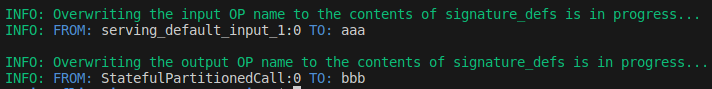
Before
tfliteiorewriter \ -i xxxx.tflite \ -r serving_default_input_1:0 aaa \ -r StatefulPartitionedCall:0 bbb
-
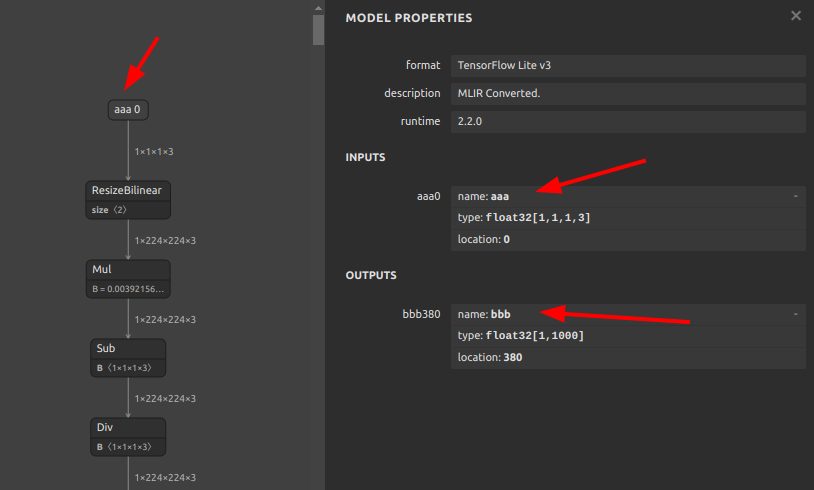
After
6. Embed metadata in tflite
Click to expand
If you want to embed label maps, quantization parameters, descriptions, etc. into your tflite file, you can refer to the official tutorial and try it yourself. For now, this tool does not plan to implement the ability to append metadata, as I do not want to write byte arrays to the tflite file that are not essential to its operation.
-
Adding metadata to TensorFlow Lite models
7. If the accuracy of the INT8 quantized model degrades significantly
Click to expand
It is a matter of model structure. The activation function (SiLU/Swish), kernel size and stride for Pooling, and kernel size and stride for Conv should be completely revised. See: https://github.com/PINTO0309/onnx2tf/issues/269
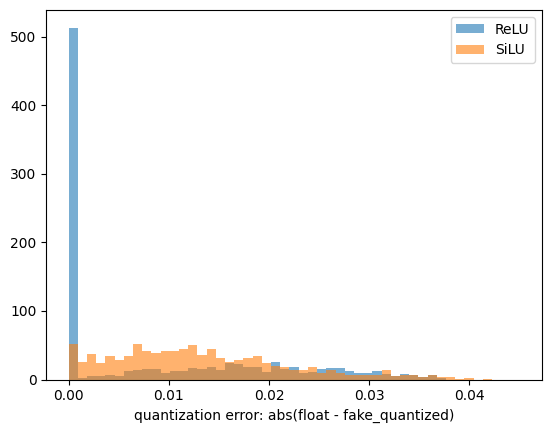
If you want to see the difference in quantization error between SiLU and ReLU, please check this Gist by @motokimura who helped us in our research. Thanks Motoki!
Gist: Quantization error simulation of SiLU (Swish) activation
The accuracy error rates after quantization for different activation functions are shown in the figure below. The graph plots the distribution of absolute error, so a position with a higher value on the horizontal axis indicates a larger error. The vertical axis is the number of samples. SiLU (Swish) produces catastrophic errors after INT8 quantization.
-
e.g. YOLOX-Nano
-
https://github.com/TexasInstruments/edgeai-yolox
Before After Swish/SiLUReLUDepthwiseConv2DConv2DMaxPool, kernel_size=5x5,9x9,13x13MaxPool, kernel_size=3x3### Float32 - YOLOX-Nano (1, 52, 52, 85) array([[[ [ 0.971787, 0.811184, 0.550566, ..., -5.962632, -7.403673, -6.735206], [ 0.858804, 1.351296, 1.231673, ..., -6.479690, -8.277064, -7.664936], [ 0.214827, 1.035119, 1.458006, ..., -6.291425, -8.229385, -7.761562], ..., [ 0.450116, 1.391900, 1.533354, ..., -5.672194, -7.121591, -6.880231], [ 0.593133, 2.112723, 0.968755, ..., -6.150078, -7.370633, -6.874294], [ 0.088263, 1.985220, 0.619998, ..., -5.507928, -6.914980, -6.234259]]]]), ### INT8 - YOLOX-Nano (1, 52, 52, 85) array([[[ [ 0.941908, 0.770652, 0.513768, ..., -5.993958, -7.449634, -6.850238], [ 0.856280, 1.284420, 1.198792, ..., -6.507727, -8.391542, -7.792146], [ 0.256884, 0.941908, 1.455676, ..., -6.336471, -8.305914, -7.877774], ..., [ 0.342512, 1.370048, 1.541304, ..., -5.737075, -7.192750, -7.107122], [ 0.513768, 2.226327, 1.027536, ..., -6.165215, -7.449634, -7.021494], [ 0.085628, 2.055072, 0.685024, ..., -5.480191, -7.021494, -6.422099]]]]),
-
Other recommended replacement OP
Before After HardSwishReLUReLU6
Paper: A Quantization-Friendly Separable Convolution for MobileNets https://arxiv.org/pdf/1803.08607.pdfReLU -
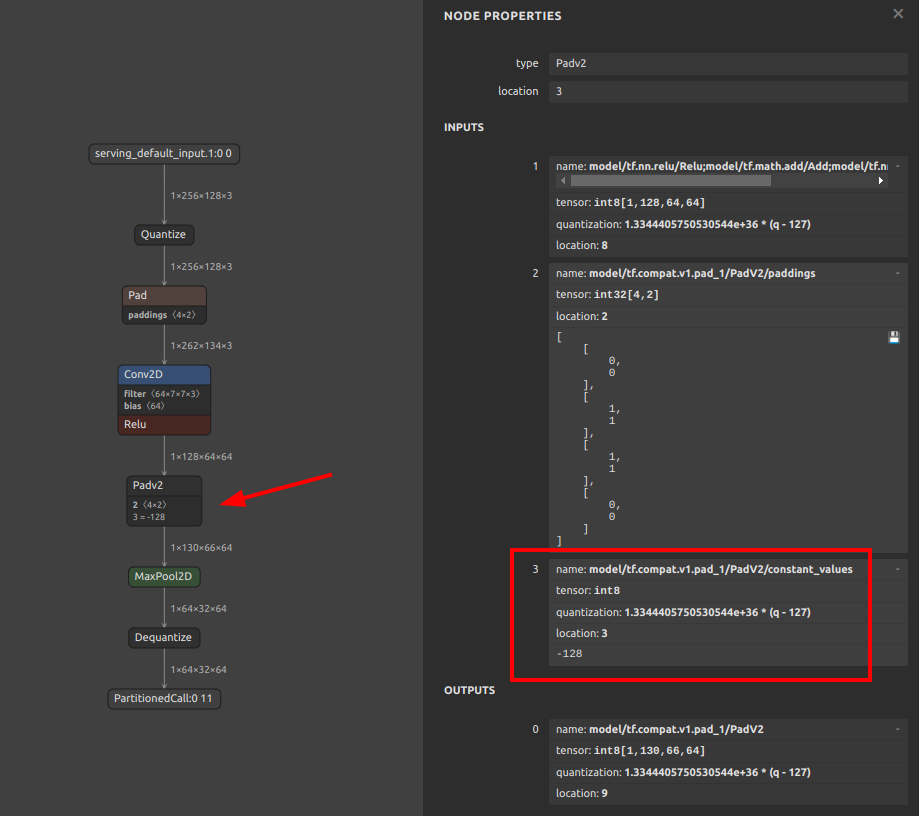
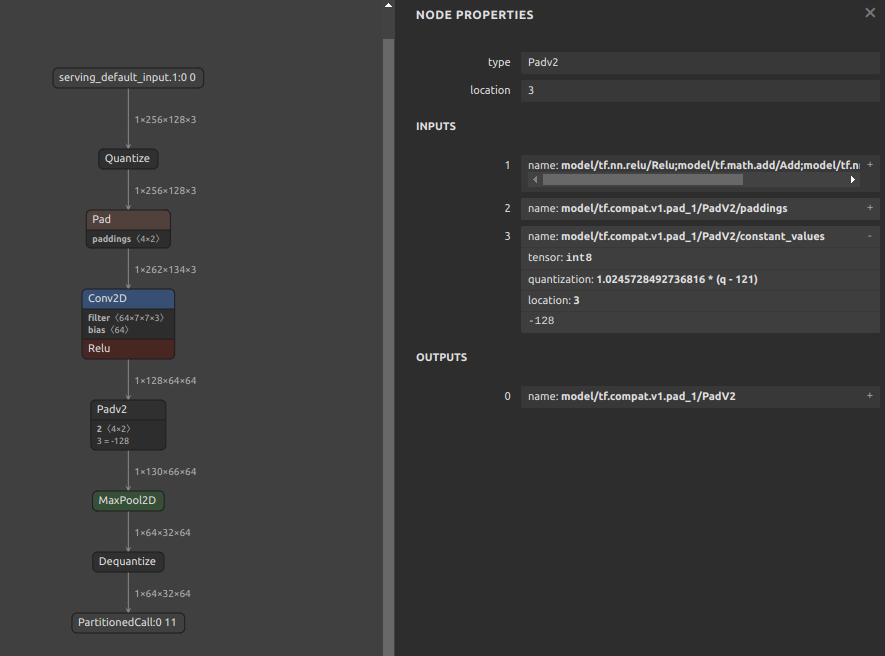
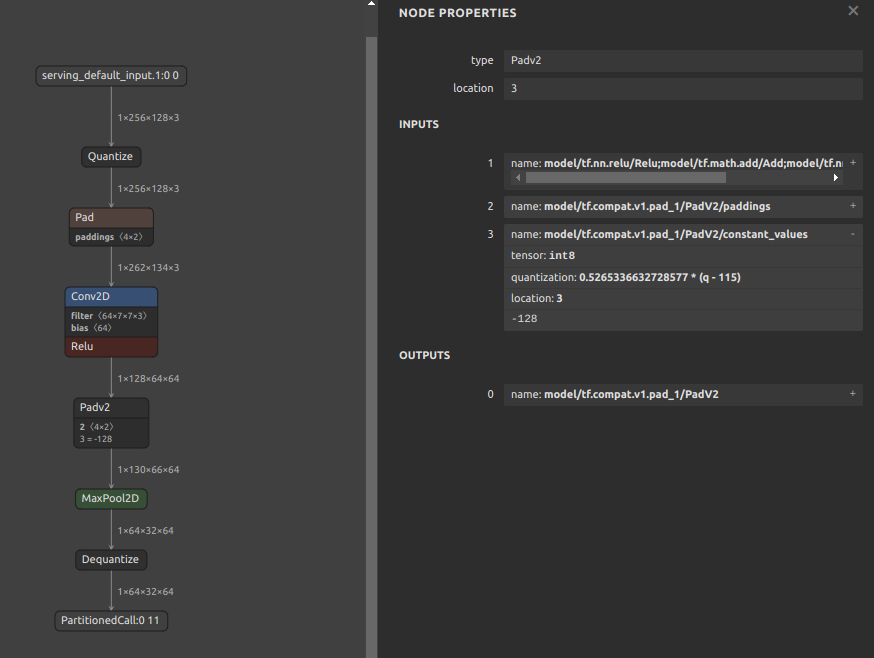
Quantization range collapse due to non-zero constant padding
If padding is performed with a constant other than zero, the padding value may destroy the quantization range of the input tensor. For example, the pattern is shown in the figure below. The
MaxPool2Dis done after padding the 4 sides of the input tensor with the minimum value of Float32. It seems that if INT8 quantization is performed with this structure, the quantization range is determined byMaxPool2Dduring quantization, including the values padded to the tensor. See: #444Therefore, the following two similar examples are equally likely to result in divergent output values for the model after INT8 quantization, with all output values being Nan or zero.
-
Pattern with fixed value
-255.0padded on 4 sides of tensor -
Pattern with fixed value
-128.0padded on 4 sides of tensor
-
8. Calibration data creation for INT8 quantization
Click to expand
Calibration data (.npy) for INT8 quantization (-cind) is generated as follows. This is a sample when the data used for training is image data. See: https://github.com/PINTO0309/onnx2tf/issues/222
https://www.tensorflow.org/lite/performance/post_training_quantization
import cv2
import glob
import numpy as np
# Not used during data generation ################################
# You will need to do the calculations yourself using the test data
MEAN = np.asarray([[[[0.485, 0.456, 0.406]]]], dtype=np.float32) # [1,1,1,3]
STD = np.asarray([[[[0.229, 0.224, 0.225]]]], dtype=np.float32) # [1,1,1,3]
# Not used during data generation ################################
files = glob.glob("data/*.png")
img_datas = []
for idx, file in enumerate(files):
bgr_img = cv2.imread(file)
rgb_img = cv2.cvtColor(bgr_img, cv2.COLOR_BGR2RGB)
resized_img = cv2.resize(rgb_img, dsize=(200,112))
extend_batch_size_img = resized_img[np.newaxis, :]
normalized_img = extend_batch_size_img / 255.0 # 0.0 - 1.0
print(
f'{str(idx+1).zfill(2)}. extend_batch_size_img.shape: {extend_batch_size_img.shape}'
) # [1,112,200,3]
img_datas.append(extend_batch_size_img)
calib_datas = np.vstack(img_datas)
print(f'calib_datas.shape: {calib_datas.shape}') # [10,112,200,3]
np.save(file='data/calibdata.npy', arr=calib_datas)
loaded_data = np.load('data/calibdata.npy')
print(f'loaded_data.shape: {loaded_data.shape}') # [10,112,200,3]
"""
-cind INPUT_NAME NUMPY_FILE_PATH MEAN STD
int8_calib_datas = (loaded_data - MEAN) / STD # -1.0 - 1.0
e.g. How to specify calibration data in CLI or Script respectively.
1. CLI
-cind "pc_dep" "data/calibdata.npy" "[[[[0.485,0.456,0.406]]]]" "[[[[0.229,0.224,0.225]]]]"
-cind "feat" "data/calibdata2.npy" "[[[[0.123,...,0.321]]]]" "[[[[0.112,...,0.451]]]]"
2. Script
custom_input_op_name_np_data_path=[
["pc_dep", "data/calibdata.npy", [[[[0.485,0.456,0.406]]]], [[[[0.229,0.224,0.225]]]]],
["feat", "data/calibdata2.npy", [[[[0.123,...,0.321]]]], [[[[0.112,...,0.451]]]],
]
"""
9. INT8 quantization of models with multiple inputs requiring non-image data
Click to expand
If you do not need to perform INT8 quantization with this tool alone, the following method is the easiest.
The -osd option will output a saved_model.pb in the saved_model folder with the full size required for quantization. That is, a default signature named serving_default is embedded in .pb. The -b option is used to convert the batch size by rewriting it as a static integer.
Note: INT8 TFLite generated by following this procedure as is will result in a model with significantly degraded accuracy. This tutorial only demonstrates the INT8 quantization procedure; if you wish to correct for accuracy, please refer to Parameter replacement to correct for transposition errors in the operation.
# Ref: https://github.com/onnx/models/tree/main/text/machine_comprehension/bert-squad
wget https://s3.ap-northeast-2.wasabisys.com/temp-models/onnx2tf_248/bertsquad-12.onnx
onnx2tf -i bertsquad-12.onnx -b 1 -osd -cotof
Use the saved_model_cli command to check the saved_model signature. INT8 quantization calibration using signatures allows correct control of the input order of data for calibration. Therefore, calibration with signatures is recommended for INT8 quantization of models with multiple inputs.
saved_model_cli show --dir saved_model/ --tag_set serve --signature_def serving_default
The given SavedModel SignatureDef contains the following input(s):
inputs['input_ids_0'] tensor_info:
dtype: DT_INT64
shape: (1, 256)
name: serving_default_input_ids_0:0
inputs['input_mask_0'] tensor_info:
dtype: DT_INT64
shape: (1, 256)
name: serving_default_input_mask_0:0
inputs['segment_ids_0'] tensor_info:
dtype: DT_INT64
shape: (1, 256)
name: serving_default_segment_ids_0:0
inputs['unique_ids_raw_output___9_0'] tensor_info:
dtype: DT_INT64
shape: (1)
name: serving_default_unique_ids_raw_output___9_0:0
Calibrate by specifying the input OP name displayed in inputs. The np.ones([xxx], dtype=np.int64) part must be replaced with the correct calibration test data. In practice, several pieces of data used for training are extracted and used.
import tensorflow as tf
import numpy as np
def representative_dataset():
unique_ids = np.ones([10, 256], dtype=np.int64)
segment_ids = np.ones([10, 256], dtype=np.int64)
input_masks = np.ones([10, 256], dtype=np.int64)
input_ids = np.ones([10], dtype=np.int64)
for unique_id, segment_id, input_mask, input_id \
in zip(unique_ids, segment_ids, input_masks, input_ids):
yield {
"unique_ids_raw_output___9_0": unique_id,
"segment_ids_0": segment_id,
"input_mask_0": input_mask,
"input_ids_0": input_id,
}
converter = tf.lite.TFLiteConverter.from_saved_model('saved_model')
converter.optimizations = [tf.lite.Optimize.DEFAULT]
converter.representative_dataset = representative_dataset
converter.target_spec.supported_ops = [tf.lite.OpsSet.TFLITE_BUILTINS_INT8]
converter.inference_input_type = tf.int8 # or tf.uint8
converter.inference_output_type = tf.int8 # or tf.uint8
tflite_quant_model = converter.convert()
with open('saved_model/int8_model.tflite', 'wb') as w:
w.write(tflite_quant_model)
https://www.tensorflow.org/lite/performance/post_training_quantization
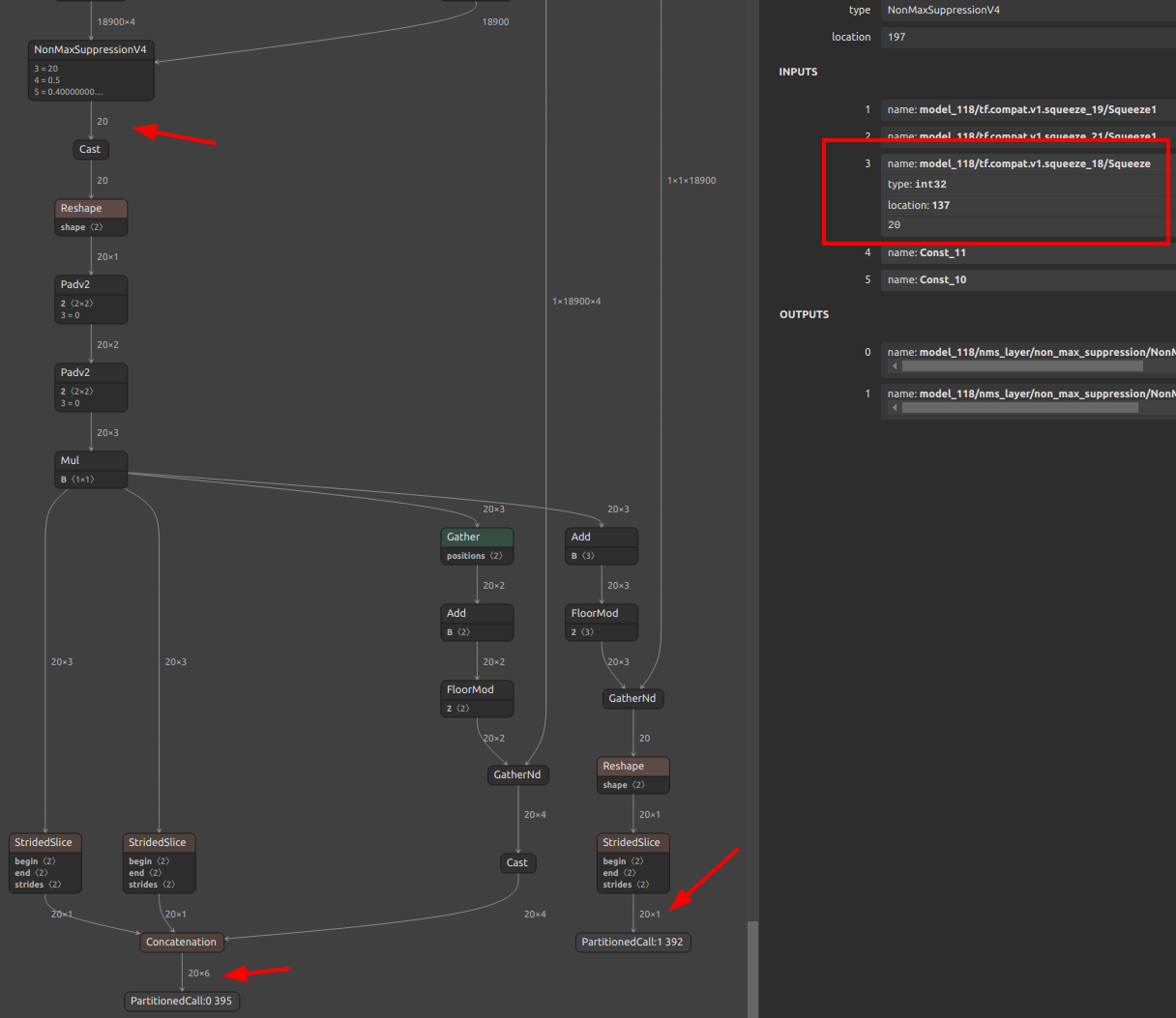
10. Fixing the output of NonMaxSuppression (NMS)
Click to expand
PyTorch's NonMaxSuppression (torchvision.ops.nms) and ONNX's NonMaxSuppression are not fully compatible. TorchVision's NMS is very inefficient. Therefore, it is inevitable that converting ONNX using NMS in object detection models and other models will be very redundant and will be converted with a structure that is difficult for TensorFlow.js and TFLite models to take advantage of in devices. This is due to the indefinite number of tensors output by the NMS. In this chapter, I share how to easily tune the ONNX generated using TorchVision's redundant NMS to generate an optimized NMS.
-
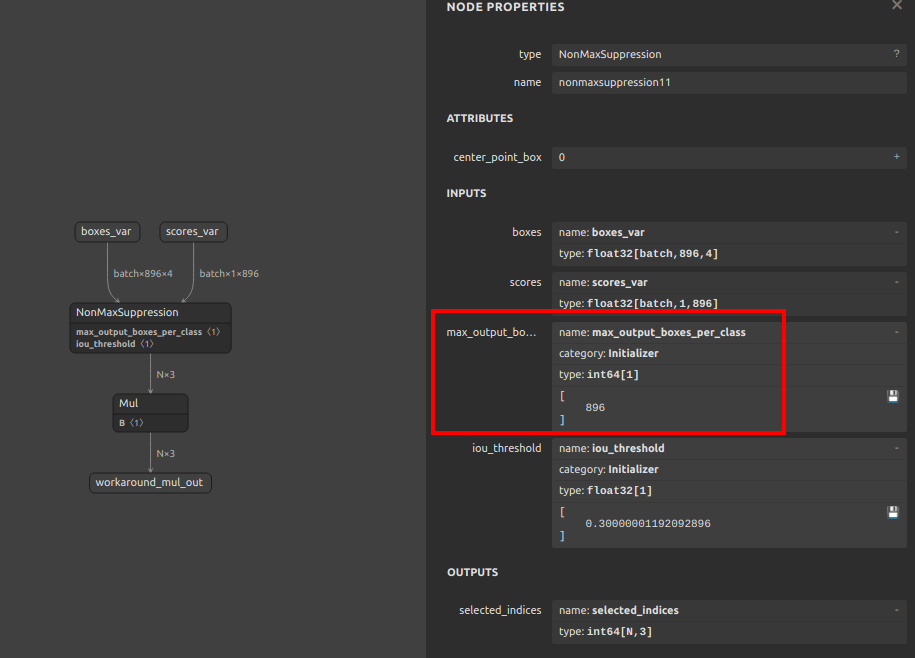
There are multiple issues with TorchVision's NMS. First, the batch size specification is not supported; second, the
max_output_boxes_per_classparameter cannot be specified. Please see the NMS sample ONNX part I generated. Themax_output_boxes_per_classhas been changed to896instead of-Infinity. The biggest problem with TorchVision NMS is that it generates ONNX withmax_output_boxes_per_classset to-Infinityor9223372036854775807 (Maximum value of INT64), resulting in a variable number of NMS outputs from zero to infinite. Thus, by rewriting-Infinityor9223372036854775807 (Maximum value of INT64)to a constant value, it is possible to output an NMS that can be effortlessly inferred by TFJS or TFLite.Here you will find committed ONNX components optimized for various devices. https://github.com/PINTO0309/components_of_onnx/tree/main/components_of_onnx/ops
-
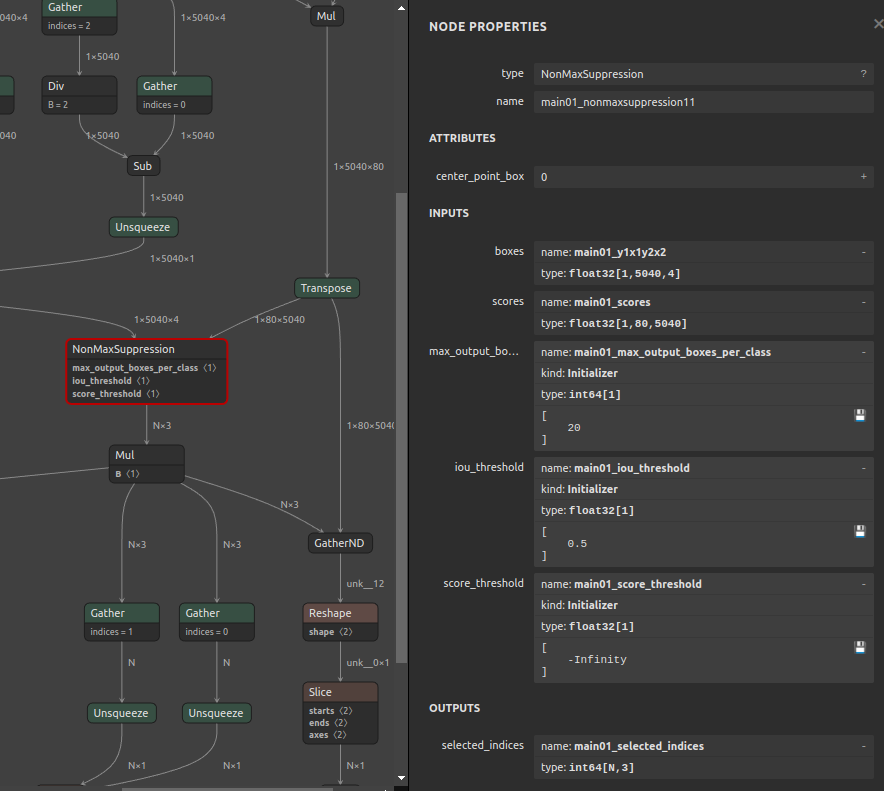
In the following example, the
max_output_boxes_per_classof NMS in the post-processing generated by YOLOv7 is changed from-Infinityor9223372036854775807 (Maximum value of INT64)to20, as shown in the figure below. The namemain01_max_output_boxes_per_classhas been rewritten by me for clarity, but it originally appears asmax_output_boxes_per_class.Simply execute the following command. The command rewrites the specified attribute value of the OP specified by ONNX.
pip install sam4onnx sam4onnx \ --op_name main01_nonmaxsuppression11 \ --input_onnx_file_path yolov7.onnx \ --output_onnx_file_path nms_yolov7_update.onnx \ --input_constants main01_max_output_boxes_per_class int64 [20]
A tutorial on one of my ONNX modification tools,
sam4onnx, can be found here.https://github.com/PINTO0309/sam4onnx
Many detailed tutorials are provided below, so if you are interested, please play with them.
https://github.com/PINTO0309/PINTO_model_zoo/tree/main/307_YOLOv7/post_process_gen_tools
-
Finally, simply convert ONNX to TFLite or saved_model or TFJS using onnx2tf. onnx2tf performs an internal operation to automatically optimize the NMS output to a fixed shape if
max_output_boxes_per_classis set to a value other than-Infinityand9223372036854775807 (Maximum value of INT64). Specify--output_nms_with_dynamic_tensoror-onwdtif you do not want to optimize for a fixed shape. If you want to shrink class scores in NMS from[B, C, N]to[B, 1, N], enable--output_nms_with_argmaxor-onwa.onnx2tf -i nms_yolov7_update.onnx -osd -cotofI would be happy if this is a reference for Android + Java or TFJS implementations. There are tons more tricky model optimization techniques described in my blog posts, so you'll have to find them yourself. I don't dare to list the URL here because it is annoying to see so many
issuesbeing posted. And unfortunately, all articles are in Japanese.
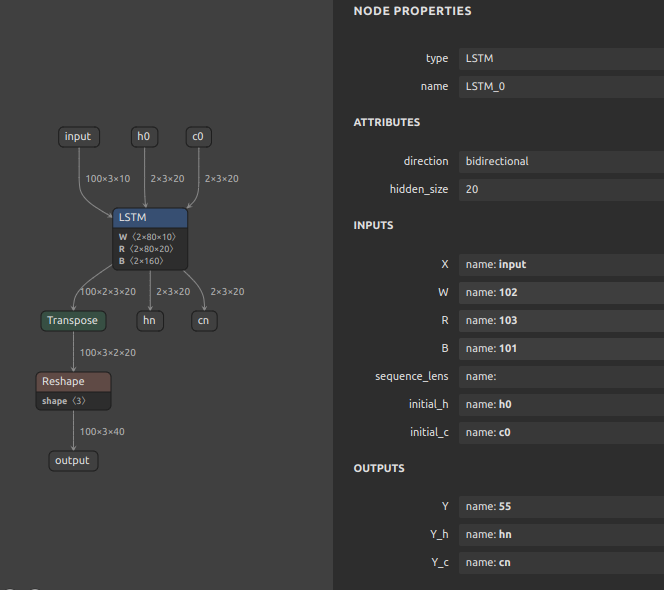
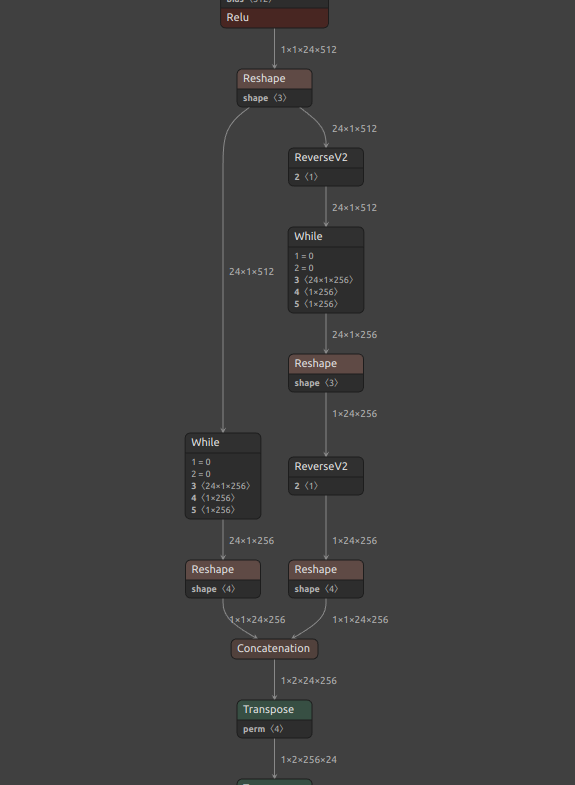
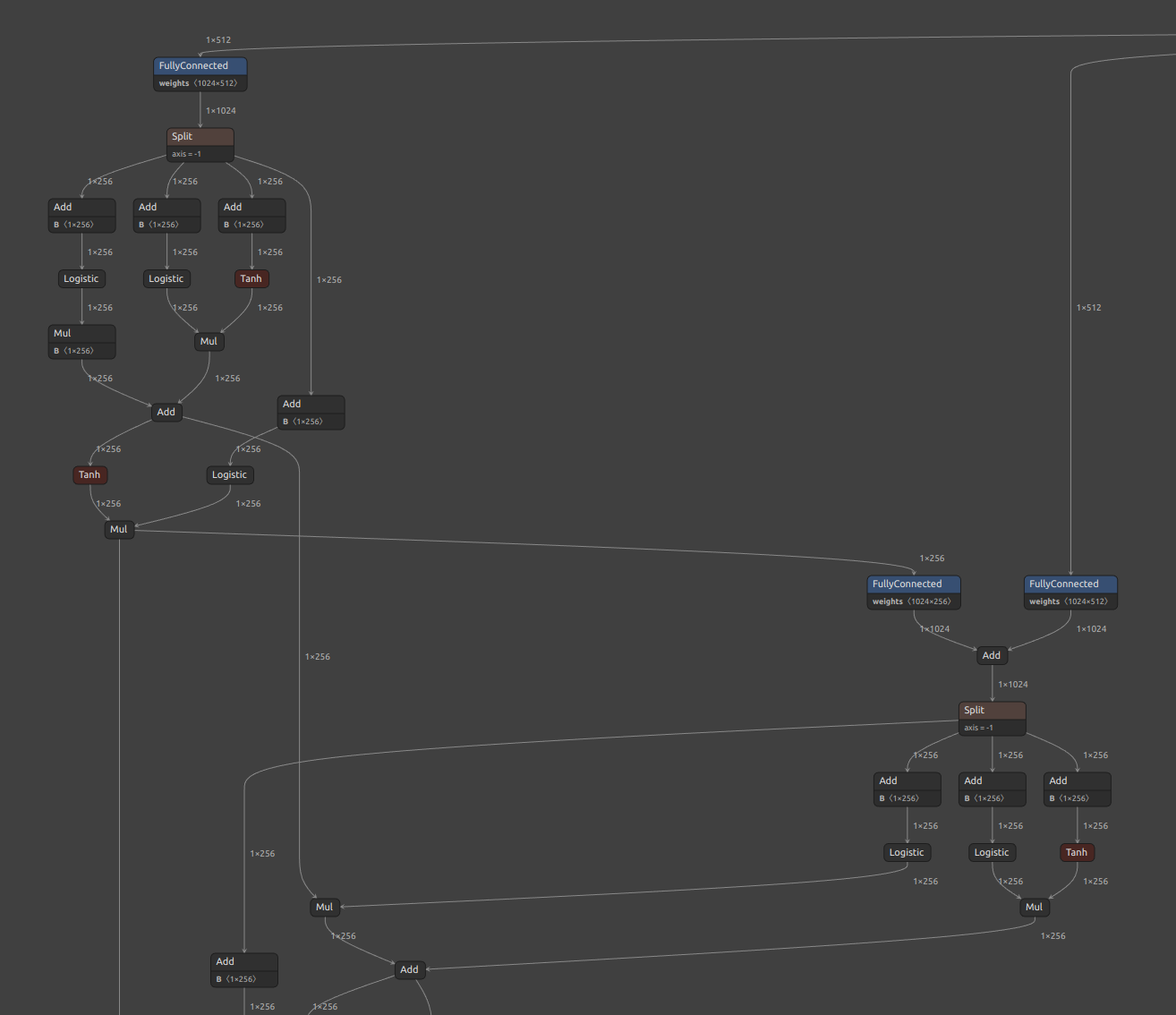
11. RNN (RNN, GRU, LSTM) Inference Acceleration
Click to expand
TensorFlow's RNN has a speedup option called unroll. The network will be unrolled, else a symbolic loop will be used. Unrolling can speed-up a RNN, although it tends to be more memory-intensive. Unrolling is only suitable for short sequences. onnx2tf allows you to deploy RNNs into memory-intensive operations by specifying the --enable_rnn_unroll or -eru options. The --enable_rnn_unroll option is available for RNN, GRU, and LSTM.
- Keras https://keras.io/api/layers/recurrent_layers/lstm/
- TensorFlow https://www.tensorflow.org/api_docs/python/tf/keras/layers/LSTM
An example of BidirectionalLSTM conversion with the --enable_rnn_unroll option is shown below. Please ignore that the shapes of the input and output tensors do not match, since the samples are shown by picking up separate models.
-
ONNX
LSTM (Bidirectional) -
BidirectionalLSTMwith--enable_rnn_unrolloption unspecifiedRecurrent layer is implemented from scratch.
-
BidirectionalLSTMwith--enable_rnn_unrolloption
12. If the accuracy of the Float32 model degrades significantly
Click to expand
The pattern of accuracy degradation of the converted model does not only occur when INT8 quantization is performed. A special edge case is when there is a problem with the implementation of a particular OP on the TFLite runtime side. Below, I will reproduce the problem by means of a very simple CNN model and further explain its workaround. Here is the issue that prompted me to add this explanation. [Conv-TasNet] Facing issue in converting Conv-TasNet model #447
Download a sample model for validation.
curl \
-L https://github.com/PINTO0309/onnx2tf/files/12367312/prelu_check.onnx.zip \
-o prelu_check.onnx.zip
unzip prelu_check.onnx.zip
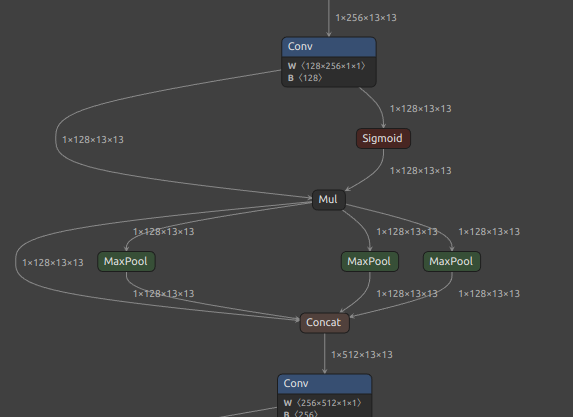
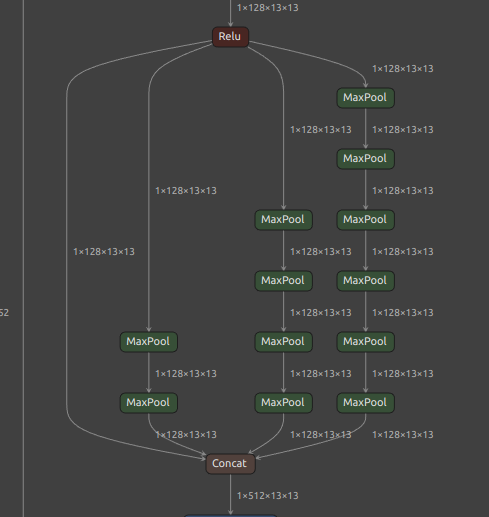
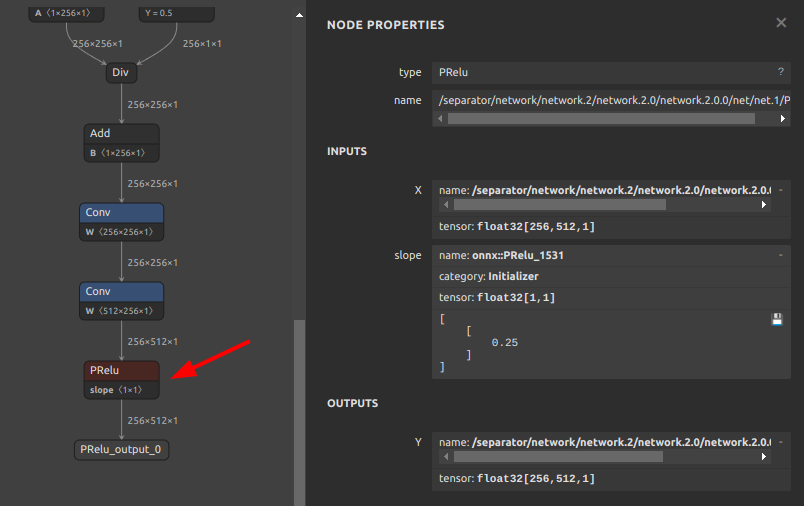
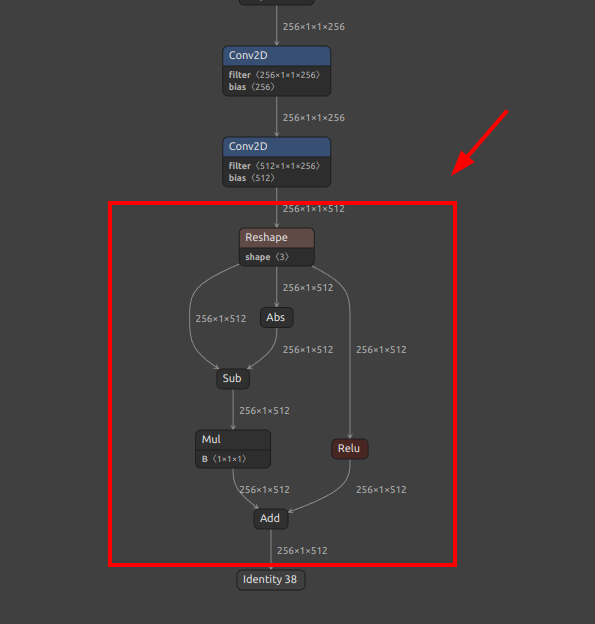
The part of the downloaded model where the problem occurs is the PRelu part in the figure below.
-
ONNX
Reproduce the problem. The following command converts an ONNX file to a TFLite file.
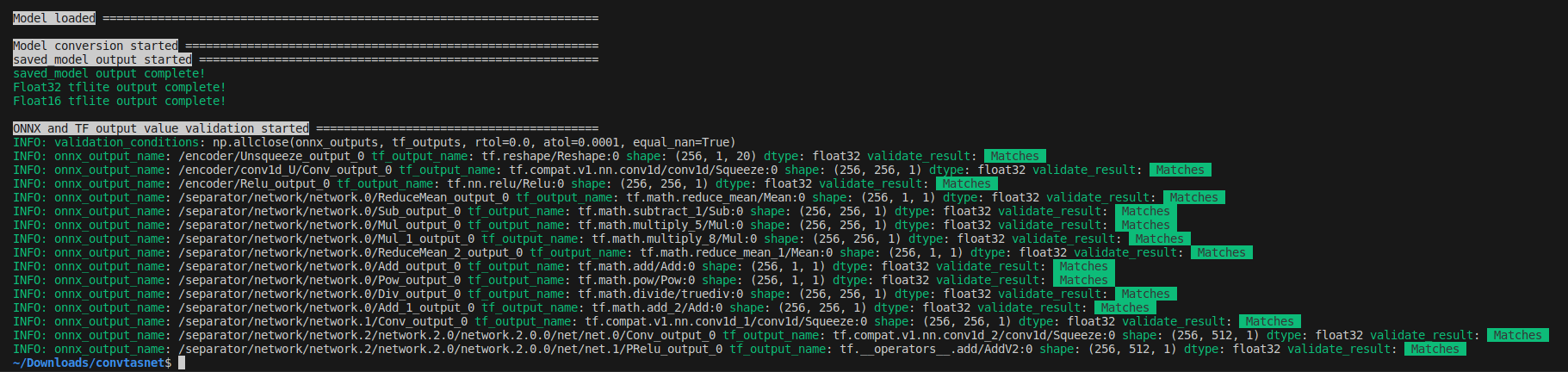
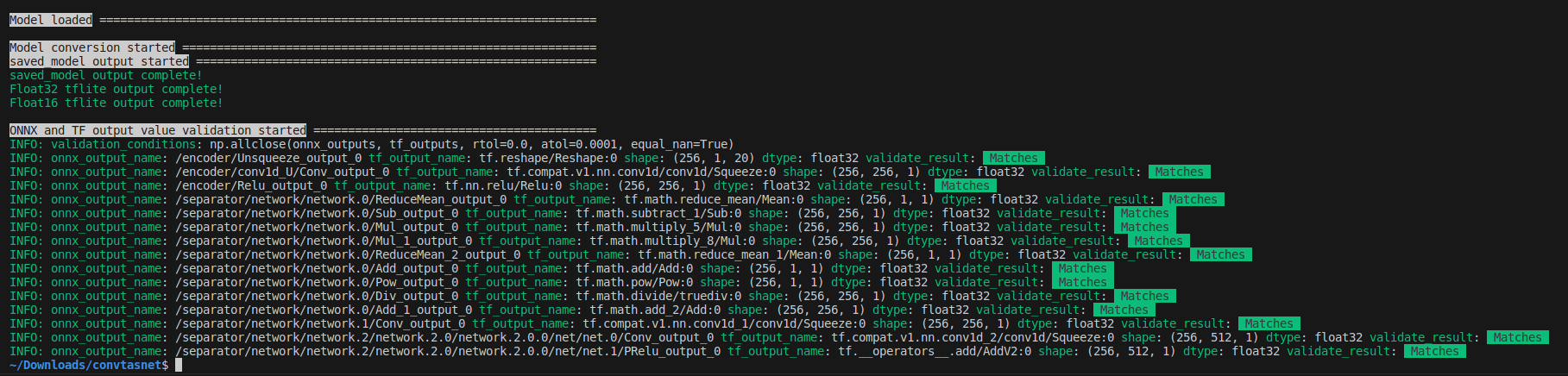
onnx2tf -i prelu_check.onnx -cotof
The conversion was successful and, as shown in the figure below, the inference test results from ONNX and the inference results for the Float32 model in TensorFlow (Keras) match perfectly. It is important to note that the comparison of inference results between ONNX and TensorFlow transformed models is comparing ONNX models with TensorFlow (Keras) models, not ONNX models with TFLite models.
-
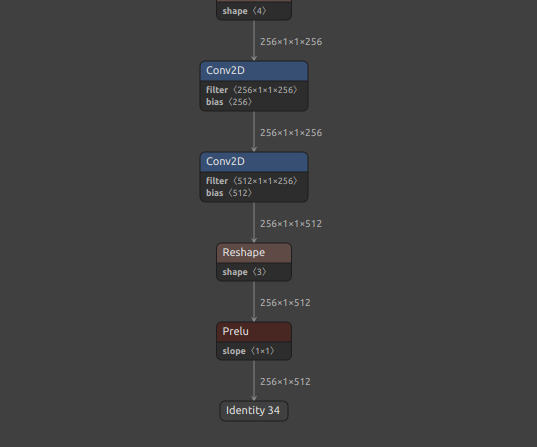
Conversion results
-
tflite
Now, let's try inference with the TFLite runtime instead of the TensorFlow runtime.
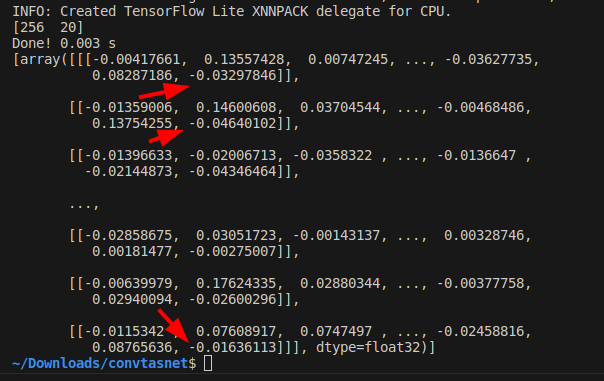
test.pyimport time import numpy as np np.random.seed(0) from ai_edge_litert.interpreter import Interpreter # Load TFLite model interpreter = Interpreter(model_path="./saved_model/prelu_check_float32.tflite") interpreter.allocate_tensors() tensor_shape = (256, 20) input_data = {'waveform': np.random.randn(*tensor_shape).astype(np.float32)} # Load and preprocess input_details = interpreter.get_input_details() input_shape = input_details[0]['shape'] print(input_shape) # Run inference interpreter.set_tensor(input_details[0]['index'], input_data["waveform"]) separate_time = time.time() interpreter.invoke() print("Done! {:.3f} s".format(time.time() - separate_time)) output_details = interpreter.get_output_details() output_data = interpreter.get_tensor(output_details[0]['index']) output_data = [] for output_detail in output_details: output_data.append(interpreter.get_tensor(output_detail['index'])) print(output_data)
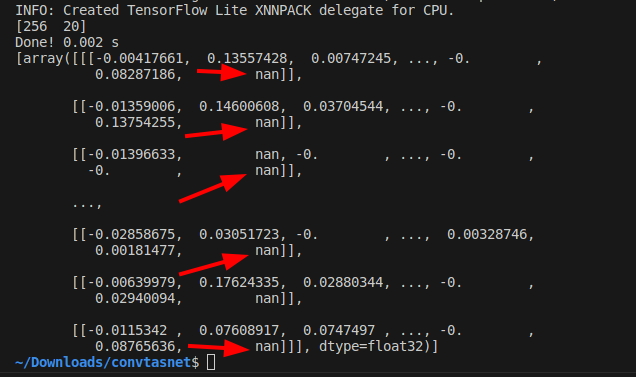
Oddly enough, the output value of PReLU contains multiple nan. However, as can be seen by converting the ONNX model to the middle of the model using the -onimc option, nan does not occur until just before PReLU. Thus, it is clear that the PReLU OP in the TFLite runtime has a problem with divergent inference results.
-
TFLite inference results
The following is a work-around to avoid this problem. Use the -rtpo option to replace PReLU with a similar primitive operation when transforming a model, and then perform the model transformation.
onnx2tf -i prelu_check.onnx -cotof -rtpo PReLU
As before, the inference results from ONNX and TensorFlow (Keras) match perfectly.
-
Conversion results
However, -rtpo PReLU will generate a .tflite file with the PRelu OP replaced by a primitive OP combination.
-
tflite
Again, run the test code to check the inference results. The figure below shows that no nan occurs when inference is performed by replacing the PReLU OP with only combinations of primitive operations. In other words, it is important to know that large arithmetic errors are not only due to the broken structure of the model, but can also be caused by internal implementations such as the TFLite runtime. I have implemented the -rtpo option to replace operators as a work-around to avoid such runtime problems.
-
TFLite inference results
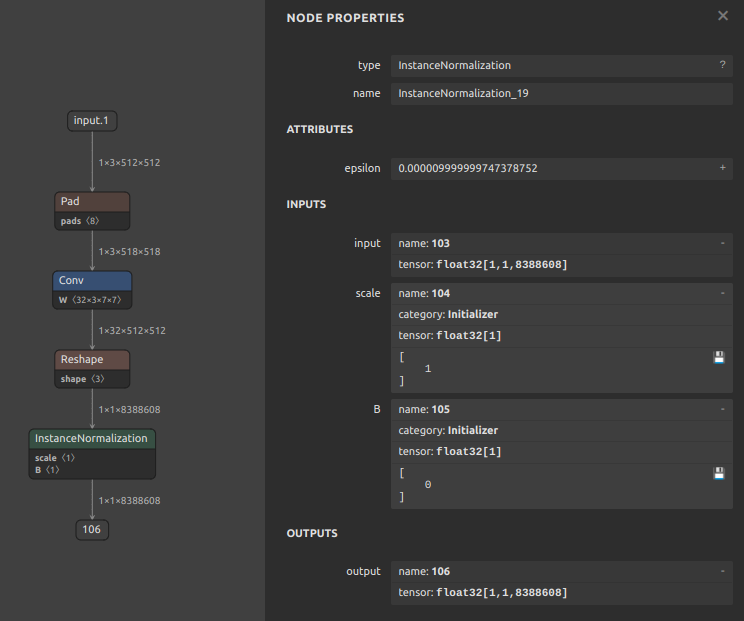
13. Problem of extremely large calculation error in InstanceNormalization
Click to expand
Even if the conversion is successful, InstanceNormalization tends to have very large errors. This is an ONNX specification.
- See.1: https://discuss.pytorch.org/t/understanding-instance-normalization-2d-with-running-mean-and-running-var/144139
- See.2: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/issues/72057
I verified this with a very simple sample model. There are more than 8 million elements, and the calculation error reached 1e-2.
14. Inference with dynamic tensors in TFLite
Click to expand
For some time now, TFLite runtime has supported inference by dynamic tensors. However, the existence of this important function is not widely recognized. In this chapter, I will show how I can convert an ONNX file that contains dynamic geometry in batch size directly into a TFLite file that contains dynamic geometry and then further infer it in variable batch conditions. The issue that inspired me to add this tutorial is here. [Dynamic batch / Dynamic shape] onnx model with dynamic input is converted to tflite with static input 1 #441, or Cannot use converted model with dynamic input shape #521
First, download the sample ONNX file.
wget https://s3.ap-northeast-2.wasabisys.com/temp-models/onnx2tf_441/osnet_x0_25_msmt17.onnx
This model calculates the similarity of features by cosine similarity. The batch size dimension of the input tensor is batch, allowing various numbers of images to be input simultaneously. This is often used, for example, to achieve tracking by calculating the similarity of people or objects reflected between successive video frames. However, the total number of objects to be tracked changes rapidly with each video frame because the number of people and objects in the image constantly increases and decreases. Therefore, there is a very significant use case for generating models with variable settings for the number of input images (batch size) of the model.
Convert the downloaded OSNet to tflite and saved_model as a variable batch. If you do not specify the -b or -ois options, onnx2tf does not change the batch size as N. The only important point is to convert the model with the -osd and -coion options. Note that if you use the -coion option, you must install flatbuffers-compiler with apt-get install, run the commands for building the environment described first in this README, or use a Docker container.
onnx2tf -i osnet_x0_25_msmt17.onnx -osd -coion
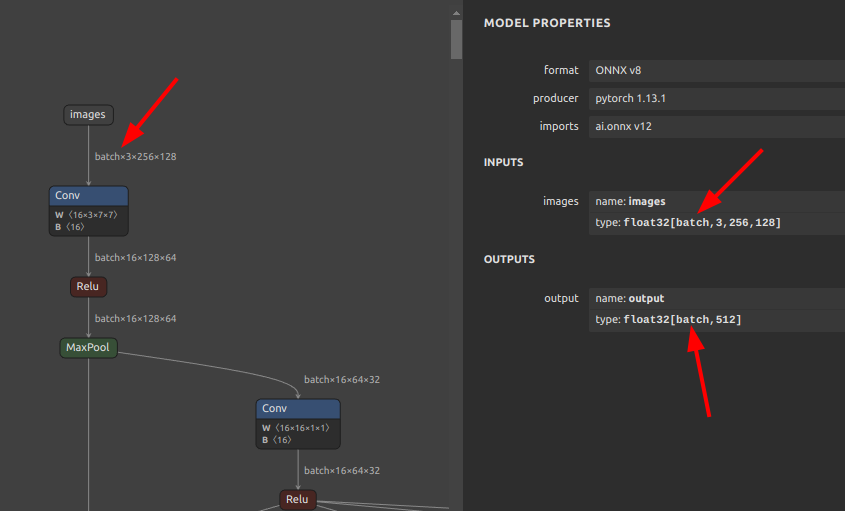
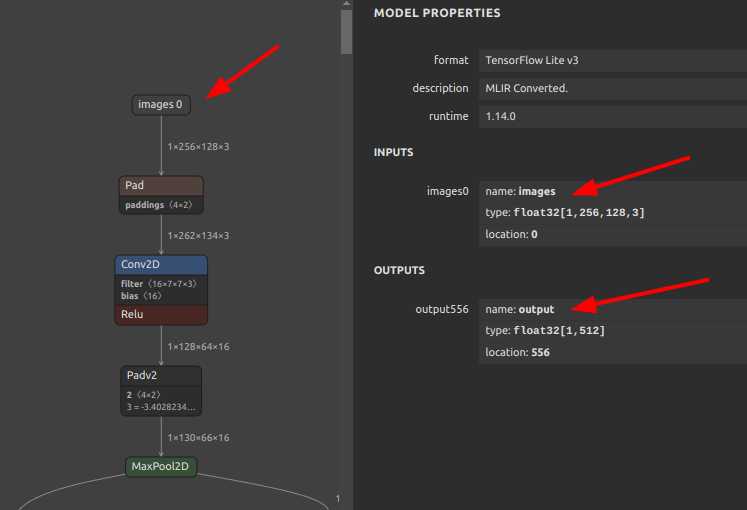
-
.tfliteWhen viewing tflite in Netron, the batch size appears to be fixed at
1. -
saved_modelHowever, checking the structure of
saved_model, the batch size is correctly set to-1.saved_model_cli show --dir saved_model/ --all MetaGraphDef with tag-set: 'serve' contains the following SignatureDefs: signature_def['__saved_model_init_op']: The given SavedModel SignatureDef contains the following input(s): The given SavedModel SignatureDef contains the following output(s): outputs['__saved_model_init_op'] tensor_info: dtype: DT_INVALID shape: unknown_rank name: NoOp Method name is: signature_def['serving_default']: The given SavedModel SignatureDef contains the following input(s): inputs['images'] tensor_info: dtype: DT_FLOAT shape: (-1, 256, 128, 3) name: serving_default_images:0 The given SavedModel SignatureDef contains the following output(s): outputs['output'] tensor_info: dtype: DT_FLOAT shape: (-1, 512) name: PartitionedCall:0 Method name is: tensorflow/serving/predict
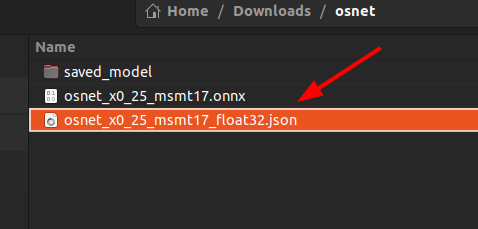
To prove that the tflite structure has been converted correctly, I will convert the tflite to JSON and look at the structure.
docker run --rm -it \
-v `pwd`:/home/user/workdir \
ghcr.io/pinto0309/tflite2json2tflite:latest
./flatc -t \
--strict-json \
--defaults-json \
-o workdir \
./schema.fbs -- workdir/saved_model/osnet_x0_25_msmt17_float32.tflite
ls -l workdir
-rw-rw-r-- 1 user user 921564 Aug 4 10:24 osnet_x0_25_msmt17.onnx
-rw-r--r-- 1 user user 10369524 Aug 4 10:30 osnet_x0_25_msmt17_float32.json
drwxrwxr-x 4 user user 4096 Aug 4 10:26 saved_model
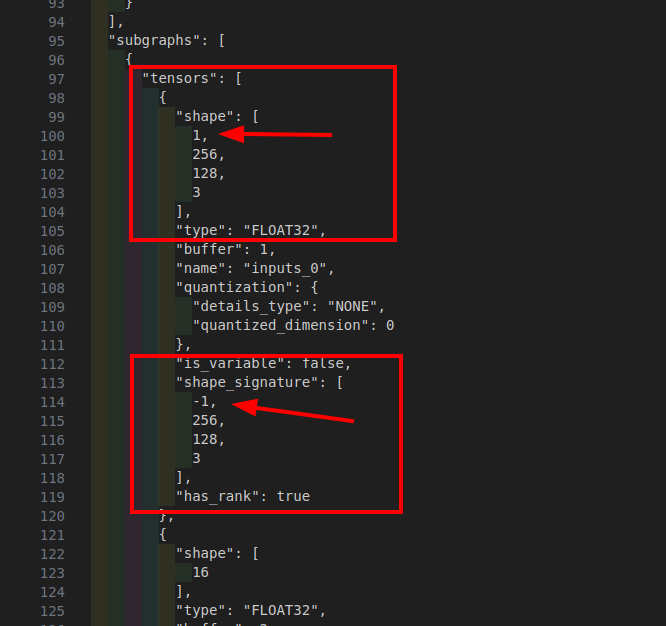
-
osnet_x0_25_msmt17_float32.json"shape_signature"is correctly set to-1. However,"shape"is set to1. This could be a problem with TFLiteConverter, or it could be a problem with Netron's graphical display capabilities.
In other words, although onnx2tf converts TFLiteConverer as specified, with the batch size of -1 without any model processing, only Netron's display is broken. This is a problem I have known for quite some time. However, the inference itself does not cause the problem.
If you want to infer in variable batches, you need to infer using signature. In such cases, the -coion option must be specified when converting the model. Note that I have identified a problem with quantization with the -coion option, which can corrupt tflite files. https://github.com/PINTO0309/onnx2tf/issues/429
https://github.com/PINTO0309/onnx2tf#4-match-tflite-inputoutput-names-and-inputoutput-order-to-onnx
You can use signature_runner to handle dynamic input tensors by performing inference using signature. Below I show that both batch_size=5 and batch_size=3 tensors can be inferred with the same model.
test.py- Batch size:5import numpy as np from ai_edge_litert.interpreter import Interpreter from pprint import pprint interpreter = Interpreter(model_path="saved_model/osnet_x0_25_msmt17_float32.tflite") tf_lite_model = interpreter.get_signature_runner() inputs = { 'images': np.ones([5,256,128,3], dtype=np.float32), } tf_lite_output = tf_lite_model(**inputs) print(f"[TFLite] Model Predictions shape: {tf_lite_output['output'].shape}") print(f"[TFLite] Model Predictions:") pprint(tf_lite_output)
- Results
[TFLite] Model Predictions shape: (5, 512) [TFLite] Model Predictions: {'output': array([[0.0000000e+00, 2.4730086e-04, 0.0000000e+00, ..., 1.0528549e+00, 3.7874988e-01, 0.0000000e+00], [0.0000000e+00, 2.4730086e-04, 0.0000000e+00, ..., 1.0528549e+00, 3.7874988e-01, 0.0000000e+00], [0.0000000e+00, 2.4730086e-04, 0.0000000e+00, ..., 1.0528549e+00, 3.7874988e-01, 0.0000000e+00], [0.0000000e+00, 2.4730086e-04, 0.0000000e+00, ..., 1.0528549e+00, 3.7874988e-01, 0.0000000e+00], [0.0000000e+00, 2.4730084e-04, 0.0000000e+00, ..., 1.0528525e+00, 3.7874976e-01, 0.0000000e+00]], dtype=float32)} test.py- Batch size:3import numpy as np from ai_edge_litert.interpreter import Interpreter from pprint import pprint interpreter = Interpreter(model_path="saved_model/osnet_x0_25_msmt17_float32.tflite") tf_lite_model = interpreter.get_signature_runner() inputs = { 'images': np.ones([3,256,128,3], dtype=np.float32), } tf_lite_output = tf_lite_model(**inputs) print(f"[TFLite] Model Predictions shape: {tf_lite_output['output'].shape}") print(f"[TFLite] Model Predictions:") pprint(tf_lite_output)
- Results
[TFLite] Model Predictions shape: (3, 512) [TFLite] Model Predictions: {'output': array([[0.0000000e+00, 2.4730084e-04, 0.0000000e+00, ..., 1.0528525e+00, 3.7874976e-01, 0.0000000e+00], [0.0000000e+00, 2.4730084e-04, 0.0000000e+00, ..., 1.0528525e+00, 3.7874976e-01, 0.0000000e+00], [0.0000000e+00, 2.4730084e-04, 0.0000000e+00, ..., 1.0528525e+00, 3.7874976e-01, 0.0000000e+00]], dtype=float32)}
15. Significant optimization of the entire model through Einsum and OneHot optimizations
Click to expand
Einsum and OneHot are not optimized to the maximum by the standard behavior of onnx-optimizer. Therefore, pre-optimizing the Einsum OP and OneHot OP using my original method can significantly improve the success rate of model conversion, and the input ONNX model itself can be significantly optimized compared to when onnxsim alone is optimized. See: https://github.com/PINTO0309/onnx2tf/issues/569
-
I have made a few unique customizations to the cited model structure.
-
spo4onnx
For example
python export.py \
--img_size 512 512 \
--lightglue_path weights/sjy_fused_static.onnx \
--end2end
pip install -U spo4onnx onnx2tf
cd weights
spo4onnx -if sjy_fused_static.onnx -of sjy_fused_static_spo.onnx
onnx2tf -i sjy_fused_static_spo.onnx
16. Add constant outputs to the model that are not connected to the model body
Click to expand
Sometimes you want to always output constants that are not connected to the model body. See: https://github.com/PINTO0309/onnx2tf/issues/627. For example, in the case of ONNX as shown in the figure below. You may want to keep scaling parameters and other parameters as fixed values inside the model and always include the same value in the output.
In such cases, the process of optimizing the ONNX file in onnxsim must be bypassed and not executed. You can bypass the execution of onnxsim by specifying -nuo or --not_use_onnxsim as a conversion option. Running onnxsim will remove constants from the model definition that are not connected to the body of the model in the process of optimizing the model structure.
wget https://github.com/PINTO0309/onnx2tf/files/15292126/toy_with_constant.onnx.zip
unzip toy_with_constant.onnx.zip
onnx2tf -i toy_with_constant.onnx -nuo -cotof
The relationship between the ONNX before conversion and the TFLite file after conversion is shown in the figure below.
| ONNX | TFLite |
|---|---|
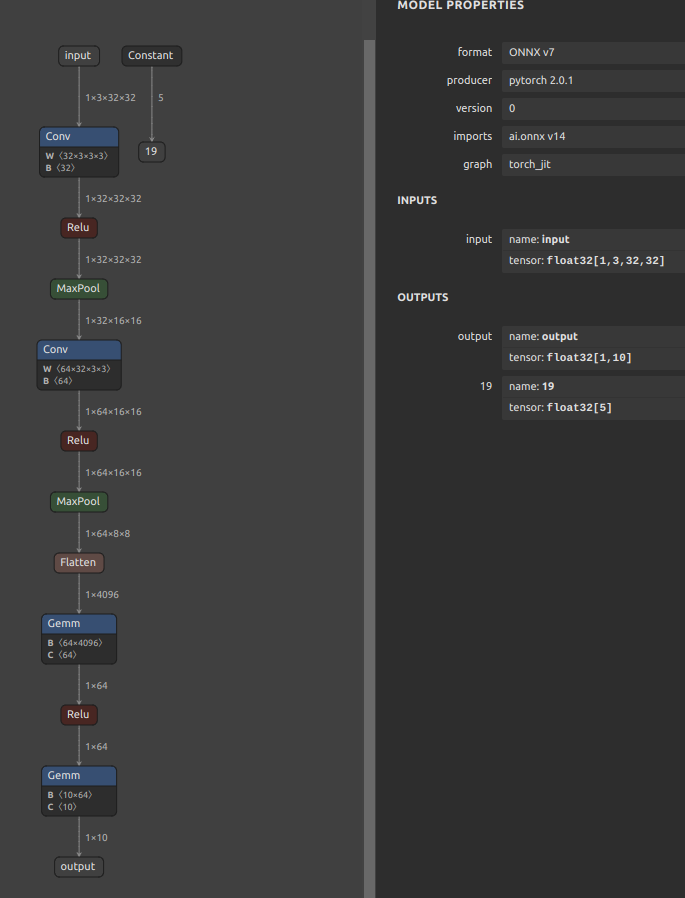 |
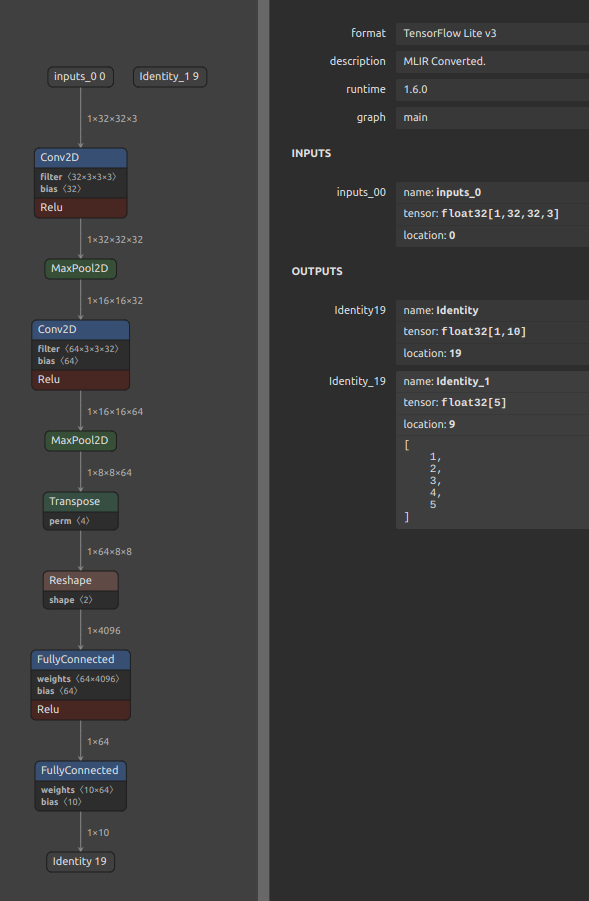 |
Use the generated TFLite file to inference and ensure that it always contains fixed value output.
from ai_edge_litert.interpreter import Interpreter
import numpy as np
from pprint import pprint
interpreter = Interpreter(model_path="saved_model/toy_with_constant_float32.tflite")
interpreter.allocate_tensors()
input_details = interpreter.get_input_details()
output_details = interpreter.get_output_details()
interpreter.set_tensor(
tensor_index=input_details[0]['index'],
value=np.ones(tuple(input_details[0]['shape']), dtype=np.float32)
)
interpreter.invoke()
variable_output = interpreter.get_tensor(output_details[0]['index'])
constant_output = interpreter.get_tensor(output_details[1]['index'])
print("=================")
print("Variable Output:")
pprint(variable_output)
print("=================")
print("Constant Output:")
pprint(constant_output)
=================
Variable Output:
array([[-0.02787317, -0.05505124, 0.05421712, 0.03526559, -0.14131774,
0.0019211 , 0.08399964, 0.00433664, -0.00984338, -0.03370604]],
dtype=float32)
=================
Constant Output:
array([1., 2., 3., 4., 5.], dtype=float32)
17. Conversion of models that use variable length tokens and embedding, such as LLM and sound models
Click to expand
This refers to a model with undefined dimensions, either all dimensions or multiple dimensions including batch size, as shown in the figure below.
-
Sample model
https://github.com/PINTO0309/onnx2tf/releases/download/1.24.0/bge-m3.onnx
-
Structure
If such a model is converted without any options, TensorFlow/Keras will abort. This is an internal TensorFlow/Keras implementation issue rather than an onnx2tf issue. TensorFlow/Keras does not allow more than two undefined dimensions in the shape attribute of Reshape due to the specification, so an error occurs during the internal transformation operation of the Reshape OP as shown below. This has been an inherent problem in TensorFlow/Keras since long ago and has not been resolved to this day. See: RuntimeError: tensorflow/lite/kernels/range.cc:39 (start > limit && delta < 0) || (start < limit && delta > 0) was not true.Node number 3 (RANGE) failed to invoke. Node number 393 (WHILE) failed to invoke. current error :RuntimeError: tensorflow/lite/kernels/reshape.cc:55 stretch_dim != -1 (0 != -1)Node number 83 (RESHAPE) failed to prepare. #40504
-
OP where the problem occurs
-
Error message
error: 'tf.Reshape' op requires 'shape' to have at most one dynamic dimension, but got multiple dynamic dimensions at indices 0 and 3
Thus, for models such as this, where all dimensions, including batch size, are dynamic shapes, it is often possible to convert by fixing the batch size to 1 with the -b 1 or --batch_size 1 option.
onnx2tf -i model.onnx -b 1 -osd
-
Results
When the converted tflite is displayed in Netron, all the dimensions of the dynamic shape are displayed as
1, but this is a display problem in Netron, and the shape is actually converted to-1orNone.
Click here to see how to perform inference using the dynamic shape tensor.
18. Convert only the intermediate structural part of the ONNX model
Click to expand
By specifying ONNX input or output names, only the middle part of the model can be converted. This is useful when you want to see what output is obtained in what part of the model after conversion, or when debugging the model conversion operation itself.
For example, take a model with multiple inputs and multiple outputs as shown in the figure below to try a partial transformation.
-
To convert by specifying only the input name to start the conversion
wget https://github.com/PINTO0309/onnx2tf/releases/download/1.25.0/cf_fus.onnx onnx2tf -i cf_fus.onnx -inimc 448 -coion -
To convert by specifying only the output name to end the conversion
wget https://github.com/PINTO0309/onnx2tf/releases/download/1.25.0/cf_fus.onnx onnx2tf -i cf_fus.onnx -onimc dep_sec -coion -
To perform a conversion by specifying the input name to start the conversion and the output name to end the conversion
wget https://github.com/PINTO0309/onnx2tf/releases/download/1.25.0/cf_fus.onnx onnx2tf -i cf_fus.onnx -inimc 448 -onimc velocity -coion
19. Conversion to TensorFlow.js
Click to expand
When converting to TensorFlow.js, process as follows.
pip install -U --no-deps \
tensorflowjs \
tensorflow_decision_forests \
ydf \
tensorflow_hub
onnx2tf -i mobilenetv2-12.onnx -ois input:1,3,224,224 -osd -dgc
tensorflowjs_converter \
--input_format tf_saved_model \
--output_format tfjs_graph_model \
saved_model \
tfjs_model
See: https://github.com/tensorflow/tfjs/tree/master/tfjs-converter
20. Conversion to CoreML
Click to expand
When converting to CoreML, process as follows. The -k option is for conversion while maintaining the input channel order in ONNX's NCHW format.
pip install coremltools==8.2
onnx2tf -i mobilenetv2-12.onnx -k input -ois input:1,3,224,224 -osd
import coremltools as ct
FOLDER_PATH = 'saved_model'
model = ct.convert(
model=FOLDER_PATH,
source='tensorflow',
)
model.save(f'{FOLDER_PATH}/model.mlpackage')
See: https://github.com/apple/coremltools
CLI Parameter
Click to expand
onnx2tf -h
usage: onnx2tf
[-h]
(-i INPUT_ONNX_FILE_PATH | -V)
[-o OUTPUT_FOLDER_PATH]
[-osd]
[-oh5]
[-okv3]
[-otfv1pb]
[-ow]
[-coion]
[-odrqt]
[-oiqt]
[-qt {per-channel,per-tensor}]
[-cind INPUT_NAME NUMPY_FILE_PATH MEAN STD]
[-iqd {int8,uint8,float32}]
[-oqd {int8,uint8,float32}]
[-nuo]
[-nuonag]
[-b BATCH_SIZE]
[-ois OVERWRITE_INPUT_SHAPE [OVERWRITE_INPUT_SHAPE ...]]
[-sh SHAPE_HINTS [SHAPE_HINTS ...]]
[-nlt]
[-onwdt]
[-snms {v4,v5}]
[-k KEEP_NCW_OR_NCHW_OR_NCDHW_INPUT_NAMES [KEEP_NCW_OR_NCHW_OR_NCDHW_INPUT_NAMES ...]]
[-kt KEEP_NWC_OR_NHWC_OR_NDHWC_INPUT_NAMES [KEEP_NWC_OR_NHWC_OR_NDHWC_INPUT_NAMES ...]]
[-kat KEEP_SHAPE_ABSOLUTELY_INPUT_NAMES [KEEP_SHAPE_ABSOLUTELY_INPUT_NAMES ...]]
[-inimc INPUT_NAMES [INPUT_NAMES ...]]
[-onimc OUTPUT_NAMES [OUTPUT_NAMES ...]]
[-dgc]
[-eatfp16]
[-ebu]
[-eru]
[-dsft]
[-nodaftc]
[-dsfs]
[-dsm]
[-nodafsc]
[-ofgd]
[-rari64 | -rarf32 | -rafi64 | -raff32]
[-fasr FUSED_ARGMAX_SCALE_RATIO]
[-rtpo REPLACE_TO_PSEUDO_OPERATORS [REPLACE_TO_PSEUDO_OPERATORS ...]]
[-me MVN_EPSILON]
[-prf PARAM_REPLACEMENT_FILE]
[-cgdc]
[-coto | -cotof]
[-coton]
[-cotor CHECK_ONNX_TF_OUTPUTS_ELEMENTWISE_CLOSE_RTOL]
[-cotoa CHECK_ONNX_TF_OUTPUTS_ELEMENTWISE_CLOSE_ATOL]
[-tdnp TEST_DATA_NHWC_PATH]
[-agj]
[-dms]
[-uc]
[-n]
[-v]
optional arguments:
-h, --help
show this help message and exit
-i INPUT_ONNX_FILE_PATH, --input_onnx_file_path INPUT_ONNX_FILE_PATH
Input onnx file path.
-V, --version
Show version and exit.
-o OUTPUT_FOLDER_PATH, --output_folder_path OUTPUT_FOLDER_PATH
Output folder path. Default: "saved_model"
-osd, --output_signaturedefs
Signature is added to the output for serving or for conversion
to other model formats. However, this can significantly reduce the speed
of model conversion and significant increase the size of the model.
-oh5, --output_h5
Output model in Keras (hdf5) format.
-okv3, --output_keras_v3
Output model in Keras (keras_v3) format.
-otfv1pb, --output_tfv1_pb
Output model in TF v1 (.pb) format.
-ow, --output_weights
Output weights in hdf5 format.
-coion, --copy_onnx_input_output_names_to_tflite
Copy the input/output OP name of ONNX to the input/output OP name of tflite.
Due to Tensorflow internal operating specifications,
the input/output order of ONNX does not necessarily match
the input/output order of tflite.
Be sure to check that the input/output OP names in the generated
tflite file have been converted as expected.
Also, this option generates a huge JSON file as a temporary file for processing.
Therefore, it is strongly discouraged to use it on large models of hundreds
of megabytes or more.
-odrqt, --output_dynamic_range_quantized_tflite
Output of dynamic range quantized tflite.
-oiqt, --output_integer_quantized_tflite
Output of integer quantized tflite.
-tb {tf_converter,flatbuffer_direct}, \
--tflite_backend {tf_converter,flatbuffer_direct}
TFLite generation backend.
"tf_converter"(default): Use TensorFlow Lite Converter.
"flatbuffer_direct": Experimental direct FlatBuffer builder path (limited OP/quantization support).
flatbuffer_direct notes:
1. `flatbuffer_direct` is experimental; always validate model-by-model before production rollout.
2. Direct export supports FP32/FP16 `.tflite` generation.
3. Dynamic range quantization (`-odrqt`) is supported in a limited form:
weight-only INT8 quantization for `CONV_2D`, `DEPTHWISE_CONV_2D`, `FULLY_CONNECTED`,
and constant tensor quantization + `DEQUANTIZE` insertion for `ADD`, `SUB`, `MUL`, `DIV`, `CONCATENATION`.
For kernel weights, `--quant_type per-channel` and `--quant_type per-tensor` are both supported in `flatbuffer_direct`.
4. Integer quantization (`-oiqt`) is supported in a limited form:
`*_integer_quant.tflite`, `*_full_integer_quant.tflite`,
`*_integer_quant_with_int16_act.tflite`, `*_full_integer_quant_with_int16_act.tflite` are generated.
5. Supported builtin OP set includes:
`ADD`, `SUB`, `MUL`, `DIV`, `FLOOR_MOD`, `MAXIMUM`, `MINIMUM`, `POW`,
`MEAN`, `SUM`, `REDUCE_MAX`, `RESHAPE`, `TRANSPOSE`, `SQUEEZE`, `SLICE`, `STRIDED_SLICE`,
`CONCATENATION`, `GATHER`, `GATHER_ND`, `ONE_HOT`,
`ARG_MAX`, `CAST`, `SHAPE`, `FILL`,
`LOGISTIC`, `RELU`, `RELU6`, `TANH`, `EXP`, `SQRT`, `NEG`, `LOG`,
`SOFTMAX`, `L2_NORMALIZATION`, `LOCAL_RESPONSE_NORMALIZATION`,
`CONV_2D`, `DEPTHWISE_CONV_2D`, `TRANSPOSE_CONV`, `AVERAGE_POOL_2D`, `MAX_POOL_2D`, `FULLY_CONNECTED`, `BATCH_MATMUL`,
`RESIZE_NEAREST_NEIGHBOR`, `RESIZE_BILINEAR`,
`BIDIRECTIONAL_SEQUENCE_LSTM`, `SPLIT`, `EXPAND_DIMS`,
`DEQUANTIZE`, `QUANTIZE`.
6. Unsupported OPs fail explicitly with `NotImplementedError`.
7. Custom OP policy (opt-in):
`--flatbuffer_direct_allow_custom_ops` enables lowering selected hard ops as TFLite `CUSTOM`.
`--flatbuffer_direct_custom_op_allowlist` (comma-separated ONNX OP names) restricts allowed custom lowering targets.
If a custom-op candidate appears while disabled, conversion fails with `reason_code=custom_op_candidate_disabled`.
If enabled but not in allowlist, conversion fails with `reason_code=custom_op_not_in_allowlist`.
8. `schema.fbs` is fetched from LiteRT by pinned tag by default (`v2.1.2`), and can be overridden by:
`ONNX2TF_TFLITE_SCHEMA_REPOSITORY`, `ONNX2TF_TFLITE_SCHEMA_TAG`, `ONNX2TF_TFLITE_SCHEMA_RELATIVE_PATH`.
9. flatbuffer_direct quantization precision controls are configurable via environment variables:
`ONNX2TF_FLATBUFFER_DIRECT_CALIBRATION_METHOD` (`max` or `percentile`),
`ONNX2TF_FLATBUFFER_DIRECT_CALIBRATION_PERCENTILE` (e.g. `99.99`),
`ONNX2TF_FLATBUFFER_DIRECT_QUANT_MIN_NUMEL`,
`ONNX2TF_FLATBUFFER_DIRECT_QUANT_MIN_ABS_MAX`,
`ONNX2TF_FLATBUFFER_DIRECT_QUANT_SCALE_FLOOR`.
10. Optional fallback:
`--flatbuffer_direct_fallback_to_tf_converter` falls back to tf_converter when direct export fails.
11. Migration guide:
See `FLATBUFFER_DIRECT_MIGRATION_GUIDE.md` for staged rollout and CI operation patterns.
-qt {per-channel,per-tensor}, --quant_type {per-channel,per-tensor}
Selects whether "per-channel" or "per-tensor" quantization is used.
Default: "per-channel"
-qnm QUANT_NORM_MEAN, --quant_norm_mean QUANT_NORM_MEAN
Normalized average value during quantization.
Only valid when the "-cind" option is not used.
Default: "[[[[0.485, 0.456, 0.406]]]]"
-qns QUANT_NORM_STD, --quant_norm_std QUANT_NORM_STD
Normalized standard deviation during quantization.
Only valid when the "-cind" option is not used.
Default: "[[[[0.229, 0.224, 0.225]]]]"
-cind INPUT_NAME NUMPY_FILE_PATH MEAN STD, \
--custom_input_op_name_np_data_path INPUT_NAME NUMPY_FILE_PATH MEAN STD
Input name of OP and path of data file (Numpy) for custom input for -cotof or -oiqt,
and mean (optional) and std (optional).
Unlike -tdnp, this option supports per-input mapping, non-image tensors, and INT8 calibration.
<Usage in -cotof>
When using -cotof, custom input defined by the user, instead of dummy data, is used.
In this case, mean and std are omitted from the input.
-cind {input_op_name} {numpy_file_path}
e.g. -cind onnx::Equal_0 test_cind/x_1.npy -cind onnx::Add_1 test_cind/x_2.npy -cotof
The input_op_name must be the same as in ONNX,
and it may not work if the input format is different between ONNX and TF.
<Usage in -oiqt>
INPUT Name of OP and path of calibration data file (Numpy) for quantization
and mean and std.
The specification can be omitted only when the input OP is a single 4D tensor image data.
If omitted, it is automatically calibrated using 20 normalized MS-COCO images.
The type of the input OP must be Float32.
Data for calibration must be pre-normalized to a range of 0 to 1.
-cind {input_op_name} {numpy_file_path} {mean} {std}
Numpy file paths must be specified the same number of times as the number of input OPs.
Normalize the value of the input OP based on the tensor specified in mean and std.
(input_value - mean) / std
Tensors in Numpy file format must be in dimension order after conversion to TF.
Note that this is intended for deployment on low-resource devices,
so the batch size is limited to 1 only.
e.g.
The example below shows a case where there are three input OPs.
Assume input0 is 128x128 RGB image data.
In addition, input0 should be a value that has been divided by 255
in the preprocessing and normalized to a range between 0 and 1.
input1 and input2 assume the input of something that is not an image.
Because input1 and input2 assume something that is not an image,
the divisor is not 255 when normalizing from 0 to 1.
"n" is the number of calibration data.
ONNX INPUT shapes:
input0: [n,3,128,128]
mean: [1,3,1,1] -> [[[[0.485]],[[0.456]],[[0.406]]]]
std: [1,3,1,1] -> [[[[0.229]],[[0.224]],[[0.225]]]]
input1: [n,64,64]
mean: [1,64] -> [0.1, ..., 0.64]
std: [1,64] -> [0.05, ..., 0.08]
input2: [n,5]
mean: [1] -> [0.3]
std: [1] -> [0.07]
TensorFlow INPUT shapes (Numpy file ndarray shapes):
input0: [n,128,128,3]
mean: [1,1,1,3] -> [[[[0.485, 0.456, 0.406]]]]
std: [1,1,1,3] -> [[[[0.229, 0.224, 0.225]]]]
input1: [n,64,64]
mean: [1,64] -> [0.1, ..., 0.64]
std: [1,64] -> [0.05, ..., 0.08]
input2: [n,5]
mean: [1] -> [0.3]
std: [1] -> [0.07]
-cind "input0" "../input0.npy" "[[[[0.485,0.456,0.406]]]]" "[[[[0.229,0.224,0.225]]]]"
-cind "input1" "./input1.npy" "[0.1,...,0.64]" "[0.05,...,0.08]"
-cind "input2" "input2.npy" "[0.3]" "[0.07]"
<Using -cotof and -oiqt at the same time>
To use -cotof and -oiqt simultaneously,
you need to enter the Input name of OP, path of data file, mean, and std all together.
And the data file must be in Float32 format,
and {input_op_name}, {numpy_file_path}, {mean}, and {std} must all be entered.
Otherwise, an error will occur during the -oiqt stage.
-iqd {int8,uint8,float32}, --input_quant_dtype {int8,uint8,float32}
Input dtypes when doing Full INT8 Quantization.
"int8"(default) or "uint8" or "float32"
-oqd {int8,uint8,float32}, --output_quant_dtype {int8,uint8,float32}
Output dtypes when doing Full INT8 Quantization.
"int8"(default) or "uint8" or "float32"
-nuo, --not_use_onnxsim
No optimization by onnx-simplifier is performed.
If this option is used, the probability of a conversion error is very high.
-nuonag, --not_use_opname_auto_generate
Automatic generation of each OP name in the old format ONNX file
and assignment of OP name are not performed.
-b BATCH_SIZE, --batch_size BATCH_SIZE
Fixes the dynamic batch size to the specified numeric batch size.
A value of 1 or more must be specified.
-ois OVERWRITE_INPUT_SHAPE [OVERWRITE_INPUT_SHAPE ...], \
--overwrite_input_shape OVERWRITE_INPUT_SHAPE [OVERWRITE_INPUT_SHAPE ...]
Overwrite the input shape.
The format is
"i1:dim0,...,dimN" "i2:dim0,...,dimN" "i3:dim0,...,dimN"
When there is only one input, for example,
"data:1,3,224,224"
When there are multiple inputs, for example,
"data1:1,3,224,224" "data2:1,3,112" "data3:5"
A value of 1 or more must be specified.
Numerical values other than dynamic dimensions are ignored.
Ignores --batch_size if specified at the same time as --batch_size.
-sh SHAPE_HINTS [SHAPE_HINTS ...], \
--shape_hints SHAPE_HINTS [SHAPE_HINTS ...]
Shape hints for input tensors containing dynamic dimensions.
Specify input shapes for test inference with -cotof or -coto.
Unlike `--overwrite_input_shape`, this operation does not overwrite
the ONNX input shape with a static shape.
The format is
"i1:dim0,...,dimN" "i2:dim0,...,dimN" "i3:dim0,...,dimN"
When there is only one input, for example,
"data:1,3,224,224"
When there are multiple inputs, for example,
"data1:1,3,224,224" "data2:1,3,112" "data3:5"
A value of 1 or more must be specified.
Numerical values other than dynamic dimensions are ignored.
-vh VALUE_HINTS [VALUE_HINTS ...], \
--value_hints VALUE_HINTS [VALUE_HINTS ...]
Value hints for dummy inference input tensors.
The format is
"input_name_1:value" "input_name_2:value" "*:default_value"
"*" applies to all inputs not explicitly specified.
Values are scalar only.
-nlt, --no_large_tensor
Suppresses constant bloat caused by Tile OP when optimizing models in onnxsim.
See: https://github.com/daquexian/onnx-simplifier/issues/178
-onwdt, --output_nms_with_dynamic_tensor
The number of bounding boxes in the NMS output results is
not fixed at the maximum number of max_output_boxes_per_class,
but rather at the smallest possible number of dynamic tensors.
If this option is disabled, NMS output is padded to the number
set in the max_output_boxes_per_class attribute.
e.g.
disable --output_nms_with_dynamic_tensor:
output_tensor_shape: [100, 7]
enable --output_nms_with_dynamic_tensor:
output_tensor_shape: [N, 7]
-onwa, --output_nms_with_argmax
Apply argmax to class scores dimension in NonMaxSuppression and shrink
scores tensor from [B, C, N] to [B, 1, N].
-snms {v4,v5}, --switch_nms_version {v4,v5}
Switch the NMS version to V4 or V5 to convert.
e.g.
NonMaxSuppressionV4(default): --switch_nms_version v4
NonMaxSuppressionV5: --switch_nms_version v5
-k KEEP_NCW_OR_NCHW_OR_NCDHW_INPUT_NAMES [KEEP_NCW_OR_NCHW_OR_NCDHW_INPUT_NAMES ...], \
--keep_ncw_or_nchw_or_ncdhw_input_names KEEP_NCW_OR_NCHW_OR_NCDHW_INPUT_NAMES \
[KEEP_NCW_OR_NCHW_OR_NCDHW_INPUT_NAMES ...]
Holds the NCW or NCHW or NCDHW of the input shape for the specified INPUT OP names.
If a nonexistent INPUT OP name is specified, it is ignored.
Valid only for 3D, 4D and 5D input tensors.
e.g. --keep_ncw_or_nchw_or_ncdhw_input_names "input0" "input1" "input2"
-kt KEEP_NWC_OR_NHWC_OR_NDHWC_INPUT_NAMES [KEEP_NWC_OR_NHWC_OR_NDHWC_INPUT_NAMES ...], \
--keep_nwc_or_nhwc_or_ndhwc_input_names KEEP_NWC_OR_NHWC_OR_NDHWC_INPUT_NAMES \
[KEEP_NWC_OR_NHWC_OR_NDHWC_INPUT_NAMES ...]
Holds the NWC or NHWC or NDHWC of the input shape for the specified INPUT OP names.
If a nonexistent INPUT OP name is specified, it is ignored.
If the input OP name is the same as the input OP name specified
in the keep_ncw_or_nchw_or_ncdhw_input_names option, it is ignored.
Valid only for 3D, 4D and 5D input tensors.
e.g. --keep_nwc_or_nhwc_or_ndhwc_input_names "input0" "input1" "input2"
-kat KEEP_SHAPE_ABSOLUTELY_INPUT_NAMES [KEEP_SHAPE_ABSOLUTELY_INPUT_NAMES ...], \
--keep_shape_absolutely_input_names KEEP_SHAPE_ABSOLUTELY_INPUT_NAMES \
[KEEP_SHAPE_ABSOLUTELY_INPUT_NAMES ...]
Name of the INPUT that unconditionally maintains its shape.
If a nonexistent INPUT OP name is specified, it is ignored.
e.g. --keep_shape_absolutely_input_names "input0" "input1" "input2"
-inimc INPUT_NAMES [INPUT_NAMES ...], \
--input_names_to_interrupt_model_conversion INPUT_NAMES [INPUT_NAMES ...]
Input names of ONNX that interrupt model conversion.
Interrupts model transformation at the specified input name and inputs the
model partitioned into subgraphs.
e.g. --input_names_to_interrupt_model_conversion "input0" "input1" "input2"
-onimc OUTPUT_NAMES [OUTPUT_NAMES ...], \
--output_names_to_interrupt_model_conversion OUTPUT_NAMES [OUTPUT_NAMES ...]
Output names of ONNX that interrupt model conversion.
Interrupts model transformation at the specified output name and outputs the
model partitioned into subgraphs.
e.g. --output_names_to_interrupt_model_conversion "output0" "output1" "output2"
-easm, --enable_auto_split_model
Force auto split regardless of the ONNX file size.
Uses --auto_split_max_size as the target partition size.
-asms AUTO_SPLIT_MAX_SIZE, --auto_split_max_size AUTO_SPLIT_MAX_SIZE
Target maximum size per partition when auto-split is triggered or forced.
Supported units: KB, MB, GB (e.g. 900MB, 1GB, 1536KB).
Bare numbers are treated as MB.
When specified, this value is also used as the target size for --auto_split_tflite_by_size.
Default: 1GB
-dgc, --disable_group_convolution
Disable GroupConvolution and replace it with SeparableConvolution for
output to saved_model format.
-eatfp16, --enable_accumulation_type_float16 ENABLE_ACCUMULATION_TYPE_FLOAT16
Hint for XNNPACK fp16 inference on float16 tflite model.
XNNPACK float16 inference on certain ARM64 cores is 2x faster.
Float16 inference doubling on devices with ARM64 ARMv8.2 or higher instruction set.
See: https://github.com/PINTO0309/onnx2tf/pull/553
-ebu, --enable_batchmatmul_unfold
BatchMatMul is separated batch by batch to generate a primitive MatMul.
-eru, --enable_rnn_unroll
Instead of increasing inference speed by expanding all symbolic loops of
the RNN (LSTM, GRU, RNN), RAM consumption will increase because all tensors
are expanded and embedded in the model.
https://keras.io/api/layers/recurrent_layers/
-dsft, --disable_suppression_flextranspose
Disables FlexTranspose generation suppression.
-nodaftc, --number_of_dimensions_after_flextranspose_compression
Number of Transpose OP dimensions generated after avoiding FlexTranspose generation.
Also suppress the creation of the Transpose itself by specifying 2.
Default: 6
-dsfs, --disable_suppression_flexstridedslice
Disables FlexStridedSlice generation suppression.
-dsm, --disable_strict_mode
If specified, the conversion speed is greatly accelerated because the strict accuracy
correction process is skipped, but the frequency of transposition errors increases
and accuracy errors are more likely to occur. Strict mode is enabled by default.
As of 2023.05.07, this is a work in progress and is an experimental feature.
Therefore, only some OPs are converted in strict mode for accuracy correction.
-nodafsc, --number_of_dimensions_after_flexstridedslice_compression
Number of StridedSlice OP dimensions generated after avoiding FlexStridedSlice generation.
Default: 5
-ofgd, --optimization_for_gpu_delegate
Replace operations that do not support gpu delegate with those
that do as much as possible.
-rari64, --replace_argmax_to_reducemax_and_indices_is_int64
Replace ArgMax with a ReduceMax. The returned indices are int64.
Only one of replace_argmax_to_reducemax_and_indices_is_int64
and replace_argmax_to_reducemax_and_indices_is_float32
and replace_argmax_to_fused_argmax_and_indices_is_int64
and replace_argmax_to_fused_argmax_and_indices_is_float32 can be specified.
-rarf32, --replace_argmax_to_reducemax_and_indices_is_float32
Replace ArgMax with a ReduceMax. The returned indices are float32.
Only one of replace_argmax_to_reducemax_and_indices_is_int64
and replace_argmax_to_reducemax_and_indices_is_float32
and replace_argmax_to_fused_argmax_and_indices_is_int64
and replace_argmax_to_fused_argmax_and_indices_is_float32 can be specified.
-rafi64, --replace_argmax_to_fused_argmax_and_indices_is_int64
Replace ArgMax with a Fused_ArgMax. The returned indices are int64.
It improves inference speed at the cost of a small sacrifice in accuracy.
See. https://github.com/tensorflow/models/tree/master/official/projects/edgetpu/vision#argmax-fusion-to-improve-segmentation-model-latency
Currently, only 4D tensors are supported.
Only one of replace_argmax_to_reducemax_and_indices_is_int64
and replace_argmax_to_reducemax_and_indices_is_float32
and replace_argmax_to_fused_argmax_and_indices_is_int64
and replace_argmax_to_fused_argmax_and_indices_is_float32 can be specified.
-raff32, --replace_argmax_to_fused_argmax_and_indices_is_float32
Replace ArgMax with a Fused_ArgMax. The returned indices are float32.
It improves inference speed at the cost of a small sacrifice in accuracy.
See. https://github.com/tensorflow/models/tree/master/official/projects/edgetpu/vision#argmax-fusion-to-improve-segmentation-model-latency
Currently, only 4D tensors are supported.
Only one of replace_argmax_to_reducemax_and_indices_is_int64
and replace_argmax_to_reducemax_and_indices_is_float32
and replace_argmax_to_fused_argmax_and_indices_is_int64
and replace_argmax_to_fused_argmax_and_indices_is_float32 can be specified.
-fasr FUSED_ARGMAX_SCALE_RATIO, --fused_argmax_scale_ratio FUSED_ARGMAX_SCALE_RATIO
For Fused ArgMax.
Scale ratio when generating Fused ArgMax.
0.0 < fused_argmax_scale_ratio <= 1.0
Default: 0.5
-rtpo, --replace_to_pseudo_operators
Replace list of operators to pseudo operators.
Full name of the target operators should be given.
Currently supported operators :
Asin, Acos, Atan, Abs, PReLU, LeakyReLU, Power, GatherND, Neg, HardSwish, Erf, GeLU, MatMulInteger
-me, --mvn_epsilon
For MeanVarianceNormalization.
The number to be added to the variance to avoid division by zero
when normalizing the value.
(input_tensor - mean) / tf.sqrt(variance + mvn_epsilon)
Default: 0.0000000001
-prf PARAM_REPLACEMENT_FILE, --param_replacement_file PARAM_REPLACEMENT_FILE
Parameter replacement file path. (.json)
-cgdc, --check_gpu_delegate_compatibility
Run TFLite ModelAnalyzer on the generated Float16 tflite model
to check if the model can be supported by GPU Delegate.
e.g.
"""
=== TFLite ModelAnalyzer ===
Your TFLite model has '1' subgraph(s). In the subgraph description below,
T# represents the Tensor numbers. For example, in Subgraph#0, the RESHAPE op takes
tensor #0 and tensor #6 as input and produces tensor #7 as output.
Subgraph#0 main(T#0) -> [T#17]
Op#0 RESHAPE(T#0, T#6[2, 8, 8, 3, 2, ...]) -> [T#7]
Op#1 SPLIT(T#5[0], T#7) -> [T#8, T#9]
Op#2 RESHAPE(T#8, T#1[8, 8, 3, 2, 2]) -> [T#10]
Op#3 TRANSPOSE(T#10, T#4[0, 3, 1, 4, 2]) -> [T#11]
Op#4 RESHAPE(T#11, T#2[1, 8, 2, 8, 2, ...]) -> [T#12]
Op#5 RESHAPE(T#9, T#1[8, 8, 3, 2, 2]) -> [T#13]
Op#6 TRANSPOSE(T#13, T#4[0, 3, 1, 4, 2]) -> [T#14]
Op#7 RESHAPE(T#14, T#2[1, 8, 2, 8, 2, ...]) -> [T#15]
Op#8 CONCATENATION(T#12, T#15) -> [T#16]
Op#9 RESHAPE(T#16, T#3[2, 16, 16, 3]) -> [T#17]
Tensors of Subgraph#0
T#0(inputs_0) shape:[2, 8, 8, 12], type:FLOAT32
T#1(model/tf.compat.v1.squeeze_2/Squeeze) shape:[5], type:INT32 RO 20 bytes, data:[8, 8, 3, 2, 2]
T#2(model/tf.expand_dims_1/ExpandDims) shape:[6], type:INT32 RO 24 bytes, data:[1, 8, 2, 8, 2, ...]
T#3(model/tf.reshape_1/Reshape/shape) shape:[4], type:INT32 RO 16 bytes, data:[2, 16, 16, 3]
T#4(model/tf.compat.v1.transpose/transpose/perm) shape:[5], type:INT32 RO 20 bytes, data:[0, 3, 1, 4, 2]
T#5(model/tf.concat/concat/axis) shape:[], type:INT32 RO 4 bytes, data:[0]
T#6(model/tf.reshape/Reshape/shape) shape:[6], type:INT32 RO 24 bytes, data:[2, 8, 8, 3, 2, ...]
T#7(model/tf.reshape/Reshape) shape:[2, 8, 8, 3, 2, 2], type:FLOAT32
T#8(model/tf.split/split) shape:[1, 8, 8, 3, 2, 2], type:FLOAT32
T#9(model/tf.split/split1) shape:[1, 8, 8, 3, 2, 2], type:FLOAT32
T#10(model/tf.compat.v1.squeeze_1/Squeeze) shape:[8, 8, 3, 2, 2], type:FLOAT32
T#11(model/tf.compat.v1.transpose/transpose) shape:[8, 2, 8, 2, 3], type:FLOAT32
T#12(model/tf.expand_dims/ExpandDims) shape:[1, 8, 2, 8, 2, 3], type:FLOAT32
T#13(model/tf.compat.v1.squeeze_2/Squeeze1) shape:[8, 8, 3, 2, 2], type:FLOAT32
T#14(model/tf.compat.v1.transpose_1/transpose) shape:[8, 2, 8, 2, 3], type:FLOAT32
T#15(model/tf.expand_dims_1/ExpandDims1) shape:[1, 8, 2, 8, 2, 3], type:FLOAT32
T#16(model/tf.concat/concat) shape:[2, 8, 2, 8, 2, 3], type:FLOAT32
T#17(Identity) shape:[2, 16, 16, 3], type:FLOAT32
Your model looks compatibile with GPU delegate with TFLite runtime version 2.10.0.
But it doesn't guarantee that your model works well with GPU delegate.
There could be some runtime incompatibililty happen.
---------------------------------------------------------------
Model size: 2988 bytes
Non-data buffer size: 2757 bytes (92.27 %)
Total data buffer size: 231 bytes (07.73 %)
(Zero value buffers): 4 bytes (00.13 %)
* Buffers of TFLite model are mostly used for constant tensors.
And zero value buffers are buffers filled with zeros.
Non-data buffers area are used to store operators, subgraphs and etc.
You can find more details from https://github.com/google-ai-edge/LiteRT/blob/v2.1.2/tflite/converter/schema/schema.fbs
"""
-coto, --check_onnx_tf_outputs_elementwise_close
Returns "Matches" if the output of onnx and the output of TF are
within acceptable proximity element by element.
Returns "Unmatched" if the output of onnx and the output of TF are
not within acceptable proximity element by element.
If the output of onnx is 1D, it returns "Skipped" and skips the comparison
between the output of onnx and that of TF. This is because when undefined
dimensions are present, a situation often arises where very large index
values are compared, causing OutOfMemory.
Only the output content of the models final output OP is checked.
-cotof, --check_onnx_tf_outputs_elementwise_close_full
Returns "Matches" if the output of onnx and the output of TF are
within acceptable proximity element by element.
Check the output of all OPs in sequence from the beginning,
including all but the final output OP of the model.
Returns "Unmatched" if the output of onnx and the output of TF are
not within acceptable proximity element by element.
If the output of onnx is 1D, it returns "Skipped" and skips the comparison
between the output of onnx and that of TF. This is because when undefined
dimensions are present, a situation often arises where very large index
values are compared, causing OutOfMemory.
It is very time consuming because it performs as many inferences as
there are operations.
-coton, --check_onnx_tf_outputs_sample_data_normalization
norm: Validate using random data normalized to the range 0.0 to 1.0
denorm: Validate using random data in the range 0.0 to 255.0
If there is a normalization layer at the model's entry point, or
if the model was trained on denormalized data, "denorm" must be specified.
Default: "norm"
-cotor CHECK_ONNX_TF_OUTPUTS_ELEMENTWISE_CLOSE_RTOL,\
--check_onnx_tf_outputs_elementwise_close_rtol CHECK_ONNX_TF_OUTPUTS_ELEMENTWISE_CLOSE_RTOL
The relative tolerance parameter.
Default: 0.0
-cotoa CHECK_ONNX_TF_OUTPUTS_ELEMENTWISE_CLOSE_ATOL,\
--check_onnx_tf_outputs_elementwise_close_atol CHECK_ONNX_TF_OUTPUTS_ELEMENTWISE_CLOSE_ATOL
The absolute tolerance parameter.
Default: 1e-4
-tdnp TEST_DATA_NHWC_PATH, --test_data_nhwc_path TEST_DATA_NHWC_PATH
Path to a numpy file (.npy) containing custom test data in NHWC format.
This is used for test inference and validation when check_onnx_tf_outputs options are enabled.
If not specified, the tool will attempt to download sample data from the internet
when the input is a 4D RGB image tensor.
The numpy array should have shape [batch_size, height, width, 3] with values
normalized to the range [0, 1].
This option is useful for offline environments or when you want to use
specific test data for validation.
For models with multiple inputs, the same test array is reused for each eligible input
after per-input resize/layout conversion.
Unlike -cind, this option is not used for INT8 calibration and does not accept mean/std.
-agj, --auto_generate_json
Automatically generates a parameter replacement JSON file that achieves minimal error
when converting the model. This option explores various parameter combinations to find
the best settings that result in successful conversion and highest accuracy.
The search stops when the final output OP accuracy check shows "Matches".
When used together with -cotof, the generated JSON is used to re-evaluate accuracy.
WARNING: This option performs an exhaustive search to find the optimal conversion patterns,
which can take a very long time depending on the model complexity.
-agje, --auto_generate_json_on_error
Attempts to generate a parameter replacement JSON when conversion fails or when accuracy
validation finds errors greater than 1e-2. Useful for quickly capturing fixes during
-cotof runs. Disabled by default to avoid unexpected file generation.
-dms, --disable_model_save
Does not save the converted model. For CIs RAM savings.
-n, --non_verbose
Shorthand to specify a verbosity of "error".
-v, --verbosity
Change the level of information printed.
Values are "debug", "info", "warn", and "error".
Default: "debug" (for backwards compatability)
In-script Usage
Click to expand
>>> from onnx2tf import convert
>>> help(convert)
Help on function convert in module onnx2tf:
convert(
input_onnx_file_path: Union[str, NoneType] = '',
onnx_graph: Union[onnx.onnx_ml_pb2.ModelProto, NoneType] = None,
output_folder_path: Union[str, NoneType] = 'saved_model',
output_signaturedefs: Optional[bool] = False,
output_h5: Optional[bool] = False,
output_keras_v3: Optional[bool] = False,
output_tfv1_pb: Optional[bool] = False,
output_weights: Optional[bool] = False,
copy_onnx_input_output_names_to_tflite: Optional[bool] = False,
output_integer_quantized_tflite: Optional[bool] = False,
tflite_backend: Optional[str] = 'tf_converter',
quant_norm_mean: Optional[str] = '[[[[0.485, 0.456, 0.406]]]]',
quant_norm_std: Optional[str] = '[[[[0.229, 0.224, 0.225]]]]',
quant_type: Optional[str] = 'per-channel',
custom_input_op_name_np_data_path: Optional[List] = None,
input_quant_dtype: Optional[str] = 'int8',
output_quant_dtype: Optional[str] = 'int8',
not_use_onnxsim: Optional[bool] = False,
not_use_opname_auto_generate: Optional[bool] = False,
batch_size: Union[int, NoneType] = None,
overwrite_input_shape: Union[List[str], NoneType] = None,
shape_hints: Union[List[str], NoneType] = None,
value_hints: Union[List[str], NoneType] = None,
no_large_tensor: Optional[bool] = False,
output_nms_with_dynamic_tensor: Optional[bool] = False,
output_nms_with_argmax: Optional[bool] = False,
switch_nms_version: Optional[str] = 'v4',
keep_ncw_or_nchw_or_ncdhw_input_names: Union[List[str], NoneType] = None,
keep_nwc_or_nhwc_or_ndhwc_input_names: Union[List[str], NoneType] = None,
keep_shape_absolutely_input_names: Optional[List[str]] = None,
input_names_to_interrupt_model_conversion: Union[List[str], NoneType] = None,
output_names_to_interrupt_model_conversion: Union[List[str], NoneType] = None,
enable_auto_split_model: Optional[bool] = False,
auto_split_max_size: Union[Any, NoneType] = None,
auto_split_max_size_mb: Union[int, NoneType] = None,
disable_group_convolution: Union[bool, NoneType] = False,
enable_batchmatmul_unfold: Optional[bool] = False,
enable_rnn_unroll: Optional[bool] = False,
disable_suppression_flextranspose: Optional[bool] = False,
number_of_dimensions_after_flextranspose_compression: Optional[int] = 6,
disable_suppression_flexstridedslice: Optional[bool] = False,
disable_strict_mode: Optional[bool] = False,
number_of_dimensions_after_flexstridedslice_compression: Optional[int] = 5,
optimization_for_gpu_delegate: Optional[bool] = False,
replace_argmax_to_reducemax_and_indices_is_int64: Union[bool, NoneType] = False,
replace_argmax_to_reducemax_and_indices_is_float32: Union[bool, NoneType] = False,
replace_argmax_to_fused_argmax_and_indices_is_int64: Union[bool, NoneType] = False,
replace_argmax_to_fused_argmax_and_indices_is_float32: Union[bool, NoneType] = False,
fused_argmax_scale_ratio: Union[float, NoneType] = 0.5,
replace_to_pseudo_operators: List[str] = None,
mvn_epsilon: Union[float, NoneType] = 0.0000000001,
param_replacement_file: Optional[str] = '',
auto_generate_json: Optional[bool] = False,
auto_generate_json_on_error: Optional[bool] = False,
check_gpu_delegate_compatibility: Optional[bool] = False,
check_onnx_tf_outputs_elementwise_close: Optional[bool] = False,
check_onnx_tf_outputs_elementwise_close_full: Optional[bool] = False,
check_onnx_tf_outputs_sample_data_normalization: Optional[str] = 'norm',
check_onnx_tf_outputs_elementwise_close_rtol: Optional[float] = 0.0,
check_onnx_tf_outputs_elementwise_close_atol: Optional[float] = 1e-4,
test_data_nhwc_path: Union[str, NoneType] = None,
disable_model_save: Union[bool, NoneType] = False,
non_verbose: Union[bool, NoneType] = False,
verbosity: Optional[str] = 'debug'
) -> keras.engine.training.Model
Convert ONNX to TensorFlow models.
Parameters
----------
input_onnx_file_path: Optional[str]
Input onnx file path.
Either input_onnx_file_path or onnx_graph must be specified.
onnx_graph: Optional[onnx.ModelProto]
onnx.ModelProto.
Either input_onnx_file_path or onnx_graph must be specified.
onnx_graph If specified, ignore input_onnx_file_path and process onnx_graph.
output_folder_path: Optional[str]
Output tensorflow model folder path.
Default: "saved_model"
output_signaturedefs: Optional[bool]
Signature is added to the output for serving or for conversion
to other model formats. However, this can significantly reduce the speed
of model conversion and significant increase the size of the model.
output_h5: Optional[bool]
Output model in Keras H5 format.
output_keras_v3: Optional[bool]
Output model in Keras (keras_v3) format.
output_tfv1_pb: Optional[bool]
Output model in TF v1 (.pb) format.
output_weights: Optional[bool]
Output weights in hdf5 format.
copy_onnx_input_output_names_to_tflite: Optional[bool]
Copy the input/output OP name of ONNX to the input/output OP name of tflite.
Due to Tensorflow internal operating specifications,
the input/output order of ONNX does not necessarily match
the input/output order of tflite.
Be sure to check that the input/output OP names in the generated
tflite file have been converted as expected.
Also, this option generates a huge JSON file as a temporary file for processing.
Therefore, it is strongly discouraged to use it on large models of hundreds
of megabytes or more.
output_integer_quantized_tflite: Optional[bool]
Output of integer quantized tflite.
tflite_backend: Optional[str]
TFLite generation backend.
"tf_converter"(default): Use TensorFlow Lite Converter.
"flatbuffer_direct": Experimental direct FlatBuffer builder path.
Note: "flatbuffer_direct" supports a limited builtin OP set,
FP32/FP16 export, limited dynamic-range quantization,
limited integer quantization, and limited int16-activation variants.
quant_norm_mean: Optional[str]
Normalized average value during quantization.
Only valid when the "-cind" option is not used.
Default: "[[[[0.485, 0.456, 0.406]]]]"
quant_norm_std: Optional[str]
Normalized standard deviation during quantization.
Only valid when the "-cind" option is not used.
Default: "[[[[0.229, 0.224, 0.225]]]]"
quant_type: Optional[str]
Selects whether "per-channel" or "per-tensor" quantization is used.
Default: "per-channel"
custom_input_op_name_np_data_path: Optional[List]
--custom_input_op_name_np_data_path INPUT_NAME NUMPY_FILE_PATH MEAN STD
Input name of OP and path of data file (Numpy) for custom input for -cotof or -oiqt,
and mean (optional) and std (optional).
<Usage in -cotof>
When using -cotof, custom input defined by the user, instead of dummy data, is used.
In this case, mean and std are omitted from the input.
-cind {input_op_name} {numpy_file_path}
e.g. -cind onnx::Equal_0 test_cind/x_1.npy -cind onnx::Add_1 test_cind/x_2.npy -cotof
The input_op_name must be the same as in ONNX,
and it may not work if the input format is different between ONNX and TF.
<Usage in -oiqt>
INPUT Name of OP and path of calibration data file (Numpy) for quantization
and mean and std.
The specification can be omitted only when the input OP is a single 4D tensor image data.
If omitted, it is automatically calibrated using 20 normalized MS-COCO images.
The type of the input OP must be Float32.
Data for calibration must be pre-normalized to a range of 0 to 1.
-cind {input_op_name} {numpy_file_path} {mean} {std}
Numpy file paths must be specified the same number of times as the number of input OPs.
Normalize the value of the input OP based on the tensor specified in mean and std.
(input_value - mean) / std
Tensors in Numpy file format must be in dimension order after conversion to TF.
Note that this is intended for deployment on low-resource devices,
so the batch size is limited to 1 only.
e.g.
The example below shows a case where there are three input OPs.
Assume input0 is 128x128 RGB image data.
In addition, input0 should be a value that has been divided by 255
in the preprocessing and normalized to a range between 0 and 1.
input1 and input2 assume the input of something that is not an image.
Because input1 and input2 assume something that is not an image,
the divisor is not 255 when normalizing from 0 to 1.
"n" is the number of calibration data.
ONNX INPUT shapes:
input0: [n,3,128,128]
mean: [1,3,1,1] -> [[[[0.485]],[[0.456]],[[0.406]]]]
std : [1,3,1,1] -> [[[[0.229]],[[0.224]],[[0.225]]]]
input1: [n,64,64]
mean: [1,64] -> [[0.1, ..., 0.64]]
std : [1,64] -> [[0.05, ..., 0.08]]
input2: [n,5]
mean: [1] -> [0.3]
std : [1] -> [0.07]
TensorFlow INPUT shapes (Numpy file ndarray shapes):
input0: [n,128,128,3]
mean: [1,1,1,3] -> [[[[0.485, 0.456, 0.406]]]]
std : [1,1,1,3] -> [[[[0.229, 0.224, 0.225]]]]
input1: [n,64,64]
mean: [1,64] -> [[0.1, ..., 0.64]]
std : [1,64] -> [[0.05, ..., 0.08]]
input2: [n,5]
mean: [1] -> [0.3]
std : [1] -> [0.07]
cind=[
["input0","../input0.npy",[[[[0.485, 0.456, 0.406]]]],[[[[0.229, 0.224, 0.225]]]]],
["input1","./input1.npy",[0.1, ..., 0.64],[0.05, ..., 0.08]],
["input2","input2.npy",[0.3],[0.07]],
]
<Using -cotof and -oiqt at the same time>
To use -cotof and -oiqt simultaneously,
you need to enter the Input name of OP, path of data file, mean, and std all together.
And the data file must be in Float32 format,
and {input_op_name}, {numpy_file_path}, {mean}, and {std} must all be entered.
Otherwise, an error will occur during the -oiqt stage.
input_quant_dtype: Optional[str]
Input dtypes when doing Full INT8 Quantization.
"int8"(default) or "uint8" or "float32"
output_quant_dtype: Optional[str]
Output dtypes when doing Full INT8 Quantization.
"int8"(default) or "uint8" or "float32"
not_use_onnxsim: Optional[bool]
No optimization by onnx-simplifier is performed.
If this option is used, the probability of a conversion error is very high.
not_use_opname_auto_generate: Optional[bool]
Automatic generation of each OP name in the old format ONNX file
and assignment of OP name are not performed.
batch_size: Optional[int]
Fixes the dynamic batch size to the specified numeric batch size.
A value of 1 or more must be specified.
overwrite_input_shape: Optional[List[str]]
Overwrite the input shape.
The format is
['i1:dim0,dim1,...,dimN', 'i2:dim0,dim1,...,dimN', 'i3:dim0,dim1,...,dimN']
When there is only one input, for example,
['data:1,3,224,224']
When there are multiple inputs, for example,
['data1:1,3,224,224','data2:1,3,112','data3:5']
A value of 1 or more must be specified.
Numerical values other than dynamic dimensions are ignored.
Ignores batch_size if specified at the same time as batch_size.
shape_hints: Optional[List[str]]
Shape hints for input tensors containing dynamic dimensions.
Specify input shapes for test inference with -cotof or -coto.
Unlike `--overwrite_input_shape`, this operation does not overwrite
the ONNX input shape with a static shape.
The format is
['i1:dim0,...,dimN', 'i2:dim0,...,dimN', 'i3:dim0,...,dimN']
When there is only one input, for example,
['data:1,3,224,224']
When there are multiple inputs, for example,
['data1:1,3,224,224', 'data2:1,3,112', 'data3:5']
A value of 1 or more must be specified.
Numerical values other than dynamic dimensions are ignored.
value_hints: Optional[List[str]]
Value hints for dummy inference input tensors.
The format is
['input_name_1:value', 'input_name_2:value', '*:default_value']
"*" applies to all inputs not explicitly specified.
Values are scalar only.
no_large_tensor: Optional[bool]
Suppresses constant bloat caused by Tile OP when optimizing models in onnxsim.
See: https://github.com/daquexian/onnx-simplifier/issues/178
output_nms_with_dynamic_tensor: Optional[bool]
The number of bounding boxes in the NMS output results is
not fixed at the maximum number of max_output_boxes_per_class,
but rather at the smallest possible number of dynamic tensors.
If this option is disabled, NMS output is padded to the number
set in the max_output_boxes_per_class attribute.
e.g.
disable --output_nms_with_dynamic_tensor:
output_tensor_shape: [100, 7]
enable --output_nms_with_dynamic_tensor:
output_tensor_shape: [N, 7]
output_nms_with_argmax: Optional[bool]
Apply argmax over scores class dimension in NonMaxSuppression to
shrink scores from [B, C, N] to [B, 1, N].
switch_nms_version {v4,v5}
Switch the NMS version to V4 or V5 to convert.
e.g.
NonMaxSuppressionV4(default): switch_nms_version="v4"
NonMaxSuppressionV5: switch_nms_version="v5"
keep_ncw_or_nchw_or_ncdhw_input_names: Optional[List[str]]
Holds the NCW or NCHW or NCDHW of the input shape for the specified INPUT OP names.
If a nonexistent INPUT OP name is specified, it is ignored.
Valid only for 3D, 4D and 5D input tensors.
e.g.
keep_ncw_or_nchw_or_ncdhw_input_names=['input0','input1','input2']
keep_nwc_or_nhwc_or_ndhwc_input_names: Optional[List[str]]
Holds the NWC or NHWC or NDHWC of the input shape for the specified INPUT OP names.
If a nonexistent INPUT OP name is specified, it is ignored.
If the input OP name is the same as the input OP name specified
in the keep_ncw_or_nchw_or_ncdhw_input_names option, it is ignored.
Valid only for 3D, 4D and 5D input tensors.
e.g.
keep_nwc_or_nhwc_or_ndhwc_input_names=['input0','input1','input2']
keep_shape_absolutely_input_names: Optional[List[str]]
Name of the INPUT that unconditionally maintains its shape.
If a nonexistent INPUT OP name is specified, it is ignored.
e.g.
keep_shape_absolutely_input_names=['input0','input1','input2']
input_names_to_interrupt_model_conversion: Optional[List[str]]
Input names of ONNX that interrupt model conversion.
Interrupts model transformation at the specified input name
and inputs the model partitioned into subgraphs.
e.g.
input_names_to_interrupt_model_conversion=['input0','input1','input2']
output_names_to_interrupt_model_conversion: Optional[List[str]]
Output names of ONNX that interrupt model conversion.
Interrupts model transformation at the specified output name
and outputs the model partitioned into subgraphs.
e.g.
output_names_to_interrupt_model_conversion=['output0','output1','output2']
enable_auto_split_model: Optional[bool]
Force auto split regardless of the ONNX file size.
Uses auto_split_max_size as the target partition size.
Short option: -easm
Default: False
auto_split_max_size: Optional[Any]
Target maximum size per partition.
Supports values such as "512KB", "900MB", and "1.5GB".
Bare numeric values are treated as MB.
Used when auto-split is triggered or forced.
When specified, also used as the split target when auto_split_tflite_by_size=True.
Default: "1GB"
auto_split_max_size_mb: Optional[int]
[Deprecated] Legacy alias of auto_split_max_size in MB.
disable_group_convolution: Optional[bool]
Disable GroupConvolution and replace it with SeparableConvolution for
output to saved_model format.
enable_accumulation_type_float16: Optional[bool]
Hint for XNNPack fp16 inference on float16 tflite model.
XNNPACK float16 inference on certain ARM64 cores is 2x faster.
Float16 inference doubling on devices with ARM64 ARMv8.2 or higher instruction set.
https://github.com/tensorflow/tensorflow/blob/master/tensorflow/lite/delegates/xnnpack/README.md#floating-point-ieee-fp16-operators
enable_batchmatmul_unfold: Optional[bool]
BatchMatMul is separated batch by batch to generate a primitive MatMul.
enable_rnn_unroll: Optional[bool]
Instead of increasing inference speed by expanding all symbolic loops of
the RNN (LSTM, GRU, RNN), RAM consumption will increase because all tensors
are expanded and embedded in the model.
https://keras.io/api/layers/recurrent_layers/
disable_suppression_flextranspose: Optional[bool]
Disables FlexTranspose generation suppression.
number_of_dimensions_after_flextranspose_compression: Optional[int]
Number of Transpose OP dimensions generated after avoiding FlexTranspose generation.
Also suppress the creation of the Transpose itself by specifying 2.
Default: 6
disable_suppression_flexstridedslice: Optional[bool]
Disables FlexStridedSlice generation suppression.
disable_strict_mode: Optional[bool]
If specified, the conversion speed is greatly accelerated because the strict accuracy
correction process is skipped, but the frequency of transposition errors increases
and accuracy errors are more likely to occur. Strict mode is enabled by default.
As of 2023.05.07, this is a work in progress and is an experimental feature.
Therefore, only some OPs are converted in strict mode for accuracy correction.
number_of_dimensions_after_flexstridedslice_compression: Optional[int]
Number of StridedSlice OP dimensions generated after avoiding FlexStridedSlice generation.
Default: 5
optimization_for_gpu_delegate: Optional[bool]
Replace operations that do not support gpu delegate with those
that do as much as possible.
replace_argmax_to_reducemax_and_indices_is_int64: Optional[bool]
Replace ArgMax with a ReduceMax. The returned indices are int64.
Only one of replace_argmax_to_reducemax_and_indices_is_int64 and
replace_argmax_to_reducemax_and_indices_is_float32 and
replace_argmax_to_fused_argmax_and_indices_is_int64 and
replace_argmax_to_fused_argmax_and_indices_is_float32 can be specified.
Default: False
replace_argmax_to_reducemax_and_indices_is_float32: Optional[bool]
Replace ArgMax with a ReduceMax. The returned indices are float32.
Only one of replace_argmax_to_reducemax_and_indices_is_int64 and
replace_argmax_to_reducemax_and_indices_is_float32 and
replace_argmax_to_fused_argmax_and_indices_is_int64 and
replace_argmax_to_fused_argmax_and_indices_is_float32 can be specified.
Default: False
replace_argmax_to_fused_argmax_and_indices_is_int64: Optional[bool]
Replace ArgMax with a ReduceMax. The returned indices are int64.
It improves inference speed at the cost of a small sacrifice in accuracy.
See. https://github.com/tensorflow/models/tree/master/official/projects/edgetpu/vision#argmax-fusion-to-improve-segmentation-model-latency
Currently, only 4D tensors are supported.
Only one of replace_argmax_to_reducemax_and_indices_is_int64 and
replace_argmax_to_reducemax_and_indices_is_float32 and
replace_argmax_to_fused_argmax_and_indices_is_int64 and
replace_argmax_to_fused_argmax_and_indices_is_float32 can be specified.
Default: False
replace_argmax_to_fused_argmax_and_indices_is_float32: Optional[bool]
Replace ArgMax with a ReduceMax. The returned indices are float32.
It improves inference speed at the cost of a small sacrifice in accuracy.
See. https://github.com/tensorflow/models/tree/master/official/projects/edgetpu/vision#argmax-fusion-to-improve-segmentation-model-latency
Currently, only 4D tensors are supported.
Only one of replace_argmax_to_reducemax_and_indices_is_int64 and
replace_argmax_to_reducemax_and_indices_is_float32 and
replace_argmax_to_fused_argmax_and_indices_is_int64 and
replace_argmax_to_fused_argmax_and_indices_is_float32 can be specified.
Default: False
fused_argmax_scale_ratio: Optional[float]
For Fused ArgMax.
Scale ratio when generating Fused ArgMax.
0.0 < fused_argmax_scale_ratio <= 1.0
Default: 0.5
replace_to_pseudo_operators: List[str]
Replace list of operators to pseudo operators.
Full name of the target operators should be given.
Currently supported operators :
Asin, Acos, Atan, Abs, PReLU, LeakyReLU, Power, GatherND, Neg, HardSwish, Erf, GeLU, MatMulInteger
mvn_epsilon: Optional[float]
For MeanVarianceNormalization.
The number to be added to the variance to avoid division by zero
when normalizing the value.
(input_tensor - mean) / tf.sqrt(variance + mvn_epsilon)
Default: 0.0000000001
param_replacement_file: Optional[str]
Parameter replacement file path. (.json)
auto_generate_json: Optional[bool]
Automatically generates a parameter replacement JSON file that achieves minimal error
when converting the model. This option explores various parameter combinations to find
the best settings that result in successful conversion and highest accuracy.
The search stops when the final output OP accuracy check shows "Matches".
When used together with check_onnx_tf_outputs_elementwise_close_full,
the generated JSON is used to re-evaluate accuracy.
Default: False
auto_generate_json_on_error: Optional[bool]
When conversion fails or accuracy validation detects errors greater than 1e-2,
attempts to generate a parameter replacement JSON as a best-effort fix.
Default: False
check_gpu_delegate_compatibility: Optional[bool]
Run TFLite ModelAnalyzer on the generated Float16 tflite model
to check if the model can be supported by GPU Delegate.
e.g.
"""
=== TFLite ModelAnalyzer ===
Your TFLite model has '1' subgraph(s). In the subgraph description below,
T# represents the Tensor numbers. For example, in Subgraph#0, the RESHAPE op takes
tensor #0 and tensor #6 as input and produces tensor #7 as output.
Subgraph#0 main(T#0) -> [T#17]
Op#0 RESHAPE(T#0, T#6[2, 8, 8, 3, 2, ...]) -> [T#7]
Op#1 SPLIT(T#5[0], T#7) -> [T#8, T#9]
Op#2 RESHAPE(T#8, T#1[8, 8, 3, 2, 2]) -> [T#10]
Op#3 TRANSPOSE(T#10, T#4[0, 3, 1, 4, 2]) -> [T#11]
Op#4 RESHAPE(T#11, T#2[1, 8, 2, 8, 2, ...]) -> [T#12]
Op#5 RESHAPE(T#9, T#1[8, 8, 3, 2, 2]) -> [T#13]
Op#6 TRANSPOSE(T#13, T#4[0, 3, 1, 4, 2]) -> [T#14]
Op#7 RESHAPE(T#14, T#2[1, 8, 2, 8, 2, ...]) -> [T#15]
Op#8 CONCATENATION(T#12, T#15) -> [T#16]
Op#9 RESHAPE(T#16, T#3[2, 16, 16, 3]) -> [T#17]
Tensors of Subgraph#0
T#0(inputs_0) shape:[2, 8, 8, 12], type:FLOAT32
T#1(model/tf.compat.v1.squeeze_2/Squeeze) shape:[5], type:INT32 RO 20 bytes, data:[8, 8, 3, 2, 2]
T#2(model/tf.expand_dims_1/ExpandDims) shape:[6], type:INT32 RO 24 bytes, data:[1, 8, 2, 8, 2, ...]
T#3(model/tf.reshape_1/Reshape/shape) shape:[4], type:INT32 RO 16 bytes, data:[2, 16, 16, 3]
T#4(model/tf.compat.v1.transpose/transpose/perm) shape:[5], type:INT32 RO 20 bytes, data:[0, 3, 1, 4, 2]
T#5(model/tf.concat/concat/axis) shape:[], type:INT32 RO 4 bytes, data:[0]
T#6(model/tf.reshape/Reshape/shape) shape:[6], type:INT32 RO 24 bytes, data:[2, 8, 8, 3, 2, ...]
T#7(model/tf.reshape/Reshape) shape:[2, 8, 8, 3, 2, 2], type:FLOAT32
T#8(model/tf.split/split) shape:[1, 8, 8, 3, 2, 2], type:FLOAT32
T#9(model/tf.split/split1) shape:[1, 8, 8, 3, 2, 2], type:FLOAT32
T#10(model/tf.compat.v1.squeeze_1/Squeeze) shape:[8, 8, 3, 2, 2], type:FLOAT32
T#11(model/tf.compat.v1.transpose/transpose) shape:[8, 2, 8, 2, 3], type:FLOAT32
T#12(model/tf.expand_dims/ExpandDims) shape:[1, 8, 2, 8, 2, 3], type:FLOAT32
T#13(model/tf.compat.v1.squeeze_2/Squeeze1) shape:[8, 8, 3, 2, 2], type:FLOAT32
T#14(model/tf.compat.v1.transpose_1/transpose) shape:[8, 2, 8, 2, 3], type:FLOAT32
T#15(model/tf.expand_dims_1/ExpandDims1) shape:[1, 8, 2, 8, 2, 3], type:FLOAT32
T#16(model/tf.concat/concat) shape:[2, 8, 2, 8, 2, 3], type:FLOAT32
T#17(Identity) shape:[2, 16, 16, 3], type:FLOAT32
Your model looks compatibile with GPU delegate with TFLite runtime version 2.10.0.
But it doesn't guarantee that your model works well with GPU delegate.
There could be some runtime incompatibililty happen.
---------------------------------------------------------------
Model size: 2988 bytes
Non-data buffer size: 2757 bytes (92.27 %)
Total data buffer size: 231 bytes (07.73 %)
(Zero value buffers): 4 bytes (00.13 %)
* Buffers of TFLite model are mostly used for constant tensors.
And zero value buffers are buffers filled with zeros.
Non-data buffers area are used to store operators, subgraphs and etc.
You can find more details from https://github.com/google-ai-edge/LiteRT/blob/v2.1.2/tflite/converter/schema/schema.fbs
"""
check_onnx_tf_outputs_elementwise_close: Optional[bool]
Returns "Matches" if the output of onnx and the output of TF are
within acceptable proximity element by element.
Returns "Unmatched" if the output of onnx and the output of TF are
not within acceptable proximity element by element.
If the output of onnx is 1D, it returns "Skipped" and skips the comparison
between the output of onnx and that of TF. This is because when undefined
dimensions are present, a situation often arises where very large index
values are compared, causing OutOfMemory.
Only the output content of the models final output OP is checked.
check_onnx_tf_outputs_elementwise_close_full: Optional[bool]
Returns "Matches" if the output of onnx and the output of TF are
within acceptable proximity element by element.
Check the output of all OPs in sequence from the beginning,
including all but the final output OP of the model.
Returns "Unmatched" if the output of onnx and the output of TF are
not within acceptable proximity element by element.
If the output of onnx is 1D, it returns "Skipped" and skips the comparison
between the output of onnx and that of TF. This is because when undefined
dimensions are present, a situation often arises where very large index
values are compared, causing OutOfMemory.
It is very time consuming because it performs as many inferences as
there are operations.
check_onnx_tf_outputs_sample_data_normalization: Optional[str]
norm: Validate using random data normalized to the range 0.0 to 1.0
denorm: Validate using random data in the range 0.0 to 255.0
If there is a normalization layer at the models entry point, or
if the model was trained on denormalized data, "denorm" must be specified.
Default: "norm"
check_onnx_tf_outputs_elementwise_close_rtol: Optional[float]
The relative tolerance parameter.
Default: 0.0
check_onnx_tf_outputs_elementwise_close_atol: Optional[float]
The absolute tolerance parameter.
Default: 1e-4
test_data_nhwc_path: Optional[str]
Path to a numpy file (.npy) containing custom test data in NHWC format.
This is used for test inference and validation when check_onnx_tf_outputs options are enabled.
If not specified, the tool will attempt to download sample data from the internet
when the input is a 4D RGB image tensor.
The numpy array should have shape [batch_size, height, width, 3] with values
normalized to the range [0, 1].
This option is useful for offline environments or when you want to use
specific test data for validation.
disable_model_save: Optional[bool]
Does not save the converted model. For CIs RAM savings.
Default: False
non_verbose: Optional[bool]
Shorthand to specify a verbosity of "error".
Default: False
verbosity: Optional[str]
Change the level of information printed.
Values are "debug", "info", "warn", and "error".
Default: "debug" (for backwards compatability)
Returns
----------
model: tf_keras.Model
Model
Parameter replacement
This tool is used to convert NCW to NWC, NCHW to NHWC, NCDHW to NDHWC, NCDDHW to NDDHWC, NCDDDDDDHW to NDDDDDDHWC. Therefore, as stated in the Key Concepts, the conversion will inevitably break down at some point in the model. You need to look at the entire conversion log to see which OP transpositions are failing and correct them yourself. I dare to explain very little because I know that no matter how much detail I put in the README, you guys will not read it at all. attribute or INPUT constant or INPUT Initializer can be replaced with the specified value.
Click to expand
Starting from v1.3.0, almost all OPs except for some special OPs support pre- and post-transposition by pre_process_transpose and post_process_transpose.
- "A conversion error occurs."
- "Output results are wrong."
Do not submit an issue that only contains an amount of information that cannot be reproduced.
-
convert option
--param_replacement_file param_replacement.json or -prf param_replacement.json -
param_replacement.json
See a sample of replacement JSON
{ "format_version": 1, "operations": [ { "op_name": "StatefulPartitionedCall/Tile_4", "param_target": "inputs", # attributes or inputs "param_name": "const_fold_opt__677", "values": [1,1,17] # Disable parameter transposition or overwrite parameters }, { "op_name": "StatefulPartitionedCall/Cast_3", "param_target": "attributes", # attributes or inputs "param_name": "to", "values": 1 # Disable parameter transposition or overwrite "to" parameters }, { "op_name": "Resize__697", "param_target": "inputs", "param_name": "Concat__696:0", "values": [26,26] # Replacement of unk__x (Resize OP, sizes height/width parameter) }, { "op_name": "Transpose__927", "param_target": "attributes", "param_name": "perm", "values": [0,1,2,3] # Disable parameter transposition or overwrite "perm" parameters }, { "op_name": "StatefulPartitionedCall/functional_1/max_unpooling2d_2/Reshape_1", "param_target": "inputs", "param_name": "const_fold_opt__911", "values": [4,131072] # Overwrite "shape" parameters }, { "op_name": "Reshape_25", "param_target": "outputs", "param_name": "onnx::InstanceNormalization_270", "post_process_transpose_perm": [0,2,1] # Extrapolate 3D Transpose after Reshape }, { "op_name": "Reshape_30", "param_target": "outputs", "param_name": "onnx::Mul_275", "post_process_transpose_perm": [0,2,3,1] # Extrapolate 4D Transpose after Reshape }, { "op_name": "flatten_1127", "param_target": "inputs", "param_name": "dropout0", "pre_process_transpose_perm": [0,3,1,2] }, { "op_name": "/Slice", "param_target": "op", "begin": [0,0,1,0], "end": [0,0,0,0], "end_mask": 15 }, { "op_name": "/Slice_1", "param_target": "op", "begin": [0,0,0,0], "end": [0,0,39,0], "end_mask": 11 }, { "op_name": "/backbone/backbone.1/Unsqueeze_1", "param_target": "op", "new_shape": [1,15,15,1] } ] }
-
Replacement Supported OPs
See list of replacement specifications
No. OP type Remarks 1 Add 1. "param_target": "inputs" pre_process_transpose_perm: Transpose is applied to the tensor before the Add operation with the perm specified as pre-processing.
2. "param_target": "outputs"post_process_transpose_perm: Transpose is applied to the tensor after the Add operation with the perm specified as post-processing.2 Cast Type Values Type Values float16 10 int8 3 float32 1 int16 5 float64 11 int32 6 bool 9 int64 7 uint8 2 uint16 4 uint32 12 uint64 13 3 Concat 1. "param_target": "attributes" axis: Value ofaxis
2. "param_target": "outputs"post_process_transpose_perm: Transpose is applied to the tensor after the Concat operation with the perm specified as post-processing.4 ConvTranspose ConvTransposeimplements special replacements separately ignore all automatic conversions and generatetf.nn.conv1d_transposeortf.nn.conv2d_transposeortf.nn.conv3d_transposedirectly by specifying all parameters.
https://www.tensorflow.org/api_docs/python/tf/nn/conv1d_transpose
https://www.tensorflow.org/api_docs/python/tf/nn/conv2d_transpose
https://www.tensorflow.org/api_docs/python/tf/nn/conv3d_transpose
1. "param_target": "op"output_shape: Value ofoutput_shapestrides: Value ofstridespadding: Value ofpaddingdilations: Value ofdilations5 Div 1. "param_target": "inputs" values: Value ofinputpre_process_transpose_perm: Transpose is applied to the tensor before the Div operation with the perm specified as pre-processing.
2. "param_target": "outputs"post_process_transpose_perm: Transpose is applied to the tensor after the Div operation with the perm specified as post-processing.6 Expand 1. "param_target": "inputs" values: Value ofshapepre_process_transpose_perm: Transpose is applied to the tensor before the Expand operation with the perm specified as pre-processing.
2. "param_target": "outputs"post_process_transpose_perm: Transpose is applied to the tensor after the Expand operation with the perm specified as post-processing.7 Flatten 1. "param_target": "attributes" axis: Value ofaxis
2. "param_target": "inputs"pre_process_transpose_perm: Transpose is applied to the tensor before the Flatten operation with the perm specified as pre-processing.
3. "param_target": "outputs"post_process_transpose_perm: Transpose is applied to the tensor after the Flatten operation with the perm specified as post-processing.8 Gemm 9 Gather 1. "param_target": "attributes" axis: Value ofaxis
2. "param_target": "inputs"values: Value ofindicespre_process_transpose_perm: Transpose is applied to the tensor before the Gather operation with the perm specified as pre-processing.
3. "param_target": "outputs"post_process_transpose_perm: Transpose is applied to the tensor after the Gather operation with the perm specified as post-processing.10 MatMul 1. "param_target": "inputs" pre_process_transpose_perm: Transpose is applied to the tensor before the MatMul operation with the perm specified as pre-processing.
2. "param_target": "outputs"post_process_transpose_perm: Transpose is applied to the tensor after the MatMul operation with the perm specified as post-processing.11 Mul 1. "param_target": "inputs" values: Value ofinputpre_process_transpose_perm: Transpose is applied to the tensor before the Mul operation with the perm specified as pre-processing.
2. "param_target": "outputs"post_process_transpose_perm: Transpose is applied to the tensor after the Mul operation with the perm specified as post-processing.12 NonMaxSuppression 13 ReduceL1
ReduceL2
ReduceLogSum
ReduceLogSumExp
ReduceMax
ReduceMean
ReduceMin
ReduceProd
ReduceSum
ReduceSumSquare1. "param_target": "attributes" axes: Value ofaxeskeepdims: Value ofkeepdims
2. "param_target": "inputs"pre_process_transpose_perm: Transpose is applied to the tensor before the ReduceXX operation with the perm specified as pre-processing.
3. "param_target": "outputs"post_process_transpose_perm: Transpose is applied to the tensor after the ReduceXX operation with the perm specified as post-processing.14 Unsqueeze 1. "param_target": "inputs" pre_process_transpose_perm: Transpose is applied to the tensor before the Unsqueeze operation with the perm specified as pre-processing.
2. "param_target": "outputs"post_process_transpose_perm: Transpose is applied to the tensor after the Unsqueeze operation with the perm specified as post-processing.
3. "param_target": "op"new_shape: Specifies directly the shape after Unsqueeze processing.
{
"op_name": "/backbone/backbone.1/Unsqueeze_1",
"param_target": "op",
"new_shape": [1,15,15,1]
}15 Reshape 1. "param_target": "inputs" values: Value ofshapepre_process_transpose_perm: Transpose is applied to the tensor before the Reshape operation with the perm specified as pre-processing.
2. "param_target": "outputs"post_process_transpose_perm: Transpose is applied to the tensor after the Reshape operation with the perm specified as post-processing.16 Resize 1. "param_target": "attributes" coordinate_transformation_mode: Value ofcoordinate_transformation_modeextrapolation_value: Value ofextrapolation_valuemode: Value ofmode
2. "param_target": "inputs"values: Value ofroiorscalesorsizes.scales=[scale_h,scale_w],sizes=[h,w]pre_process_transpose_perm: Transpose is applied to the tensor before the Resize operation with the perm specified as pre-processing.
3. "param_target": "outputs"post_process_transpose_perm: Transpose is applied to the tensor after the Resize operation with the perm specified as post-processing.17 Slice Sliceimplements special replacements separately ignore all automatic conversions and generatetf.strided_slicedirectly by specifying all parameters oftf.strided_slicedirectly.
https://www.tensorflow.org/api_docs/python/tf/strided_slice
See json_samples/replace_slice.json for a sample description.
1. "param_target": "op"begin: Value ofbeginend: Value ofendstrides: Value ofstridesbegin_mask: Value ofbegin_maskend_mask: Value ofend_maskellipsis_mask: Value ofellipsis_masknew_axis_mask: Value ofnew_axis_maskshrink_axis_mask: Value ofshrink_axis_mask
{
"op_name": "/Slice",
"param_target": "op",
"begin": [0,0,1,0],
"end": [0,0,0,0],
"end_mask": 15
}18 Softmax 1. "param_target": "attributes" axis: Value ofaxis. The transpositions corresponding to the specified axis are extrapolated before and afterSoftmax.
2. "param_target": "inputs"values: Value oftensor19 Split 1. "param_target": "inputs" values: Value ofsplit
2. "param_target": "attributes"axis: Value ofaxis.num_outputs: Value ofnum_outputs.20 Sub 1. "param_target": "inputs" values: Value ofinputpre_process_transpose_perm: Transpose is applied to the tensor before the Sub operation with the perm specified as pre-processing.
2. "param_target": "outputs"post_process_transpose_perm: Transpose is applied to the tensor after the Sub operation with the perm specified as post-processing.21 Tile 1. "param_target": "inputs" values: Value ofinputpre_process_transpose_perm: Transpose is applied to the tensor before the Tile operation with the perm specified as pre-processing.
2. "param_target": "outputs"post_process_transpose_perm: Transpose is applied to the tensor after the Tile operation with the perm specified as post-processing.22 Transpose 1. "param_target": "attributes" perm: Value ofperm
2. "param_target": "inputs"values: Value oftensor
Generated Model
-
YOLOv7-tiny with Post-Process (NMS) ONNX to TFLite Float32 https://github.com/PINTO0309/onnx2tf/releases/download/0.0.33/yolov7_tiny_head_0.768_post_480x640.onnx
See the structure of the model
onnx2tf onnx-tensorflow
(Super redundant + Broken) -
YOLACT-Edge MobileNetV2 with Post-Process (MultiClass-NMS) ONNX to TFLite Float32 https://github.com/PINTO0309/onnx2tf/releases/download/1.0.11/yolact_edge_mobilenetv2_550x550.onnx
See the structure of the model
-
MoveNet MultiPose ONNX to TFLite Float32 (
CastandTrueDivstandard OP support) https://github.com/PINTO0309/onnx2tf/releases/download/1.0.24/movenet_multipose_lightning_192x256_p6.onnxSee the structure of the model
Validated models (without replacement.json)
ONNX file for testing. https://github.com/PINTO0309/onnx2tf/releases/tag/1.1.28
See a list of verified models
| No. | Model | Pass |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | age_googlenet.onnx | :heavy_check_mark: |
| 2 | alike_t_opset11_192x320.onnx | :heavy_check_mark: |
| 3 | arcfaceresnet100-8.onnx | :heavy_check_mark: |
| 4 | baseline_simplified.onnx | :heavy_check_mark: |
| 5 | big_slice_11.onnx | :heavy_check_mark: |
| 6 | bvlcalexnet-12.onnx | :heavy_check_mark: |
| 7 | caffenet-12.onnx | :heavy_check_mark: |
| 8 | convtranspose_3_1_5_2.onnx | :heavy_check_mark: |
| 9 | convtranspose_4_5_2_2.onnx | :heavy_check_mark: |
| 10 | convtranspose_5_5_6_1.onnx | :heavy_check_mark: |
| 11 | convtranspose_6_5_5_8.onnx | :heavy_check_mark: |
| 12 | convtranspose_7_1_3_4.onnx | :heavy_check_mark: |
| 13 | damoyolo_tinynasL20_T_192x192_post.onnx | :heavy_check_mark: |
| 14 | deeplabv3_mobilenet_v3_large.onnx | :heavy_check_mark: |
| 15 | densenet-12.onnx | :heavy_check_mark: |
| 16 | depth_to_spase_17.onnx | :heavy_check_mark: |
| 17 | double_gru.onnx | :heavy_check_mark: |
| 18 | digits.onnx | :heavy_check_mark: |
| 19 | detr_demo.onnx | :heavy_check_mark: |
| 20 | efficientformer_l1.onnx | :heavy_check_mark: |
| 21 | efficientdet_lite2_detection_1.onnx | :heavy_check_mark: |
| 22 | efficientnet-lite4-11_nchw.onnx | :heavy_check_mark: |
| 23 | effnet_opset11_dynamic_axis.onnx | :heavy_check_mark: |
| 24 | emotion-ferplus-8_rename.onnx | :heavy_check_mark: |
| 25 | face_detection_yunet_2022mar.onnx | :heavy_check_mark: |
| 26 | face_recognition_sface_2021dec-act_int8-wt_int8-quantized.onnx | :heavy_check_mark: |
| 27 | face_recognition_sface_2021dec.onnx | :heavy_check_mark: |
| 28 | faster_rcnn-10.onnx | :heavy_check_mark: |
| 29 | fastestdet.onnx | :heavy_check_mark: |
| 30 | fused_conv_clip.onnx | :heavy_check_mark: |
| 31 | fused_conv_hardsigmoid.onnx | :heavy_check_mark: |
| 32 | fused_conv_leakyrelu.onnx | :heavy_check_mark: |
| 33 | fused_conv_relu.onnx | :heavy_check_mark: |
| 34 | fused_conv_sigmoid.onnx | :heavy_check_mark: |
| 35 | fused_conv_tanh.onnx | :heavy_check_mark: |
| 36 | gender_googlenet.onnx | :heavy_check_mark: |
| 37 | gmflow-scale1-mixdata-train320x576-4c3a6e9a_1x3x480x640_bidir_flow_sim.onnx | :heavy_check_mark: |
| 38 | handpose_estimation_mediapipe_2022may.onnx | :heavy_check_mark: |
| 39 | htnet_1x17x2_without_norm.onnx | :heavy_check_mark: |
| 40 | iat_llie_180x320.onnx | :heavy_check_mark: |
| 41 | if_p1_11.onnx | :heavy_check_mark: |
| 42 | if_p2_11.onnx | :heavy_check_mark: |
| 43 | if_p3_11.onnx | :heavy_check_mark: |
| 44 | imageclassifier.onnx | :heavy_check_mark: |
| 45 | inception-v2-9.onnx | :heavy_check_mark: |
| 46 | inverse11.onnx | :heavy_check_mark: |
| 47 | mhformer_NxFxKxXY_1x27x17x2.onnx | :heavy_check_mark: |
| 48 | mnist.onnx | :heavy_check_mark: |
| 49 | mnist-12.onnx | :heavy_check_mark: |
| 50 | mobilenetv2-12.onnx | :heavy_check_mark: |
| 51 | mosaic_11.onnx | :heavy_check_mark: |
| 52 | mosaic-9.onnx | :heavy_check_mark: |
| 53 | movenet_multipose_lightning_192x256_p6.onnx | :heavy_check_mark: |
| 54 | nanodet-plus-m_416.onnx | :heavy_check_mark: |
| 55 | object_tracking_dasiamrpn_kernel_cls1_2021nov.onnx | :heavy_check_mark: |
| 56 | object_tracking_dasiamrpn_kernel_r1_2021nov.onnx | :heavy_check_mark: |
| 57 | object_tracking_dasiamrpn_model_2021nov.onnx | :heavy_check_mark: |
| 58 | pidnet_S_cityscapes_192x320.onnx | :heavy_check_mark: |
| 59 | ppmattingv2_stdc1_human_480x640.onnx | :heavy_check_mark: |
| 60 | qlinear_conv_tensor_test.onnx | :heavy_check_mark: |
| 61 | rcnn-ilsvrc13-9.onnx | :heavy_check_mark: |
| 62 | regnet_x_400mf.onnx | :heavy_check_mark: |
| 63 | ResNet101-DUC-12.onnx | :heavy_check_mark: |
| 64 | resnet18-v1-7.onnx | :heavy_check_mark: |
| 65 | resnet50-v1-12.onnx | :heavy_check_mark: |
| 66 | resnet50-v2-7.onnx | :heavy_check_mark: |
| 67 | retinanet-9.onnx | :heavy_check_mark: |
| 68 | sinet_320_op.onnx | :heavy_check_mark: |
| 69 | squeezenet1.0-12.onnx | :heavy_check_mark: |
| 70 | super-resolution-10.onnx | :heavy_check_mark: |
| 71 | swinir-m_64x64_12.onnx | :heavy_check_mark: |
| 72 | text_recognition_CRNN_EN_2021sep.onnx | :heavy_check_mark: |
| 73 | tinyyolov2-8.onnx | :heavy_check_mark: |
| 74 | version-RFB-640.onnx | :heavy_check_mark: |
| 75 | vit-b-32_textual.onnx | :heavy_check_mark: |
| 76 | vit-b-32_visual.onnx | :heavy_check_mark: |
| 77 | yolact_edge_mobilenetv2_550x550.onnx | :heavy_check_mark: |
| 78 | yolact_regnetx_600mf_d2s_31classes_512x512.onnx | :heavy_check_mark: |
| 79 | yolact_regnetx_800mf_20classes_512x512.onnx | :heavy_check_mark: |
| 80 | yolo_free_nano_crowdhuman_192x320_post.onnx | :heavy_check_mark: |
| 81 | yolov7_tiny_head_0.768_post_480x640.onnx | :heavy_check_mark: |
| 82 | yolox_nano_192x192.onnx | :heavy_check_mark: |
| 83 | yolox_nano_416x416.onnx | :heavy_check_mark: |
| 84 | yolox_s.onnx | :heavy_check_mark: |
| 85 | yolox_x_crowdhuman_mot17_bytetrack.onnx | :heavy_check_mark: |
| 86 | zero_dce_640_dele.onnx | :heavy_check_mark: |
| 87 | zfnet512-12.onnx | :heavy_check_mark: |
Related tools
- tflite2tensorflow
- openvino2tensorflow
- tflite2json2tflite
- tensorflowjs_converter
- coremltools
- simple-onnx-processing-tools
- tflite-input-output-rewriter
- onnx-simplifier
- onnx_graphsurgeon
- onnx
- onnx-tensorflow
- onnx2keras
- TinyNeuralNetwork
- nobuco
- onnx2torch
- ai-edge-torch
- LiteRT.js
- eiq-onnx2tflite
Acknowledgement
- https://github.com/onnx/models
- https://github.com/opencv/opencv_zoo
- https://pytorch.org/vision/stable/models.html
- https://tfhub.dev/
- https://www.kaggle.com/models
- https://github.com/TexasInstruments/edgeai-modelzoo
Contributors

Made with contrib.rocks.
Project details
Release history Release notifications | RSS feed
Download files
Download the file for your platform. If you're not sure which to choose, learn more about installing packages.
Source Distribution
Built Distribution
Filter files by name, interpreter, ABI, and platform.
If you're not sure about the file name format, learn more about wheel file names.
Copy a direct link to the current filters
File details
Details for the file onnx2tf-2.0.19.tar.gz.
File metadata
- Download URL: onnx2tf-2.0.19.tar.gz
- Upload date:
- Size: 630.8 kB
- Tags: Source
- Uploaded using Trusted Publishing? No
- Uploaded via: twine/6.2.0 CPython/3.9.25
File hashes
| Algorithm | Hash digest | |
|---|---|---|
| SHA256 |
ff297e6db15907dc71250f88bee866c4c46452f68f334c736aa39587570ba8af
|
|
| MD5 |
e283e57a44a598fbb833e28b8e56d2ae
|
|
| BLAKE2b-256 |
abb0318da370c400c52a7cb8904a724f65414bb7a48b111b9faa0c6382e9d6e5
|
File details
Details for the file onnx2tf-2.0.19-py3-none-any.whl.
File metadata
- Download URL: onnx2tf-2.0.19-py3-none-any.whl
- Upload date:
- Size: 822.4 kB
- Tags: Python 3
- Uploaded using Trusted Publishing? No
- Uploaded via: twine/6.2.0 CPython/3.9.25
File hashes
| Algorithm | Hash digest | |
|---|---|---|
| SHA256 |
e8d9bd769db0af6f8ae1298a1bffbe474778b2d61a1c92e24d9599694b59e1fe
|
|
| MD5 |
7cddfccbe67412f5fe6db91abd705cba
|
|
| BLAKE2b-256 |
676999259447061f972984bf9dc9a34178a5ebeded85f3891e4ace1247975212
|