The Deep Learning framework to train, deploy, and ship AI products Lightning fast.
Project description

The Deep Learning framework to train, deploy, and ship AI products Lightning fast.
NEW- Lightning 2.0 is featuring a clean and stable API!!
Lightning.ai • PyTorch Lightning • Fabric • Lightning Apps • Docs • Community • Contribute •
Install Lightning
Simple installation from PyPI
pip install lightning
Lightning has 3 core packages
PyTorch Lightning: Train and deploy PyTorch at scale.
Lightning Fabric: Expert control.
Lightning Apps: Build AI products and ML workflows.
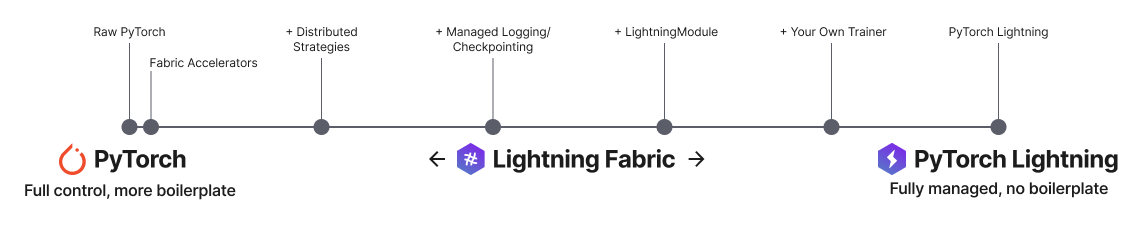
Lightning gives you granular control over how much abstraction you want to add over PyTorch.
PyTorch Lightning: Train and Deploy PyTorch at Scale
PyTorch Lightning is just organized PyTorch - Lightning disentangles PyTorch code to decouple the science from the engineering.
Hello simple model
# main.py
# ! pip install torchvision
import torch, torch.nn as nn, torch.utils.data as data, torchvision as tv, torch.nn.functional as F
import lightning as L
# --------------------------------
# Step 1: Define a LightningModule
# --------------------------------
# A LightningModule (nn.Module subclass) defines a full *system*
# (ie: an LLM, diffusion model, autoencoder, or simple image classifier).
class LitAutoEncoder(L.LightningModule):
def __init__(self):
super().__init__()
self.encoder = nn.Sequential(nn.Linear(28 * 28, 128), nn.ReLU(), nn.Linear(128, 3))
self.decoder = nn.Sequential(nn.Linear(3, 128), nn.ReLU(), nn.Linear(128, 28 * 28))
def forward(self, x):
# in lightning, forward defines the prediction/inference actions
embedding = self.encoder(x)
return embedding
def training_step(self, batch, batch_idx):
# training_step defines the train loop. It is independent of forward
x, y = batch
x = x.view(x.size(0), -1)
z = self.encoder(x)
x_hat = self.decoder(z)
loss = F.mse_loss(x_hat, x)
self.log("train_loss", loss)
return loss
def configure_optimizers(self):
optimizer = torch.optim.Adam(self.parameters(), lr=1e-3)
return optimizer
# -------------------
# Step 2: Define data
# -------------------
dataset = tv.datasets.MNIST(".", download=True, transform=tv.transforms.ToTensor())
train, val = data.random_split(dataset, [55000, 5000])
# -------------------
# Step 3: Train
# -------------------
autoencoder = LitAutoEncoder()
trainer = L.Trainer()
trainer.fit(autoencoder, data.DataLoader(train), data.DataLoader(val))
Run the model on your terminal
pip install torchvision
python main.py
Advanced features
Lightning has over 40+ advanced features designed for professional AI research at scale.
Here are some examples:

Train on 1000s of GPUs without code changes
# 8 GPUs
# no code changes needed
trainer = Trainer(accelerator="gpu", devices=8)
# 256 GPUs
trainer = Trainer(accelerator="gpu", devices=8, num_nodes=32)
Train on other accelerators like TPUs without code changes
# no code changes needed
trainer = Trainer(accelerator="tpu", devices=8)
16-bit precision
# no code changes needed
trainer = Trainer(precision=16)
Experiment managers
from lightning import loggers
# tensorboard
trainer = Trainer(logger=TensorBoardLogger("logs/"))
# weights and biases
trainer = Trainer(logger=loggers.WandbLogger())
# comet
trainer = Trainer(logger=loggers.CometLogger())
# mlflow
trainer = Trainer(logger=loggers.MLFlowLogger())
# neptune
trainer = Trainer(logger=loggers.NeptuneLogger())
# ... and dozens more
Early Stopping
es = EarlyStopping(monitor="val_loss")
trainer = Trainer(callbacks=[es])
Checkpointing
checkpointing = ModelCheckpoint(monitor="val_loss")
trainer = Trainer(callbacks=[checkpointing])
Export to torchscript (JIT) (production use)
# torchscript
autoencoder = LitAutoEncoder()
torch.jit.save(autoencoder.to_torchscript(), "model.pt")
Export to ONNX (production use)
# onnx
with tempfile.NamedTemporaryFile(suffix=".onnx", delete=False) as tmpfile:
autoencoder = LitAutoEncoder()
input_sample = torch.randn((1, 64))
autoencoder.to_onnx(tmpfile.name, input_sample, export_params=True)
os.path.isfile(tmpfile.name)
Advantages over unstructured PyTorch
- Models become hardware agnostic
- Code is clear to read because engineering code is abstracted away
- Easier to reproduce
- Make fewer mistakes because lightning handles the tricky engineering
- Keeps all the flexibility (LightningModules are still PyTorch modules), but removes a ton of boilerplate
- Lightning has dozens of integrations with popular machine learning tools.
- Tested rigorously with every new PR. We test every combination of PyTorch and Python supported versions, every OS, multi GPUs and even TPUs.
- Minimal running speed overhead (about 300 ms per epoch compared with pure PyTorch).
Lightning Fabric: Expert control.
Run on any device at any scale with expert-level control over PyTorch training loop and scaling strategy. You can even write your own Trainer.
Fabric is designed for the most complex models like foundation model scaling, LLMs, diffusion, transformers, reinforcement learning, active learning. Of any size.
| What to change | Resulting Fabric Code (copy me!) |
|---|---|
+ import lightning as L
import torch; import torchvision as tv
dataset = tv.datasets.CIFAR10("data", download=True,
train=True,
transform=tv.transforms.ToTensor())
+ fabric = L.Fabric()
+ fabric.launch()
model = tv.models.resnet18()
optimizer = torch.optim.SGD(model.parameters(), lr=0.001)
- device = "cuda" if torch.cuda.is_available() else "cpu"
- model.to(device)
+ model, optimizer = fabric.setup(model, optimizer)
dataloader = torch.utils.data.DataLoader(dataset, batch_size=8)
+ dataloader = fabric.setup_dataloaders(dataloader)
model.train()
num_epochs = 10
for epoch in range(num_epochs):
for batch in dataloader:
inputs, labels = batch
- inputs, labels = inputs.to(device), labels.to(device)
optimizer.zero_grad()
outputs = model(inputs)
loss = torch.nn.functional.cross_entropy(outputs, labels)
- loss.backward()
+ fabric.backward(loss)
optimizer.step()
print(loss.data)
|
import lightning as L
import torch; import torchvision as tv
dataset = tv.datasets.CIFAR10("data", download=True,
train=True,
transform=tv.transforms.ToTensor())
fabric = L.Fabric()
fabric.launch()
model = tv.models.resnet18()
optimizer = torch.optim.SGD(model.parameters(), lr=0.001)
model, optimizer = fabric.setup(model, optimizer)
dataloader = torch.utils.data.DataLoader(dataset, batch_size=8)
dataloader = fabric.setup_dataloaders(dataloader)
model.train()
num_epochs = 10
for epoch in range(num_epochs):
for batch in dataloader:
inputs, labels = batch
optimizer.zero_grad()
outputs = model(inputs)
loss = torch.nn.functional.cross_entropy(outputs, labels)
fabric.backward(loss)
optimizer.step()
print(loss.data)
|
Key features
Easily switch from running on CPU to GPU (Apple Silicon, CUDA, …), TPU, multi-GPU or even multi-node training
# Use your available hardware
# no code changes needed
fabric = Fabric()
# Run on GPUs (CUDA or MPS)
fabric = Fabric(accelerator="gpu")
# 8 GPUs
fabric = Fabric(accelerator="gpu", devices=8)
# 256 GPUs, multi-node
fabric = Fabric(accelerator="gpu", devices=8, num_nodes=32)
# Run on TPUs
fabric = Fabric(accelerator="tpu")
Use state-of-the-art distributed training strategies (DDP, FSDP, DeepSpeed) and mixed precision out of the box
# Use state-of-the-art distributed training techniques
fabric = Fabric(strategy="ddp")
fabric = Fabric(strategy="deepspeed")
fabric = Fabric(strategy="fsdp")
# Switch the precision
fabric = Fabric(precision="16-mixed")
fabric = Fabric(precision="64")
All the device logic boilerplate is handled for you
# no more of this!
- model.to(device)
- batch.to(device)
Build your own custom Trainer using Fabric primitives for training checkpointing, logging, and more
import lightning as L
class MyCustomTrainer:
def __init__(self, accelerator="auto", strategy="auto", devices="auto", precision="32-true"):
self.fabric = L.Fabric(accelerator=accelerator, strategy=strategy, devices=devices, precision=precision)
def fit(self, model, optimizer, dataloader, max_epochs):
self.fabric.launch()
model, optimizer = self.fabric.setup(model, optimizer)
dataloader = self.fabric.setup_dataloaders(dataloader)
model.train()
for epoch in range(max_epochs):
for batch in dataloader:
input, target = batch
optimizer.zero_grad()
output = model(input)
loss = loss_fn(output, target)
self.fabric.backward(loss)
optimizer.step()
You can find a more extensive example in our examples
Lightning Apps: Build AI products and ML workflows
Lightning Apps remove the cloud infrastructure boilerplate so you can focus on solving the research or business problems. Lightning Apps can run on the Lightning Cloud, your own cluster or a private cloud.

Hello Lightning app world
# app.py
import lightning as L
class TrainComponent(L.LightningWork):
def run(self, x):
print(f"train a model on {x}")
class AnalyzeComponent(L.LightningWork):
def run(self, x):
print(f"analyze model on {x}")
class WorkflowOrchestrator(L.LightningFlow):
def __init__(self) -> None:
super().__init__()
self.train = TrainComponent(cloud_compute=L.CloudCompute("cpu"))
self.analyze = AnalyzeComponent(cloud_compute=L.CloudCompute("gpu"))
def run(self):
self.train.run("CPU machine 1")
self.analyze.run("GPU machine 2")
app = L.LightningApp(WorkflowOrchestrator())
Run on the cloud or locally
# run on the cloud
lightning run app app.py --setup --cloud
# run locally
lightning run app app.py
Examples
Self-supervised Learning
Convolutional Architectures
Reinforcement Learning
GANs
Classic ML
Continuous Integration
Lightning is rigorously tested across multiple CPUs, GPUs, TPUs, IPUs, and HPUs and against major Python and PyTorch versions.
*Codecov is > 90%+ but build delays may show less
Current build statuses
| System / PyTorch ver. | 1.12 | 1.13 | 2.0 | 2.1 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Linux py3.9 [GPUs] |  |
 |
 |
 |
| Linux py3.9 [TPUs] |  |
|||
| Linux py3.8 [IPUs] | - |  |
 |
 |
| Linux (multiple Python versions) |  |
 |
 |
 |
| OSX (multiple Python versions) |  |
 |
 |
 |
| Windows (multiple Python versions) |  |
 |
 |
 |
Community
The lightning community is maintained by
- 10+ core contributors who are all a mix of professional engineers, Research Scientists, and Ph.D. students from top AI labs.
- 800+ community contributors.
Want to help us build Lightning and reduce boilerplate for thousands of researchers? Learn how to make your first contribution here
Lightning is also part of the PyTorch ecosystem which requires projects to have solid testing, documentation and support.
Asking for help
If you have any questions please:
Project details
Release history Release notifications | RSS feed
Download files
Download the file for your platform. If you're not sure which to choose, learn more about installing packages.
Source Distribution
Built Distribution
Filter files by name, interpreter, ABI, and platform.
If you're not sure about the file name format, learn more about wheel file names.
Copy a direct link to the current filters
File details
Details for the file lightning-2.1.0.tar.gz.
File metadata
- Download URL: lightning-2.1.0.tar.gz
- Upload date:
- Size: 1.7 MB
- Tags: Source
- Uploaded using Trusted Publishing? No
- Uploaded via: twine/4.0.2 CPython/3.9.18
File hashes
| Algorithm | Hash digest | |
|---|---|---|
| SHA256 |
1f78f5995ae7dcffa1edf34320db136902b73a0d1b304404c48ec8be165b3a93
|
|
| MD5 |
ecb08e41a419ef2037492fab4cf42504
|
|
| BLAKE2b-256 |
5dc0a0d015d166f7124c6d6774cbd19b6dd02783fc25547533c9b9ba767de25b
|
File details
Details for the file lightning-2.1.0-py3-none-any.whl.
File metadata
- Download URL: lightning-2.1.0-py3-none-any.whl
- Upload date:
- Size: 2.0 MB
- Tags: Python 3
- Uploaded using Trusted Publishing? No
- Uploaded via: twine/4.0.2 CPython/3.9.18
File hashes
| Algorithm | Hash digest | |
|---|---|---|
| SHA256 |
c12bd10bd28b9e29a8e877be039350a585f248c10b76360faa2aa2497f980de6
|
|
| MD5 |
a6e94f194c493c68bb84d03b2b68db2e
|
|
| BLAKE2b-256 |
08c78c33e2660161a99923fa9b46c72c31884efd482b89f7ead970cee5c0072a
|





















