Heuristic Algorithms in Python
Project description
scikit-opt
Heuristic Algorithms in Python
(Genetic Algorithm, Particle Swarm Optimization, Simulated Annealing, Ant Colony Algorithm, Immune Algorithm,Artificial Fish Swarm Algorithm in Python)
- Documentation: https://scikit-opt.github.io/scikit-opt/#/docs/en,
- 文档: https://scikit-opt.github.io/scikit-opt/#/docs/zh
install
pip install scikit-opt
News:
All algorithms will be available on TensorFlow/Spark on version 0.4, getting parallel performance.
feature: UDF
UDF (user defined function) is available now!
For example, you just worked out a new type of selection function.
Now, your selection function is like this:
def selection_tournament(self, tourn_size):
FitV = self.FitV
sel_index = []
for i in range(self.size_pop):
aspirants_index = np.random.choice(range(self.size_pop), size=tourn_size)
sel_index.append(max(aspirants_index, key=lambda i: FitV[i]))
self.Chrom = self.Chrom[sel_index, :] # next generation
return self.Chrom
Regist your udf to GA (Here we provide some operators)
from sko.GA import GA, GA_TSP
from sko.GA import ranking_linear, ranking_raw, crossover_2point, selection_roulette_2, mutation
demo_func = lambda x: x[0] ** 2 + (x[1] - 0.05) ** 2 + x[2] ** 2
ga = GA(func=demo_func, n_dim=3, size_pop=100, max_iter=500, lb=[-1, -10, -5], ub=[2, 10, 2])
#
ga.register(operator_name='ranking', operator=ranking_linear). \
register(operator_name='crossover', operator=crossover_2point). \
register(operator_name='mutation', operator=mutation). \
register(operator_name='selection', operator=selection_tournament, tourn_size=3)
Now do GA as usual
best_x, best_y = ga.run()
print('best_x:', best_x, '\n', 'best_y:', best_y)
Until Now, the udf surport
crossover,mutation,selection,rankingof GA
We provide a dozen of operators see here
demo
1. Genetic Algorithm
from sko.GA import GA
def demo_func(x):
x1, x2, x3 = x
return x1 ** 2 + (x2 - 0.05) ** 2 + x3 ** 2
ga = GA(func=demo_func, lb=[-1, -10, -5], ub=[2, 10, 2], max_iter=500)
best_x, best_y = ga.fit()
plot the result using matplotlib:
import pandas as pd
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
Y_history = ga.all_history_Y
Y_history = pd.DataFrame(Y_history)
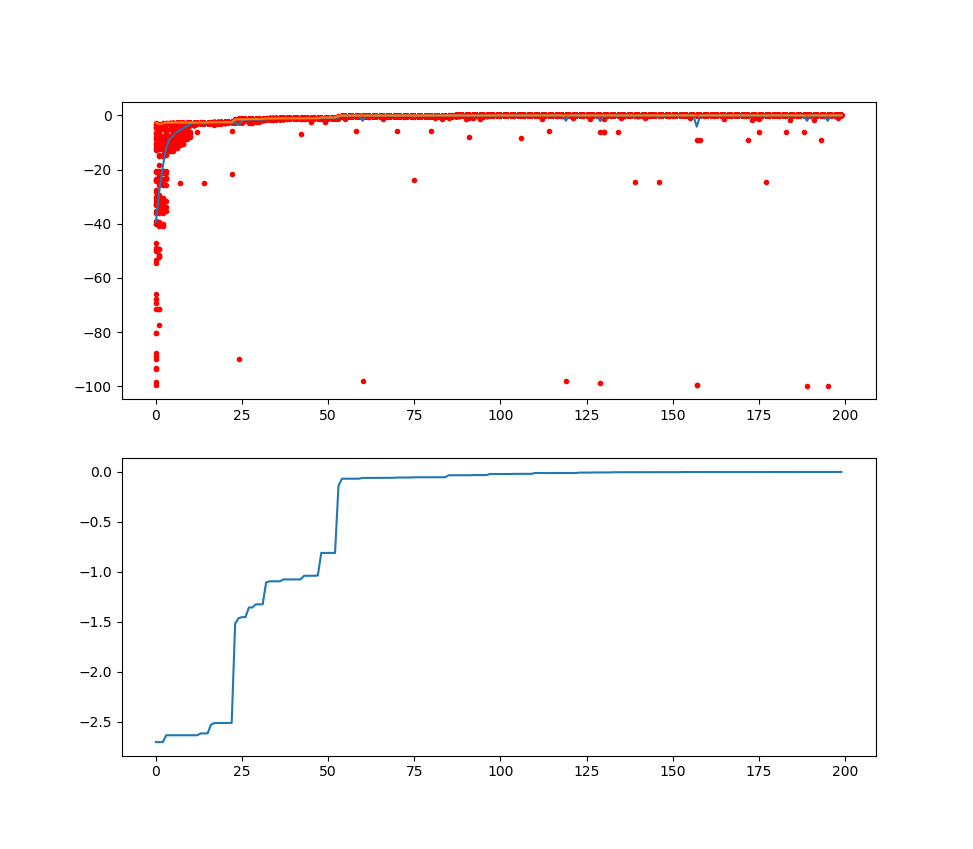
fig, ax = plt.subplots(3, 1)
ax[0].plot(Y_history.index, Y_history.values, '.', color='red')
plt_mean = Y_history.mean(axis=1)
plt_max = Y_history.min(axis=1)
ax[1].plot(plt_mean.index, plt_mean, label='mean')
ax[1].plot(plt_max.index, plt_max, label='min')
ax[1].set_title('mean and all Y of every generation')
ax[1].legend()
ax[2].plot(plt_max.index, plt_max.cummin())
ax[2].set_title('best fitness of every generation')
plt.show()
1.1 Genetic Algorithm for TSP(Travelling Salesman Problem)
Just import the GA_TSP, it overloads the crossover, mutation to solve the TSP
Firstly, your data (the distance matrix). Here I generate the data randomly as a demo:
import numpy as np
num_points = 8
points = range(num_points)
points_coordinate = np.random.rand(num_points, 2)
distance_matrix = np.zeros(shape=(num_points, num_points))
for i in range(num_points):
for j in range(num_points):
distance_matrix[i][j] = np.linalg.norm(points_coordinate[i] - points_coordinate[j], ord=2)
print('distance_matrix is: \n', distance_matrix)
def cal_total_distance(points):
num_points, = points.shape
total_distance = 0
for i in range(num_points - 1):
total_distance += distance_matrix[points[i], points[i + 1]]
total_distance += distance_matrix[points[i + 1], points[0]]
return total_distance
Do GA
from sko.GA import GA_TSP
ga_tsp = GA_TSP(func=cal_total_distance, points=points, pop=50, max_iter=200, Pm=0.001)
best_points, best_distance = ga_tsp.fit()
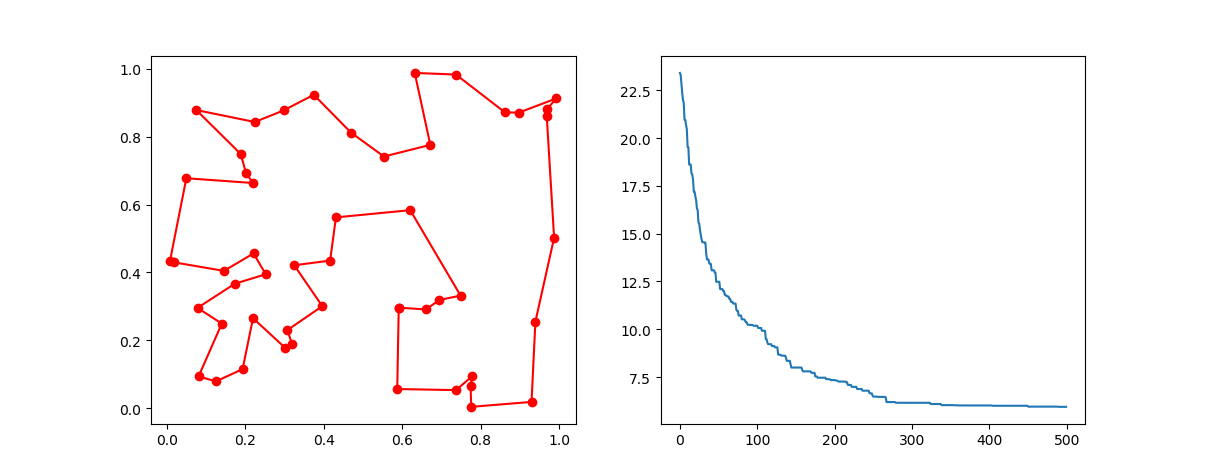
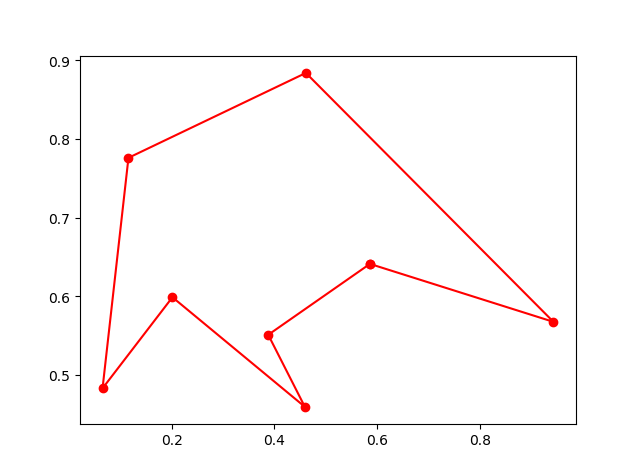
Plot the result:
fig, ax = plt.subplots(1, 1)
best_points_ = np.concatenate([best_points, [best_points[0]]])
best_points_coordinate = points_coordinate[best_points_, :]
ax.plot(best_points_coordinate[:, 0], best_points_coordinate[:, 1],'o-r')
plt.show()
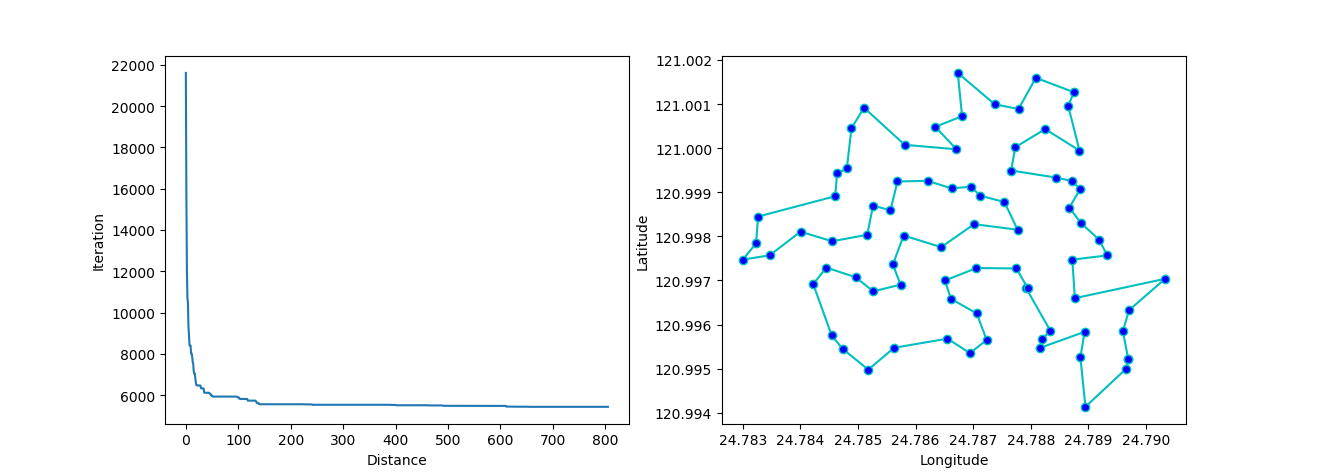
2. PSO(Particle swarm optimization)
def demo_func(x):
x1, x2, x3 = x
return x1 ** 2 + (x2 - 0.05) ** 2 + x3 ** 2
from sko.PSO import PSO
pso = PSO(func=demo_func, dim=3)
fitness = pso.fit()
print('best_x is ',pso.gbest_x)
print('best_y is ',pso.gbest_y)
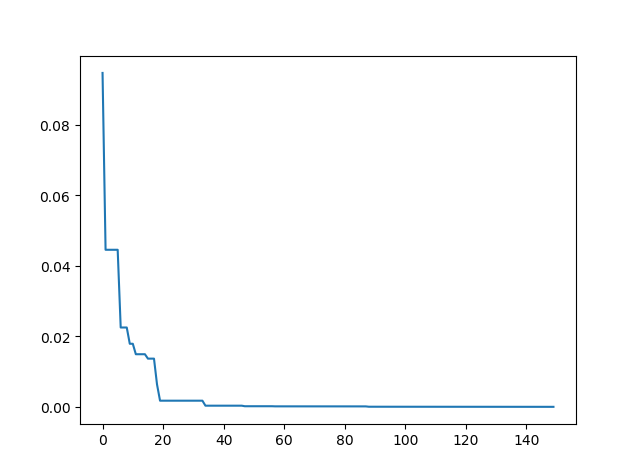
pso.plot_history()
3. SA(Simulated Annealing)
def demo_func(x):
x1, x2, x3 = x
return x1 ** 2 + (x2 - 0.05) ** 2 + x3 ** 2
from sko.SA import SA
sa = SA(func=demo_func, x0=[1, 1, 1])
x_star, y_star = sa.fit()
print(x_star, y_star)
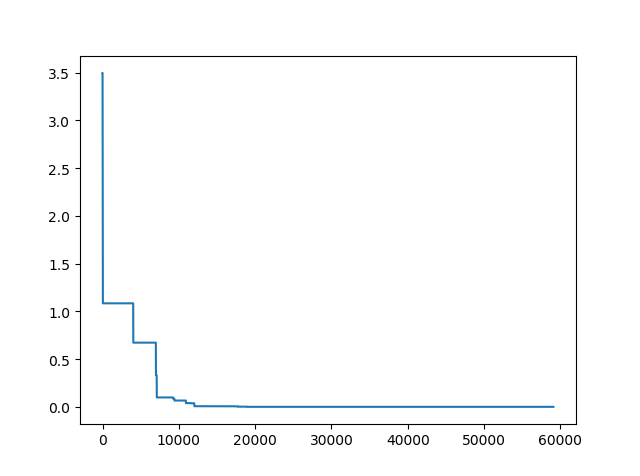
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import pandas as pd
plt.plot(pd.DataFrame(sa.f_list).cummin(axis=0))
plt.show()
3.1 SA for TSP
Firstly, your data (the distance matrix). Here I generate the data randomly as a demo (find it in GA for TSP above)
DO SA for TSP
from sko.SA import SA_TSP
sa_tsp = SA_TSP(func=demo_func, x0=range(num_points))
best_points, best_distance = sa_tsp.fit()
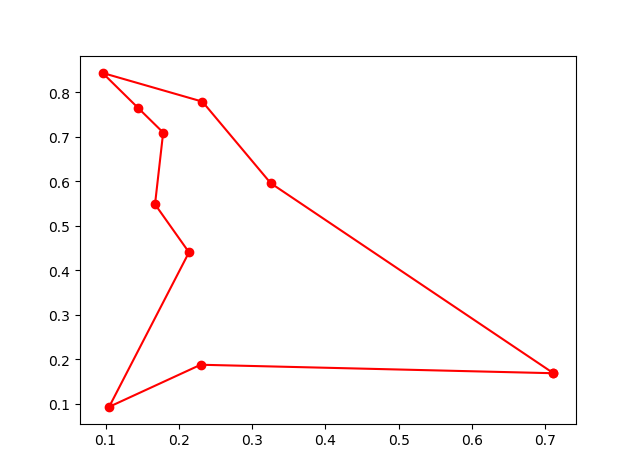
plot the result
fig, ax = plt.subplots(1, 1)
best_points_ = np.concatenate([best_points, [best_points[0]]])
best_points_coordinate = points_coordinate[best_points_, :]
ax.plot(best_points_coordinate[:, 0], best_points_coordinate[:, 1], 'o-r')
plt.show()
4. ASA for tsp (Ant Colony Algorithm)
aca = ACA_TSP(func=cal_total_distance, n_dim=8,
size_pop=10, max_iter=20,
distance_matrix=distance_matrix)
best_x, best_y = aca.fit()
5. immune algorithm (IA)
from sko.IA import IA_TSP_g as IA_TSP
ia_tsp = IA_TSP(func=cal_total_distance, n_dim=num_points, pop=500, max_iter=2000, Pm=0.2,
T=0.7, alpha=0.95)
best_points, best_distance = ia_tsp.fit()
print('best routine:', best_points, 'best_distance:', best_distance)
6. artificial fish swarm algorithm (AFSA)
def func(x):
x1, x2 = x
return 1 / x1 ** 2 + x1 ** 2 + 1 / x2 ** 2 + x2 ** 2
from sko.ASFA import ASFA
asfa = ASFA(func, n_dim=2, size_pop=50, max_iter=300,
max_try_num=100, step=0.5, visual=0.3,
q=0.98, delta=0.5)
best_x, best_y = asfa.fit()
print(best_x, best_y)
Project details
Release history Release notifications | RSS feed
Download files
Download the file for your platform. If you're not sure which to choose, learn more about installing packages.
Source Distribution
Built Distribution
Filter files by name, interpreter, ABI, and platform.
If you're not sure about the file name format, learn more about wheel file names.
Copy a direct link to the current filters
File details
Details for the file scikit-opt-0.3.2.tar.gz.
File metadata
- Download URL: scikit-opt-0.3.2.tar.gz
- Upload date:
- Size: 13.8 kB
- Tags: Source
- Uploaded using Trusted Publishing? No
- Uploaded via: twine/1.13.0 pkginfo/1.5.0.1 requests/2.21.0 setuptools/40.8.0 requests-toolbelt/0.9.1 tqdm/4.31.1 CPython/3.7.1
File hashes
| Algorithm | Hash digest | |
|---|---|---|
| SHA256 |
41f5cf4e338f5561481ec3ae3e523ef7687f68e4ea9d8eea9ba0b041dd47abbd
|
|
| MD5 |
518aedfe102f369ff3ca7395b137ad17
|
|
| BLAKE2b-256 |
8c85fcdb3359190b7a8f460016674b69f166895885ebf274e8837956c84b6814
|
File details
Details for the file scikit_opt-0.3.2-py3-none-any.whl.
File metadata
- Download URL: scikit_opt-0.3.2-py3-none-any.whl
- Upload date:
- Size: 17.4 kB
- Tags: Python 3
- Uploaded using Trusted Publishing? No
- Uploaded via: twine/1.13.0 pkginfo/1.5.0.1 requests/2.21.0 setuptools/40.8.0 requests-toolbelt/0.9.1 tqdm/4.31.1 CPython/3.7.1
File hashes
| Algorithm | Hash digest | |
|---|---|---|
| SHA256 |
ab71d546999cfeb158da3aaa014e76d3f77015ce21fc9017e16d0bc8da91e9fb
|
|
| MD5 |
6bccc9cc01544373b66a14210c6e19b1
|
|
| BLAKE2b-256 |
d944f31102fcc5d416e669d5c119f541566f97ea429ddbe62f2f76bce327edbd
|